Some people realize that they have blood concentration after receiving their blood test results. Blood concentration can happen for various reasons, including an increase in the number of red blood cells. This may increase the risk of blood clots and related problems. Sometimes some of these problems threaten your life; Therefore, in this article, we are going to focus more on the blood concentration in the test and the important points related to it. Stay with us until the end of the article.
Blood concentration symbol in the test Symptoms, quick treatment and prevention tips

Dr. Reza Bahadur
MashhadOrthopedic specialist
What is blood concentration?
Most people usually use the term blood concentration to describe polycythemia vera (PV), but blood concentration is caused by various reasons such as a large number of red cells in the circulatory system or an imbalance in the blood coagulation system. Having too many red blood cells can slow down blood flow, resulting in impaired movement of oxygen, hormones, and nutrients throughout the body, preventing them from reaching tissues and cells. This issue may cause a decrease in oxygen levels, hormonal imbalance and nutritional deficiencies.
Blood density is not an independent disease, but is caused by other vascular problems. On the other hand, blood clots alone have no symptoms, but may cause blood clots that usually cause symptoms. When a person has blood clots, their blood has a greater tendency to clot, so that a blood clot may form even without bleeding. A blood clot (thrombus) in an artery or vein may block blood flow to vital organs such as the brain, heart, or lungs. Because of this, clot formation can be dangerous and life-threatening.

Diagnosis of blood concentration
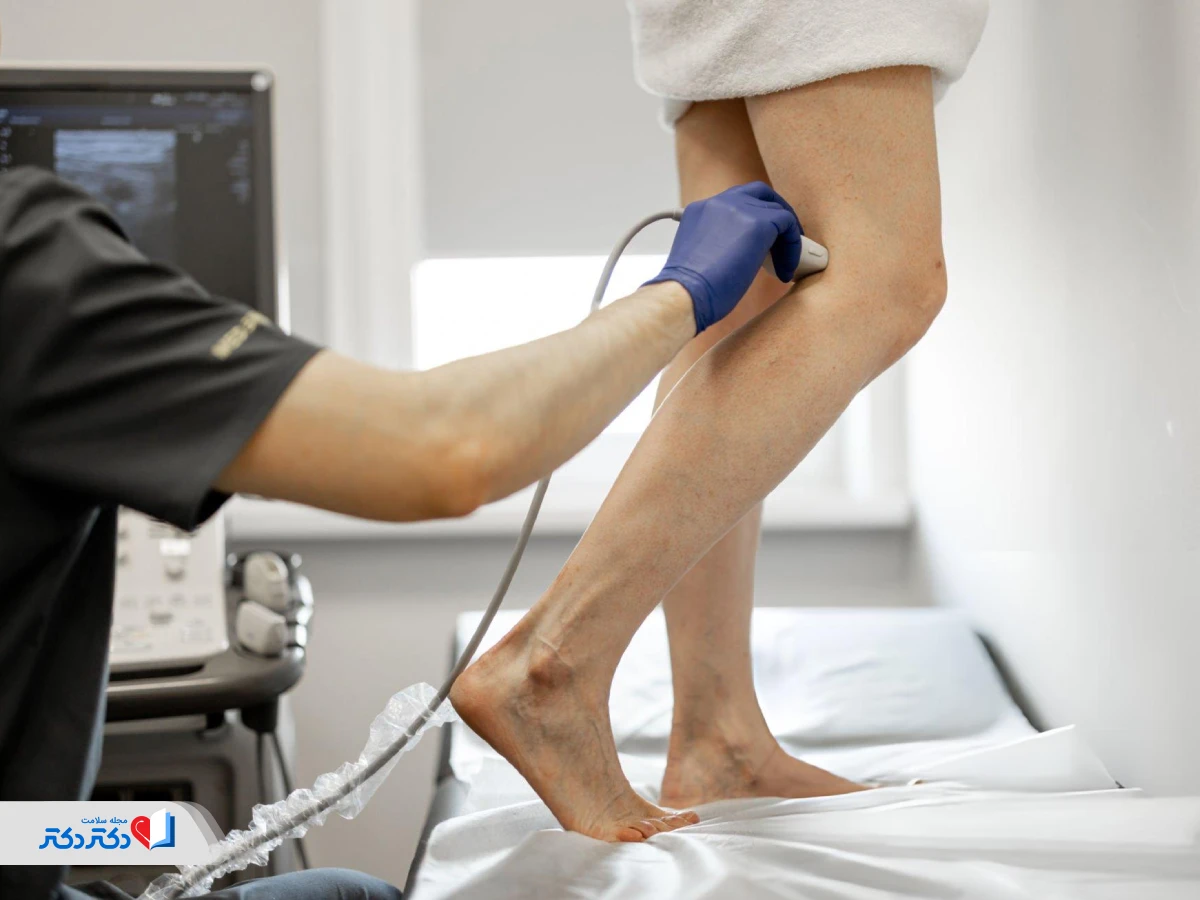
If your doctor suspects abnormal blood clotting, he may perform a physical exam, review your medical history carefully, and finally order some tests.
There are various tests to diagnose blood concentration. have, including:
- Genetic tests: Because genetics plays an important role in blood concentration, your doctor will want to know your family history. In particular, he will ask you about relatives who have had blood clots or miscarriages and may prescribe genetic testing. Blood: These tests help the doctor identify hypercoagulopathy (high tendency of blood to clot). These tests include a complete blood count (CBC), coagulation tests to check the blood's ability to clot and measure its duration, and a test to check the amount of fibrinogen in the blood plasma. A blood test may also be performed to check for gene mutations.
On the other hand, more tests may be performed to identify suspected underlying conditions.
What is the symbol of blood concentration in the test result?
Blood concentration in the test result is usually shown as HCT or Hct. This symbol stands for hematocrit or the percentage of red blood cells in the blood. This index shows the ratio of red blood cells to the total blood volume and is considered one of the main criteria for checking blood concentration. The hematocrit test is a simple blood test that is sometimes called the packed cell volume test. This test is usually done as part of a complete blood count test.
When the hematocrit is low, it means that the proportion of red blood cells in the blood is lower than normal. This condition can indicate various things, including:
- The blood has a small number of healthy red blood cells, which is called anemia;
- The body is lacking vitamins or minerals;
- You have lost a lot of blood.
If you have blood clots, usually the ratio of red blood cells in the blood is higher than normal and Hematocrit shows a higher number. This state can indicate various things, including:
- Dehydration;
- Creating a disorder that causes excessive production of red blood cells, such as polycythemia vera;
- Presence of lung or heart diseases;
- Living at high altitudes, such as mountainous areas.
The cause of blood concentration
Various factors can cause blood concentration, including:
- The presence of a large number of blood cells in the blood circulation;
- Diseases that affect the blood clotting process;
- Increase of clotting proteins in the blood.
Since There are many reasons for blood concentration, the doctor does not have a standard and general definition for blood concentration, but defines this condition based on any disease or condition that causes blood concentration.
Exposure to some hormones, drugs and certain conditions can play a role in creating blood concentration, including:
- Surgery;
- Pregnancy;
- Contraceptive drugs Hormonal;
- Hormone replacement therapy;
- Cancer;
- Inflammatory diseases such as lupus;
- Blood disorders such as polycythemia vera (increased number of red blood cells);
- Infection;
- Carbon monoxide poisoning;
- Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (decreased number platelets).
Symptoms of blood concentration in the body
In most cases, blood concentration has no symptoms. Most people realize that their blood is thick after they are diagnosed with a blood clot. However, sometimes blood clots can cause symptoms related to blood clots. These symptoms depend on where the clot forms in the body and may include:
- chest pain;
- shortness of breath;
- heart attack symptoms, such as murmurs or pain in the arm, back, or jaw;
- headache;
- stuttering or difficulty speaking;
- dizziness;
- difficulty understanding speech. others;
- pain or redness in the lower leg

