Table of contents
Listen to the summary of this article in this podcast:
Ovulation occurs when hormonal changes signal the ovaries to release a mature egg. This process usually happens naturally as part of the menstrual cycle every month in women who have no fertility problems. Ovulation plays a key role in fertility, because only at this time is the egg ready to be fertilized by sperm. Knowing exactly when you ovulate can help you get pregnant at the best possible time. Next, by using the ovulation calendar and various methods, you can identify the exact time of your fertility and significantly increase the chances of pregnancy.
What is ovulation?
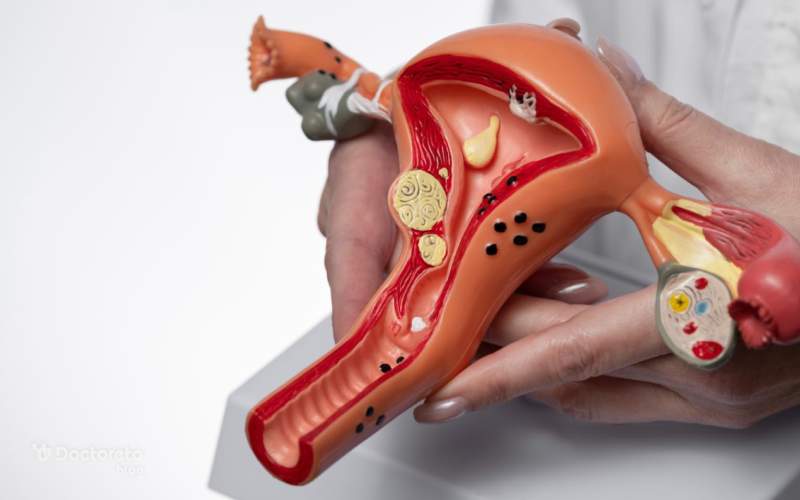
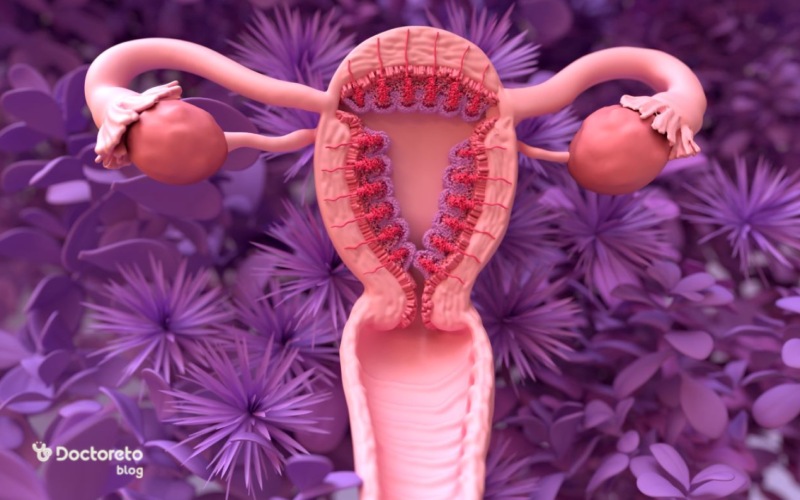
Ovulation is the process in which the mature egg is released from the ovary and transferred to the fallopian tubes to be fertilized if sperm is present. At birth, a woman has about 1 to 2 million immature eggs, which begin releasing these eggs when she reaches puberty. During her lifetime, a woman releases about 300 to 400 eggs in different menstrual cycles. This process is influenced by sex hormones such as estrogen, progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which help regulate the different stages of the menstrual cycle.
During ovulation, the uterine wall thickens to accommodate the fertilized egg. If the egg is not fertilized, the lining of the uterus sheds at the end of the menstrual cycle and causes period bleeding. Ovulation plays an essential role in fertility, because it is only at this time that the egg is ready to be fertilized by sperm.
What are the symptoms of ovulation?
