Warts in children - Dr. Ali Faraji

Dr. Ali Faraji
تهرانSpecialist in children and babies

Are warts in children dangerous?
- 10/19/2024
- 5 minutes

What are warts in children?
Warts in children are small, non-cancerous lumps that usually appear on the skin, especially on the hands, feet, and face. This complication is caused by a viral infection with the human papilloma virus (HPV) and is usually seen as circular or oval bumps with an uneven surface and the same color as the skin or a little darker. Warts are usually painless, but in some cases they itch or cause discomfort. This complication generally occurs in children due to a weaker immune system and contact with contaminated surfaces. In most cases, warts will heal naturally over time, but in case of discomfort or concern, it is recommended to consult a doctor so that appropriate treatments can be provided.The cause of warts in children
Warts in children are caused by a viral infection. The virus that causes warts is called human papilloma virus (HPV). The virus is transmitted through direct contact with infected skin or indirect contact through items such as towels, shoes, or contaminated surfaces, if there is wart discharge from an infected person on these objects. Some of the effective factors in increasing the risk of warts in children are:- Weak immune system: Children with a weaker immune system are more likely to get warts.
- Skin damage: Wounds, cuts or scratches facilitate the entry of the virus into the skin.
- Moist environments: Moist environments such as swimming pools, public bathrooms and gyms are suitable places for virus transmission. Contact with infected people: If the child comes in contact with someone who has warts, the virus is more likely to be transmitted. Some children will come into contact with the mother's genital wart during natural delivery.
- Sharing of personal items: Using items such as towels or shoes that have been used by infected people leads to the transmission of the virus.

Symptoms of warts in children
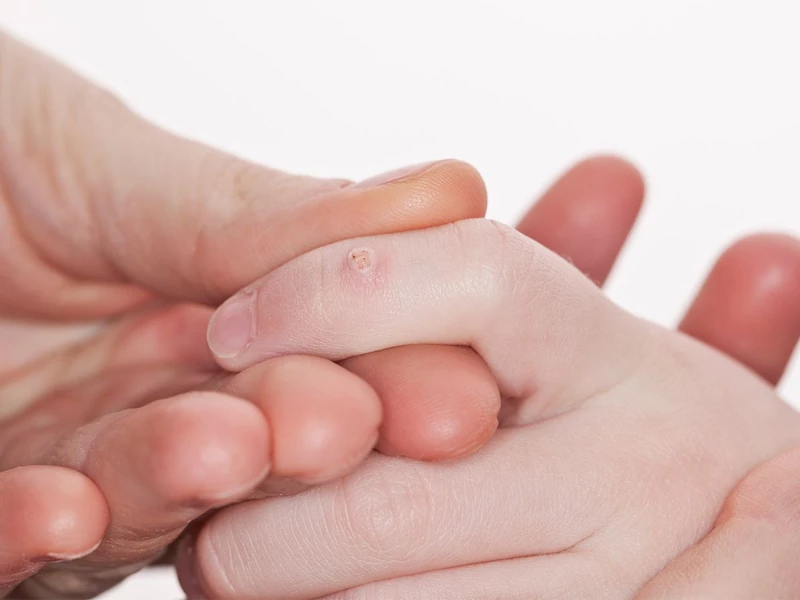
Warts in children usually appear as small, fleshy bumps on the skin. These bumps are a color close to the skin color or slightly darker. Common symptoms of warts in children are:- Warts usually have a rough surface and grow larger over time.
- Warts are usually round or oval and appear singly or in clusters.
- Warts often appear on the hands, fingers, feet, knees and face of children.
- Some warts itch or become painful when pressed or repeatedly touched.
- Warts can be transferred to other parts of the body or to other people through contact with infected skin or sharing personal items, such as towels or shoes.
Warts are usually painless, but in some cases they can cause discomfort, especially if they are in areas such as the soles of the feet where there is a lot of pressure. If your child has warts, it is better to consult a doctor so that appropriate treatment can be done if needed.
Diagnosis of warts in children
Diagnosis of warts in children is usually done by a physical examination by a doctor. The doctor diagnoses the wart by observing fleshy and rough bumps on the skin, which are often round and the same color as the skin or a little darker. In some rare cases, if a definitive diagnosis requires further investigation, the doctor will take a small sample of the wart for further tests (biopsy). This method is usually used in complex or unusual cases. However, most warts can be easily recognized by observing the external signs.
Treatment of warts in children
The treatment of warts in children is different depending on the type, location and severity of the wart. Many warts go away on their own without any special treatment. But if the wart causes discomfort or pain or spreads quickly, there are different treatment methods. Using topical drugs containing salicylic acid, freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy) and burning the wart are common treatment methods. In more resistant cases or larger warts, the doctor uses other methods such as laser therapy or surgery.
Frequently asked questions about warts in children
Is wart treatment necessary for children?In many cases, warts go away on their own over time. But if the warts are painful or cause discomfort, treatments such as topical medications, freezing or other methods are recommended by the doctor.
How long does it take for warts in children to disappear?Warts may disappear naturally between a few months and two years, but this period depends on the child's immune system and the type of wart.
Do warts in children come back after treatment?Sometimes warts come back after treatment because the HPV virus remains in the body. Frequent treatments are necessary.
Conclusion
Warts in children are an almost harmless complication caused by the human papilloma virus (HPV). Although most warts disappear on their own without the need for treatment, in some cases they can cause discomfort or pain. It is very important to prevent warts by observing hygiene, avoiding contact with other people's warts and using personal items. Also, if you see painful or persistent warts, it is necessary to consult a doctor to choose the best treatment method. With parental support and awareness, this skin problem is often easily manageable. Related contentHow to treat a child's flatulence? The Complete Guide for Parents
Abdominal bloating in children is one of the common problems that
The best pediatrician on Government Street, a safe choice for your child's health
Choosing the best pediatrician is one of the most important decisions
Anemia in infants: symptoms, causes and effective treatment methods
Anemia in babies is one of the common problems during pregnancy
Write your comment Cancel reply