بیش از ۳۰ گونه از ویروس HPV می تواند بر اندام تناسلی شما تأثیر بگذارد. These include harmless forms of HPV, such as those that cause genital warts. Only certain types of HPV are considered high risk because they can lead to cervical cancer, which is the fourth most common cancer among women. Vaccination against HPV and regular pap smear can prevent cervical cancer.
What is human papillomavirus (HPV)?
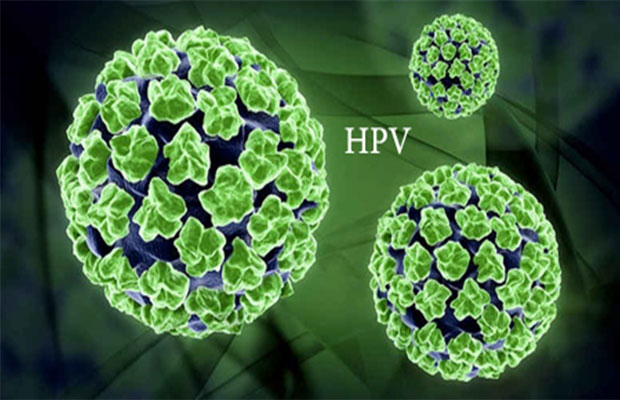
HPV is a common virus that can affect different parts of your body. There are more than 100 types of HPV, including HPV strains that cause warts on the genitals, hands, feet, face, and more. About 30 types of HPV can affect your genitals, including your vagina, cervix, penis, and scrotum.
HPV, which affects your genitals, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact. Some HPV types are high risk and can lead to cancer such as cervical cancer. Early diagnosis and treatment can usually prevent this from happening.
Types of HPV virus
There are more than 100 types of HPV. About 60 out of 100 types cause warts in areas such as hands or feet. About 40 others enter the body during sexual contact. They are drawn to the mucous membranes of the body, such as the moist layers around the anus and genitals. All 40 sexually transmitted human papillomaviruses do not cause serious health problems.
High-risk HPV strains include HPV 16 and 18, which cause about 70% of cervical cancers. Other high-risk human papillomaviruses include 31, 33, 45, 52, 58 and several others.
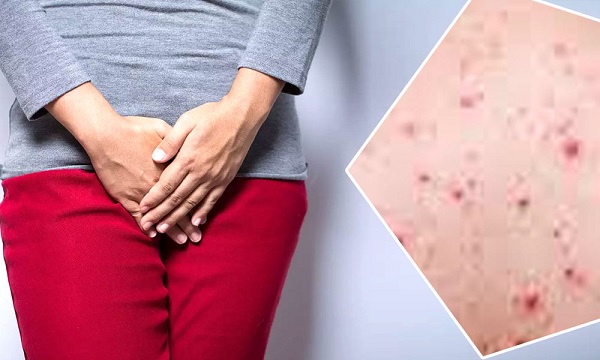
Low-risk strains of HPV, such as HPV 6 and 11, cause about 90 percent of genital warts, which rarely turn into cancer. These growths can look like bumps. Sometimes, they are shaped like cauliflower. Warts can appear weeks or months after having sex with an infected partner.
Your immune system usually controls HPV virus infections so they don't cause cancer. High-risk HPV infections, if they persist, can cause cancer, including cervical cancer in women. Because sometimes HPV infections are not successfully controlled by the immune system. When high-risk HPV infection continues for years, it can lead to cell changes that, if left untreated, may worsen over time and turn into cancer.
Who does the HPV virus affect?
Anyone can get HPV if they have sex or have close skin-to-skin contact with a partner who has the virus. Similarly, anyone who has the virus can spread it to their partner during intercourse, oral sex, anal sex, or other close genital contact. If you have the following, you are more likely to be infected with the HPV virus:
- Multiple sexual partners
- Sex at a young age
- A sexual partner who has had many partners
Prevention of HPV virus
The only way to prevent HPV is to avoid unprotected sex. For many people, more realistic goals include reducing the risk of HPV and preventing cervical cancer while enjoying a healthy sex life. You can reduce your risk of getting HPV if you:
Get the HPV vaccine. The best way to protect against HPV is to get vaccinated before becoming sexually active. There are three FDA-approved HPV vaccines that prevent HPV strains that cause cervical cancer and genital warts, and are approved for everyone ages 9 to 45.