Ovulation is a natural process in which a mature egg is released from the ovary and ready for fertilization. This process occurs due to hormonal changes in the body and can be followed by symptoms that indicate the right time for pregnancy. Although ovulation symptoms may vary from woman to woman, there are usually some common signs that will help you identify when you're ovulating. Ovulation symptoms can include the following:
- Changes in the cervical mucus (increase in secretions and its thinning)
- Slight pain or stretching sensation in the abdomen (known as ovulation pain)
- increasing sensitivity and swelling of breasts
- Mood changes or increased irritability
- Increasing libido
- Change in body temperature (increase in temperature usually after ovulation)
- Feeling of bloating or increased water in the body
- Slight spotting or slight bleeding
Many women experience these symptoms up to five days before ovulation and on the day of ovulation, and these symptoms may continue for up to a day after ovulation. If you don't see any signs of ovulation, don't worry because it doesn't mean you're not ovulating. Many women have no symptoms of ovulation, but recognizing common symptoms can help you predict when you're ovulating.

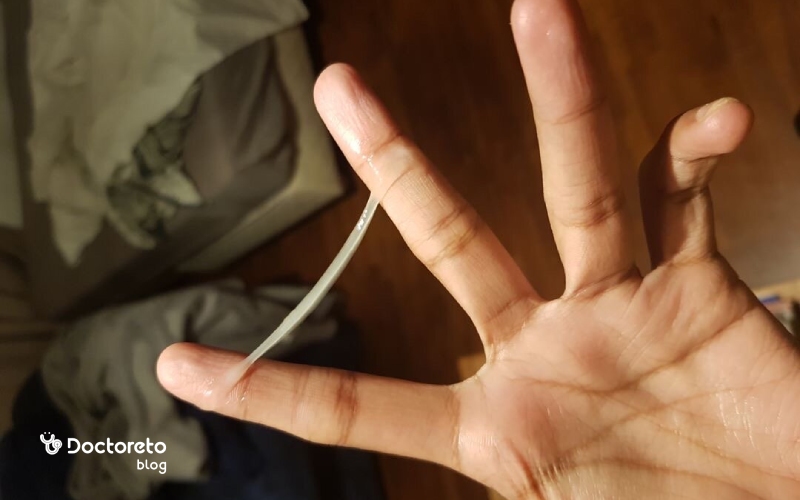
1. Changes in cervical mucus from ovulation symptoms
Vaginal secretions and cervical mucus changes are one of the important signs of ovulation that can help identify the fertile time. Close to ovulation, estrogen production increases, which causes changes in the cervical mucus. The mucus typically becomes stretched, clear, and similar to egg white, a change that helps the sperm swim more easily toward the egg. However, you should note that vaginal discharge does not always mean ovulation and sometimes it may indicate certain diseases. To diagnose ovulation more accurately, you can check the cervical mucus by inserting a clean finger into the vagina and stretching the secretions between the thumb and forefinger and checking its stretch and slippage. If the secretions were sticky, stretchy and wet, you are probably in the fertile phase.

2. Increased senses and ovulation in the 30-day cycle
For some women, a more sensitive sense of smell in the second half of the normal menstrual cycle can be a sign of poor ovulation. At this stage of fertility, your body is ready to absorb more of the male hormone androsterone. Some women also report an increased sense of taste.
3. Pain and tenderness in the breast during the ovulation cycle of women
Tender breasts or sore nipples can be another sign of ovulation. Breast pain is caused by the rush of hormones that enter your body right before and after ovulation. Some women experience this sensitivity right before ovulation, while others may feel it immediately after ovulation.English text:
quoted from betterhealth
About 40% of women experience pain and discomfort during ovulation.
Persian translation:
About 40% of women experience pain and discomfort during ovulation.
Many women may feel ovulation, which usually manifests as mild pain or cramping in their abdomen or pelvis. This pain, known as Mittelschmerz, is usually felt on one side of the abdomen (where the ovary is releasing the egg) and can last from a few minutes to a few hours. In some cases, ovulation pain may be accompanied by mild vaginal bleeding, discharge, or nausea, which are usually temporary and mild.
