Genital warts are one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases worldwide caused by human papillomavirus (HPV). What distinguishes genital warts from other diseases is its high transmission power even in the absence of outward symptoms. Despite the wide spread of this virus, unfortunately, many people still do not know how genital warts are transmitted and what are the ways to prevent it.
In this article, we have tried to examine in detail how genital warts are transmitted, factors that increase the risk of infection, ways of prevention and false beliefs that exist in this field; Because awareness is the most important step in maintaining sexual and general health.
Table of Contents
What is a genital wart? class="ez-toc-section-end">
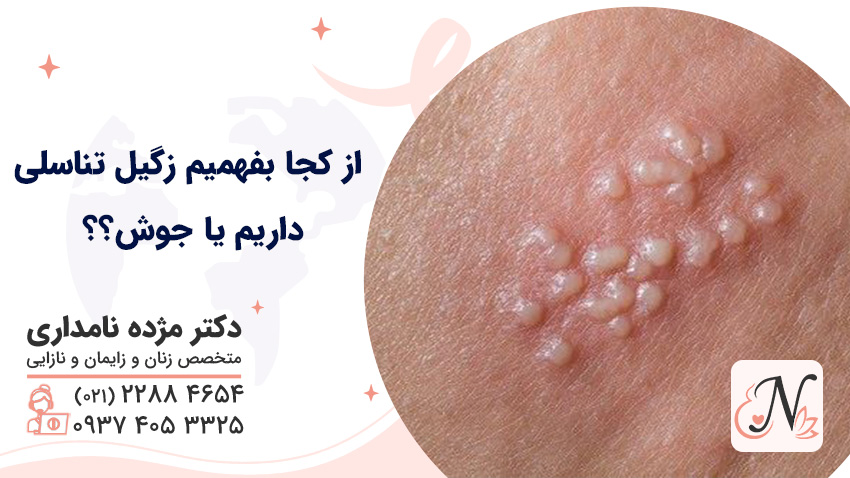
Genital warts is one of the common sexually transmitted diseases caused by a virus called HPV . This virus has more than 100 different types, some of which are low-risk and others are high-risk; High-risk types may be associated with cervical cancer or other genital cancers.

Warts are usually seen in the form of small, fleshy bumps and sometimes clusters in the genital area, anus or around it, but in some cases; A person may be infected without having any visible symptoms. Unlike common warts on hands and feet, genital warts are usually transmitted through sexual contact and require specialized examination and treatment.
Genital warts are usually transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact during sexual relations; This contact can be vaginal, anal or oral. Even if a person has no symptoms, it is still possible to transmit the HPV virus. In rare cases,hand contact with warts, oral contact with an infected person, or transmission from mother to baby during childbirth may also cause infection.
In the following, we will examine some of the cases that may cause the transmission of genital warts.
Genital warts through oral saliva
HPV may be transmitted through close oral contact, but it depends on the type of contact. Saliva alone (for example, when talking or eating from a shared glass) is usually not the agent of transmission. But during a kiss when there is an exchange of saliva and one of the parties has oral or throat warts, there is a possibility of virus transmission.
In addition, oral contact with someone with genital HPV can transmit the virus to the mouth or throat. Some types of HPV are linked to oral warts or even cancers of the oropharynx, although these are rare.
Genital warts through the examination bed
The examination bed in medical centers is usually covered with a disposable cover or antiseptic material. Since HPV requires direct skin or mucosal contact and is rapidly inactivated in a dry environment, the risk of transmission from a dry surface such as an examination bed is very low.
However, if there are fresh secretions or if the principles of disinfection are not observed, there is a very small possibility of transmission.
HPV transmission through the bathroom

Unlike fungi or some bacteria, the HPV virus is not transmitted through a moist environment or warm water. Healthy skin is an effective protective barrier against viruses.
Sitting on wet surfaces, using a shared towel or loofah in a public bathroom, or indirect contact can rarely pose a risk, and there is only a small risk if the skin is cut or scratched.
ways of transmission of hpv pool
One of the common questions is Are genital warts spread through swimming pools?
In answer to this question, we must say that the swimming pool is an environment full of water and chlorine, and the HPV virus does not last long in such environments. Direct skin-to-skin contact in the pool (eg, close bodily contact) can be the agent of transmission, not the pool water itself.
Sitting on wet chairs and the edge of the pool or using shared items such as towels may rarely pose a risk, but is not considered the main route of transmission.
Can genital warts be transmitted through the toilet?
The possibility of HPV virus transmission through the toilet is very low and close to zero. The HPV virus needs living cells of the skin or mucus to survive and be transmitted to the body, and it cannot remain for a long time on dry surfaces such as the toilet seat.
In addition, the skin of the external genitalia, unless there is an active wound or scratch, is not easily susceptible to the virus. Therefore, sitting on the toilet - even if the infected person has already used it - can rarely lead to HPV transmission.
Transfer Genital warts through the toilet hose
The HPV virus is mainly transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact in the genital area, not through objects. Although it is possible for the virus to be present on the surface of the toilet hose, because HPV is inactivated outside the body in a short time, transmission through the hose is very rare and almost impossible. Unless your skin has an open wound and contact is made with an infected person immediately after using it.
Hygiene in public restrooms is always recommended, but there is no serious concern about the toilet hose.
Does touching a genital wart cause transmission?