What cancers does the HPV virus cause?
Long-term infections with high-risk HPV viruses can cause cancer in parts of the body where HPV infects cells, such as the cervix, oropharynx (the part of the throat behind the mouth, the back of the oral cavity that also contains these cells). Cancers associated with HPV include:
1- Cervical cancer
Almost all cervical cancers are caused by HPV. Routine screening can prevent most cervical cancers by allowing healthcare practitioners to find and remove precancerous cells before they become cancerous.
2- Oropharyngeal cancers
Most of these cancers that develop in the throat (usually the tonsils or the back of the tongue) are caused by HPV. The number of new cases is increasing each year, and oral and pharyngeal cancers are now the most common HPV-related cancers in the United States.3- Anal cancer
More than 90% of anal cancers are caused by HPV. The number of new cases and deaths from rectal cancer is increasing every year. Anal cancer is almost twice as common in women as in men.4- Penile cancer
Most penile cancers (more than 60%) are caused by HPV. Learn about the importance of getting the recommended treatments for penile cancer, a rare type of cancer.5- Vaginal cancer
Most vaginal cancers (75%) are caused by HPV. Worldwide, the burden of HPV-related cancers is much higher. High-risk HPVs cause about 5% of cancers worldwide, with an estimated 570,000 women and 60,000 men developing HPV-related cancers each year. Cervical cancer is one of the most common cancers and a leading cause of cancer-related deaths in low- and middle-income countries, where screening tests and treatment for early cervical cell changes are not readily available.
Types of HPV virus treatment methods
HPV virus with visible genital warts may recover after a few years without treatment, but the virus of this wart remains in the body and returns after some time. Therefore, the goal of treatment is to control the symptoms of the disease and prevent its transmission to others. The methods of treating male genital warts and treating female genital warts are not much different from each other, and both should choose one of the common treatments according to the size and exact location of the warts. In short, the methods of treating the HPV virus that has led to warts are as follows:
1- Treatment of warts with laser
This method is very useful for removing single or cluster warts. The best treatment of genital warts with laser involves the direct irradiation of infrared rays on the warts, which removes the genital wart and treats it quickly. Laser is mostly used to treat larger genital warts, but due to its ease compared to other methods, it is more welcomed by patients.

Dr. Irfaneh Salimi, Surgeon and specialist in Gynecology, Obstetrics, Infertility - Genital Cosmetic Surgeon
Practice address: Tehranpars, between the second and third floors, 188 East Rahmani St., building 107, second floor
Hours Attendance at the office: Even days 16:00 to 20:00 Sunday 9:30 to 12:30
2- cryotherapy or freezing the wart
Using a special chemical, the wart will be frozen and destroyed. But some people have experienced the return of warts after this method.
3- Burning or electrocautery
This method, which is a common surgical method, is used to remove fleshy and soft appendages.4- Genital wart surgery
Wart surgery is often used for appendages that are located on the skin. If you have warts inside the vagina or anus, it is recommended to use a laser to remove them.
5- Drug treatment
Some medicines and ointments are used to eliminate the HPV virus, which must be prescribed and recommended by a doctor. Read more about the types of HPV treatment and genital wart ointment.
Frequently Asked Questions
1- Is the presence of the HPV virus in the body always associated with the appearance of warts?No. In most cases, this virus does not have significant symptoms. For this reason, it is recommended to use physical barriers for sexual intercourse and Pap test every few months.
2- Can HPV be caught from the fingers?HPV disease can also be transmitted through fingers. A patient or their partner may have the HPV virus on the skin of their fingers as a result of touching an infected area. Alternatively, they may have HPV under their nails.
3- Is there a definitive method to treat the HPV virus?This virus is not able to disappear, but only weakens in the body as the immune system increases. So if you get this condition, the people around you should know this.