Although this pain is usually nothing to worry about and can be relieved with anti-inflammatory drugs, if the pain persists or becomes severe, there may be a need for medical evaluation to rule out diseases such as endometriosis or complications of ovarian cyst. In most cases, ovulation pain is close to the egg being released in the ovary, and the egg is usually released within a few hours of the pain. Doctors suggest that you record your ovulation symptoms every month in order to better identify the natural changes in your body and to pay attention to them faster if abnormal symptoms appear.
5. Ovulation with spotting (what is the cause of spotting during ovulation?)
Brown discharge and bleeding during ovulation or spotting during ovulation is normal, but not that common. This sign of ovulation occurs when the follicle that surrounds and protects the developing egg matures, grows, and then ruptures, resulting in a small amount of bleeding.
6. Ovulation without discharge, is ovulation always accompanied by discharge?
Blood turns brown with age, which is why ovulation discharge may range from red to dark brown. It's nothing to worry about unless the spotting continues, in which case you should see a doctor to check for signs of infection and the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy if you've been sexually active.
Is ovulation without discharge possible?
Yes. Some women who experience vaginal dryness may not have discharge and may not see signs of ovulation. This is not the reason why the egg is not released from the mature follicle, and even these women may experience painful ovulation and pregnancy and never see cheesy mucus like the cervix.
7. Changes in sexual desire during ovulation
Change in libido is another common symptom of ovulation. Some women find that their libido increases during ovulation, which may be Mother Nature's way of ensuring the species survives! But as you know, libido can be influenced by almost anything.
8. Changes in the cervix during ovulation
During ovulation, the cervix experiences changes that can help identify when you are fertile. At this time, the cervix is usually higher, softer and more open. To check these changes, you can touch the cervix with your finger. In women with regular menstrual cycles, the cervix is softer just before ovulation and feels similar to the touch of the lips. After ovulation, the cervix becomes firmer and resembles the tip of the nose. Although this method may require practice and is a little more difficult than other signs of ovulation, according to the changes in the cervix, it is possible to more accurately identify the time of ovulation.

9. Ovulation nausea and headache
Nausea and headache are minor but possible symptoms during ovulation. Hormonal changes that occur in the body at this time can affect the nervous and digestive systems. An increase in the level of hormones such as estrogen and progesterone can cause hormonal headaches or even nausea in some women. These symptoms usually appear temporarily in a few days close to ovulation and decrease after the egg is released. If these symptoms bother you, consulting a doctor can be helpful for managing them.
10. Changes in basal body temperature from symptoms of painful ovulation
The change in basal body temperature is one of the symptoms of ovulation that can help identify the time of fertility. Although you may not feel the temperature change directly, your basal body temperature rises significantly during ovulation and remains elevated for several days afterward. By tracking your body temperature over several months, you can identify certain patterns and more accurately predict when you will ovulate. This information will not only help you get pregnant, but it can also give you clues about the specific symptoms you're experiencing. By knowing the signs of ovulation and being in better harmony with your body, you can predict the time of ovulation more easily.
11. Changes in oral saliva during the ovulation cycle in women
Estrogen and progesterone change the consistency of dried saliva before or during ovulation and cause patterns to form. These patterns in dried saliva may look like crystals or ferns in some women. Smoking, eating, drinking, and brushing can all mask these effects, and this indicator of ovulation is less visible than other symptoms.
12. Ovulation with bleeding after abortion
In most cases, miscarriage does not affect fertility or ovulation in subsequent pregnancies. There is a possibility of left and right ovary ovulation and pregnancy within 2 weeks after abortion. Lower abdominal pain is a sign of ovulation.
13. Boiling and ovulation in girls
Pimples on the face during ovulation can mean hormonal imbalance. Acne is caused by the increase in the production of sebum and fat by increasing testosterone and binding to fat receptors.

When the egg is fertilized outside the uterus, an ectopic pregnancy (in the fallopian tube) occurs. The fallopian tube is not designed to hold a growing fetus, so it can lead to uterine bleeding and miscarriage.
15. What are the signs of the end of ovulation?
To confirm that ovulation has ended, you can test for progesterone 6 to 8 days after your usual ovulation time. At this time, your progesterone level reaches its highest level, and a high progesterone level indicates successful ovulation.