Yes, if a person has direct contact with the genital warts of another person or himself, especially if the skin has cracks, wounds or cuts, there is a possibility of transmitting the virus.
Also, if you touch the genital area or mouth after touching the wart, the possibility of infection increases.
All people who have sex can be infected with HPV during their lifetime, but some people are more likely to get it than others. There are factors that can increase the risk or severity of infection. Knowing these factors helps to prevent transmission or activation of the virus with better prevention. In the following, we examine the most important factors:
-
Having multiple sexual partners
-
Not using condoms regularly
-
weak immune system (for example, in people with HIV or taking immunosuppressive drugs)
-
Having a sexual partner with HPV or other sexually transmitted diseases
-
History of other sexually transmitted infections (such as herpes or chlamydia)
-
No vaccination gardasil
-
presence of wound, inflammation or scratch in the genital area
-
Smoking (due to the weakening of body mucosa immunity)
-
Using shared personal items in unsanitary conditions (low but significant probability)

ways Preventing the transmission of genital warts
In this section, we get to know the most important ways to prevent the transmission of genital warts. These tips will help you protect your and your partner's sexual health by following a few simple principles and minimize the possibility of contracting or transmitting this virus:
-
Using condoms in every sexual relationship: Condoms reduce transmission significantly, but because HPV can also be transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, it is not 100% protective.
-
Gardasil vaccine injection: As a vaccine to prevent genital warts, Gardasil prevents up to 90% of high-risk types of warts. The best time to inject is before starting sexual activity, but it is also useful at an older age.
-
Having a stable and reliable sexual partner: Reducing the number of sexual partners reduces the possibility of contact with infected people.
-
Strengthening the immune system: A strong immune system can control or even clear the HPV virus in many cases. To strengthen it, it is necessary to include enough sleep, healthy eating and consumption of fruits and vegetables, regular exercise, reducing stress and quitting smoking and alcohol in your lifestyle.
-
Avoid sexual contact with people who have symptoms: If you see an appendage or wart in someone's genital area, you should avoid sexual contact until a thorough examination.
-
Raising awareness and conducting screening tests: Especially for women, conducting Pap smear and HPV test at regular intervals It is very important.
-
Not sharing contaminated personal items: The probability of transmission from contaminated towels or underwear is very low, but personal hygiene is important.
-
Personal and sexual hygiene: Regular washing of the genital area, keeping it dry and checking regularly to observe any changes or appendages is important.
Duration Genital wart transmission time
The duration of transmission of the genital wart virus is very fast and usually happens during the first sexual contact (vaginal, anal or oral) with an infected person. Your sex doesn't have to be perfect or long; Even skin-to-skin contact in the genital area is enough to transmit warts.

How long does genitalia appear?
The duration of symptoms after being infected with the HPV virus is different in different people. But usually:
-
Warts may appear between 2 weeks and 8 months after sexual contact.
-
In some people, the virus remains dormant for months or even years and causes no symptoms.
-
Sometimes the warts are never seen, but the virus is still present in the body and it is possible to transmit it to others.
Genital warts, if not treated in time, may spread and even cause more serious problems. Fortunately with progress Genital wart treatment methods, no need to worry anymore.
Dr. Mojdeh Namdari gynecologist and obstetrician, by using the latest treatment technologies such as specialized laser and cryotherapy (freeze) provide quick, painless and low-complication treatment for genital warts gives These methods are suitable for all types of warts and are an excellent choice, especially for people who are looking for a safe and effective treatment.
If you have genital warts, know that this disease can be treated. It is enough to check and start the treatment process with Dr. Namdari's office Call.
![How are genital warts transmitted? [Methods of transmission and prevention]](/storage/posts/covers/2026/01/05/611586d40e18c7fb5ce391e45d70d8da5c360bfc78c983844c3ab9281662f86f.jpg)



![Does large labia cause infection? [Dr. Namdari's answer]](/storage/posts/covers/2026/01/05/5934b8522af93e8344a3aaf305b54aa207824ade51b1c60210883b69eb6d11fb.jpg)





![Vaginal RF for infection [a safe and effective method to treat recurrent infections]](/storage/posts/covers/2026/01/05/23c604df3f0de35f0eef05bacb2971f87b552fc0274d69bf3c14b469fbab6978.jpg)