16. Does ovulation hurt?
The process of ovulation and the symptoms of egg release from the follicle are associated with pain and discomfort in more than half of women. This pain can last from a few minutes to 2 days and includes twisting under the heart, muscle cramps or severe abdominal pain.
English text:
When you ovulate, usually only one side of your lower abdomen (the side that releases the egg) hurts.
Persian translation:
In ovulation, usually only one side of your lower abdomen (the side that releases the egg) hurts. href="https://www.whattoexpect.com/getting-pregnant/fertility/five-ways-to-tell-you-are-ovulating.aspx" target="_blank" rel="noreferrer noopener">whattoexpect
the smallest signs of ovulation
Ovulation is one of the important stages in the menstrual cycle that many women may experience symptoms that indicate the release of the egg from the ovaries. These symptoms can vary and be more obvious in some women and milder in others. Paying attention to ovulation symptoms can help women better identify their fertile time. Microovulation symptoms usually occur a few days before or during ovulation and can include physical and emotional changes. Ovulation symptoms you may experience include:
- Changes in the cervical mucus: The cervical mucus naturally becomes thin, clear and elastic during ovulation, similar to egg white. These changes can be one of the first signs of ovulation.
- Increased breast sensitivity: In some women, ovulation can cause sensitivity or pain in the breast area.
- Increased energy and libido: Some women feel more energetic during ovulation and their libido may also increase.
- Mild abdominal pain or cramping (ovulation pain): Some women may feel mild pain or cramping in the lower abdomen, on the left or right side, due to the release of the egg from the ovary.
- Changes in body temperature: A woman's body temperature changes during the menstrual cycle. After ovulation, the body temperature usually increases a little (about half a degree Celsius).
- Mood changes: In some women, ovulation can cause mood changes such as increased sensitivity or changes in feelings.
- Increased appetite or fluid retention: Some women may feel more hungry during ovulation or witness fluid retention and body swelling.
symptoms of ovulation after taking letrozole
Symptoms of ovulation after taking Letrozole (Letrozole) are usually similar to normal ovulation, but these symptoms may be more obvious or severe due to stimulation of the ovaries. The most common symptoms are:
- Increasing vaginal secretions: transparent, stretchy and egg white-like secretions, which is a sign of high fertility.
- Mild pain on one side of the abdomen (mittelschmerz): Ovulation pain is usually on the side of the ovary that releases the egg.
- Increase in basal body temperature: Body temperature rises slightly in the morning after ovulation.
- Breast sensitivity
- Increasing libido
- Slight spotting: in some cases, pink spots may be seen after ovulation.
In people taking letrozole to stimulate ovulation (especially in cases of infertility or polycystic ovary syndrome), these symptoms can be a sign of an adequate response to the drug. However, to ensure that ovulation has occurred, an ultrasound or blood test (checking LH or progesterone levels) is recommended.
symptoms of successful ovulation
Symptoms of successful ovulation are usually signs that the egg has been released and is ready to be fertilized. Some of these symptoms include:
- Changes in the cervical mucus: The vaginal mucus usually becomes clear, stretched and similar to egg white, which helps the sperm to reach the egg more easily.
- Slight pain or cramping in the abdomen (Mittelschmerz): Some women experience mild pain or cramping on one side of the abdomen, which indicates the release of the egg from the ovary.
- Increased breast sensitivity: Many women feel sensitivity and swelling in their breasts during ovulation.
- Increased libido: Some women have a higher libido during this period, which is caused by hormonal changes.
- Changes in body temperature: After ovulation, the basal body temperature usually increases by 0.4 to 1°C, and this increase indicates the release of the egg.
- Light Bleeding or Spotting: In some cases, women may experience very light spotting or bleeding due to hormonal changes and egg release.
When does ovulation occur?
How many days are the days of ovulation and when is ovulation called? Ovulation usually occurs on day 15 of your menstrual cycle, but it is not the same for everyone. If you are like most women of reproductive age, your menstrual cycle lasts between 28 and 32 days, and ovulation usually occurs between days 10 and 19 of this cycle, that is, about 12 to 16 days before your next period.When is the best time for women to ovulate?
Generally, in healthy women, ovulation occurs 14 days before menstruation. So if your cycle is 35 days, ovulation will occur on day 21 of the cycle, but if your cycle is 21 days, ovulation will occur on day 7.
Ovulation time chart: when is the best time to ovulate for pregnancy?
Women's menstrual cycle is affected by hormonal changes that play a key role in ovulation. Ovulation usually occurs on days 13 and 14 of a 28-day cycle, and knowing exactly when it is requires understanding the body's hormonal changes. For women who have sex two days before ovulation or on the same day, the chances of pregnancy increase. Normally, women with a 28-day menstrual cycle ovulate on day 14, and the best time for pregnancy and uterine preparation symptoms is between days 11 and 14.
- The first days of the cycle (day 1 to 12): At the beginning of the cycle, the level of hormones gradually increases. This increase stimulates the ovaries to produce eggs, and the level of estrogen hormone gradually increases during this period.
- Ovulation days (13th and 14th day): In these days, the level of hormones reaches its peak. The estrogen hormone is at its highest level and the egg is released from the ovary. This process causes changes in the lining of the uterus that prepares the body to accept the fertilized egg. In the diagram below, ovulation days are marked with a red bar.
- After ovulation (day 15 to 28): After the egg is released, the level of progesterone hormone increases. This hormone is necessary to maintain pregnancy and support the uterus in case of pregnancy. If the egg is not fertilized, the level of hormones will decrease and the menstrual cycle will begin.
Ovulation time chart in 28 days cycle
Ovulation cycle and pregnancy, is the egg released during pregnancy? (When is the best fertile time)
The best time to try to get pregnant is when the mature egg is released from the surface of the ovary and can potentially remain fertile for about 24 hours. You don't have to have sex exactly on the day of ovulation to get pregnant! In fact, there is a 6-day "fertile window" in your cycle, the five days leading up to ovulation and the day you ovulate.
Of these six days, you will be most fertile in the two to three days before ovulation and on the day of ovulation. More than 24 hours after ovulation, the egg will no longer be fertile, so you will not be able to get pregnant until your next menstrual cycle.

Natural prevention of pregnancy by determining the days of ovulation
Today's contraceptive methods are usually done using contraceptives. Since these drugs work by disrupting the function of hormones, they have many side effects. Therefore, the best method is to use the ovulation calendar for natural pregnancy prevention.
As we mentioned, eggs are fertilized only up to 24 hours after release, so if you know exactly when you ovulate, you can prevent pregnancy without drugs.
Is ovulation with birth control pills possible?
The hormones in the birth control pill completely stop ovulation. Absence of ovulation means that there is no egg to fertilize the sperm in the fallopian tube, so pregnancy cannot happen.
calculation of ovulation time after period
To calculate the exact time of ovulation, record the start and end days of your period for several consecutive months. If your menstrual cycle is normal (between 25 and 35 days), ovulation usually occurs about 14 days before your next period. To be more specific, also note ovulation symptoms such as lower abdominal cramping, increased cervical mucus (which usually becomes clear and stretchy), breast tenderness, fluid retention, increased appetite, and mood changes. By combining this information, you can predict your ovulation time more accurately and increase your chances of pregnancy.
Ovulation Kit (OTC) to check the exact ovulation date
Ovulation prediction kits measure the level of luteinizing hormone (LH) that can be detected in urine. These kits work because ovulation usually occurs 10-12 hours after the LH surge (usually on days 14-15 of a 28-day cycle). For complete egg maturation, LH concentration must remain high between 14 and 27 hours. How the ovulation kit works is as follows:
- Kit preparation: Unpack the ovulation kit and make sure the expiration date has not passed. Make sure that the kit is designed for use in urine.
- Choosing the right time: The right time to do the test is usually in the morning, because urine is more concentrated at this time. Before the test, reduce your fluid intake four hours before.
- Using the test stick: Place the ovulation kit on a flat surface. Pour your urine on the test stick or immerse the stick in your urine (exact instructions for use are explained in the kit instructions).
- Waiting for the line to appear: After urinating or dipping the stick in the urine, wait for the line or lines to appear. It usually takes between 5 and 10 minutes.
- Checking the results: The kit usually displays two lines: a control line (which shows the accuracy of the test) and a test line (which shows the LH level). If the color of the test line is similar or darker than the control line, it means that the LH level is high and ovulation is near.
- Repeat the test on different days: kits usually contain five test sticks that you can use on several days. It is recommended to perform the test at the same time every day to obtain more accurate results.
If the test line becomes noticeably darker on different days, it is more likely that you will ovulate in the next 24-48 hours. During this time, sex can increase the chances of pregnancy. With these steps, you can identify your ovulation time more accurately and have a better planning for pregnancy.
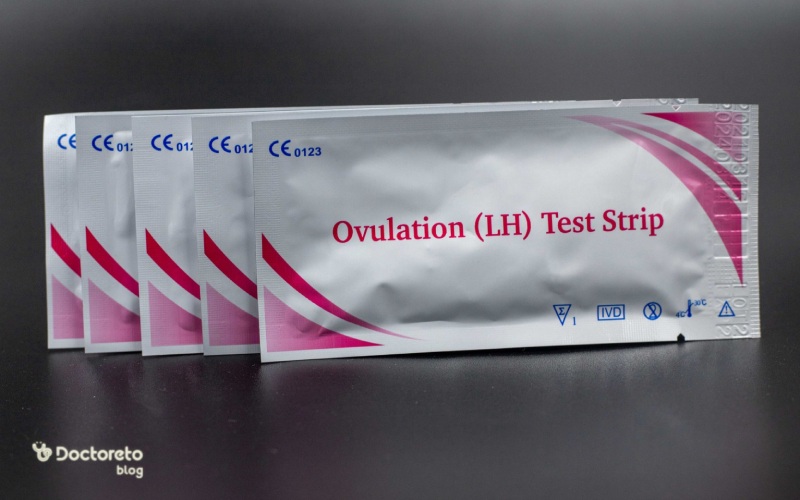
Test to determine the day of ovulation (when is the ovulation period?)
Ovulation kits (OTC) are one of the effective tools for ovulation date calculation. These kits measure the level of luteinizing hormone (LH) in urine. Ovulation usually occurs 10 to 12 hours after the LH surge, which is on days 14 to 15 of the menstrual cycle for women with 28-day cycles. The concentration of LH must remain high for 14 to 27 hours so that the full maturation of the egg is possible.
The way these kits work is that by urinating on the test stick, you have to wait for a line to appear. If the color of the line matches the color indicated in the instructions, this means that ovulation will occur in the next 24-48 hours. Most kits come with five test sticks to be used on several different days, but it's best to check the expiration date, as most kits only last two years. For best results, perform the test at the same time every day after reducing fluid intake (about 4 hours before the test) so that your urine is more concentrated and LH is easier to detect.
What are the stages of the menstrual cycle and ovulation?
Menstrual cycle lasts an average of 28 days. In these stages, egg follicles in the ovary begin to grow and the inner lining of the uterus becomes thicker, then the egg is released and the body is more ready for a possible pregnancy, but if pregnancy does not occur, the uterine wall falls and we have a period. In general, the entire cycle can be divided into 4 stages:
| Stages of menstruation | Symptoms of each stage of the menstrual cycle |
|---|---|
| Periovulatory or follicular phase | A layer of cells around the egg begins to enlarge and looks more like It becomes mucus. At this stage, the inner lining of the uterus starts to thicken. |
| Ovulation stage | The egg and its cell network leave the ovary through the hole formed by enzymes and go to the fallopian tube. This is also the fertile period and usually lasts 24 to 48 hours. |
| The post-ovulatory or luteal phase | The body secretes luteinizing hormone. A fertilized egg implants in the uterus, while an unfertilized egg slowly stops producing hormones and dissolves within 24 hours. |
| Menstrual Phase | If there is no pregnancy, the lining of the uterus begins to break down, preparing to leave the body during a period. |
What is irregular ovulation?
Oligoovulation is the medical term for irregular ovulation (early or late ovulation). Irregular ovulation can happen due to various physical problems and diseases. Ovulating for an irregular period even reduces your chances of pregnancy. The following can indicate irregular ovulation:- Irregular or missed periods: It is completely normal for the menstrual cycle to change a few days a month. A "normal" cycle can last as little as 21 days or as long as 35 days. If your periods are usually shorter or longer than this and you have irregular periods, you may have ovulation problems.
- No increase in body temperature is a sign of failed ovulation: If you have charted your cycles and do not see a slight increase in your body temperature, you may not be ovulating.
- Discrepancy in the results of the Medicore Ovulation Test and other tests: Ovulation test kits detect the hormone LH, which rises just before ovulation. If you never get a positive result, you may not be ovulating. This is common in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
If you don't ovulate, will you get your period?
Menstruation occurs when the egg released from your ovary is not fertilized and the uterus loses its lining. This is why you cannot have a period without ovulation. However, uterine bleeding may occur for other reasons.
diseases related to irregular ovulation (who doesn't ovulate?)
Anything that interferes with ovulation may lead to infertility or difficulty getting pregnant. Regular ovulation is necessary for pregnancy, because without the release of the egg, fertilization will not be possible. Factors such as hormonal problems, disorders in the regulation of ovulation, structural disorders in the reproductive system, and even changes in weight and stress can have negative effects on the ovulation process. In the following, we will examine these factors and how they affect ovulation.
English text:
quoted from the site my.clevelandclinic
Irregular ovulation occurs due to the imbalance of one or more specific hormones, especially hormones involved in ovulation.
Persian translation:
Irregular ovulation occurs due to the imbalance of one or more specific hormones, especially hormones involved in ovulation.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Also known as ovarian laziness, this condition causes the ovaries to enlarge and form small, fluid-filled cysts. PCOS leads to hormonal imbalances that can disrupt ovulation. Symptoms include insulin resistance, obesity, irregular hair growth, and acne. Hypothalamus dysfunction This disorder is caused by problems in the production of FSH and LH hormones that stimulate ovulation. Dysfunction of the hypothalamus can affect the menstrual cycle and lead to irregular cycles or amenorrhea (absence of menstruation).
- Premature Ovarian Failure This condition refers to the early cessation of egg production and a decrease in estrogen levels. Premature ovarian failure may be caused by autoimmune problems, genetic abnormalities, or environmental toxins and usually occurs before the age of 40.
- Excess prolactin (hyperprolactinemia) Increased prolactin levels, which may be due to the use of certain medications or disorders in the pituitary gland, can reduce estrogen production and disrupt ovulation. This disorder, in turn, can cause a decrease in fertility.
What is the treatment of irregular ovulation?
Treatment of irregular ovulation usually involves medication and lifestyle changes. One common treatment is to take an ovarian enhancement pill such as Clomid (clomiphene), which is used to stimulate the ovaries and regulate ovulation. This drug has few side effects and usually results in successful pregnancy. Also, Vitagrenos, as a herbal treatment, helps regulate female hormones and improves the functioning of the menstrual cycle.
Before starting treatment with ovarian enhancement pills, your doctor will usually check your male partner's fertility status and your fallopian tubes. This includes a semen analysis for the man and an HSG test (a special type of X-ray) to check the fallopian tubes. Also, following a period diet and managing premenstrual symptoms can help regulate ovulation and improve fertility.
Your doctor's final words about ovulation
You can use what you've learned about ovulation to get pregnant faster. However, even if your fertility is excellent, don't expect to get pregnant within the first month of trying. According to research done on couples who knew how to recognize ovulation signs and time sex to get pregnant, 68% got pregnant within three months. After six months, 81% were pregnant. However, ovulation is not the only key to conception. This is only one part of the puzzle. The overall health of the reproductive system is also important on both sides. If you're trying to get pregnant and you're pretty sure you're ovulating, don't assume that means everything is fine.
Your doctor takes care of your health!