General symptoms of blood concentration
Increased red blood cells It can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Blurred vision;
- Dizziness;
- Easy bruising;
- Heavy menstrual bleeding;
- Gout;
- Headache;
- High blood pressure;
- Itchy skin;
- Lack of energy;
- Congestion. breath.
Symptoms of blood concentration in the legs
Symptoms of blood concentration in the legs usually appear due to the formation of blood clots or disruption of blood flow and may include various things, including:
- Swelling in one or both legs;
- Pain or a feeling of heaviness and pressure in Legs;
- Redness or discoloration of the skin of the legs;
- Heat sensation in one area of the leg;
- Pain when walking or bending the leg;
- Muscle cramps, especially in the leg;
- Easy bruising of the leg area;
- Numbness or burning sensation in the leg.
normal measurement of blood concentration on the test sheet
Hematocrit test results are reported as a percentage of blood cells that make up red blood cells. Normal ranges vary considerably according to the race, age and gender of individuals. On the other hand, the definition of the normal range of red blood cells may vary slightly between different medical centers, as each laboratory determines the healthy range based on the population of its region.
Normal Hematocrit Range (HCT)
In general, the normal range of hematocrit is usually different in different groups, including:
- Men: between 38.3 and 48.6%;
- Women: between 35.5 and 44.9%.
The normal range for children under 15 years old varies according to age and gender. However, in general it is:
- Newborns: 45 to 61%;
- Infants: 32 to 42%.
The hematocrit test provides only part of the information about your health. Talk to your doctor about what your test results mean.
When is blood concentration abnormal?
Blood concentration is considered abnormal when the hematocrit, or the ratio of red blood cells to the total blood volume, is out of the normal range, that is, too high or too low, including:
- High hematocrit (high blood concentration): is when the percentage of red blood cells is higher than normal, the blood becomes thicker and its flow slows down. This condition may be caused by diseases such as polycythemia vera, dehydration, lung diseases or heart problems.
- Low hematocrit (low blood concentration): is when the percentage of red blood cells is lower than normal, usually caused by anemia, bleeding, vitamin deficiency or chronic diseases.
How effective is the accuracy of the test result?
In some cases, the amount of hematocrit is outside the normal range, but this does not necessarily mean the presence of disease. Various factors can affect the result of the hematocrit test, including:
- Living at high altitudes (increased hematocrit);
- Pregnancy (decreased hematocrit);
- Loss of blood (decreased hematocrit);
- Blood transfusion (increased hematocrit);
- Severe dehydration (increased hematocrit).

When interpreting the results of the hematocrit test, the doctor considers these possible factors. If the results are inconsistent with your other medical information or are unexpected, your doctor may want you to repeat the hematocrit test or have other blood tests done. If blood concentration is due to diseases such as polycythemia vera or other serious problems, immediate action by a doctor is necessary. The treatment depends on whether the doctor wants to manage the emergency caused by the active clot or is trying to prevent future blood clots. Due to this, the treatment method can be different, including:
- Thrombolytics: These drugs dissolve blood clots in emergency situations such as heart attack, stroke, pulmonary embolism, and deep vein thrombosis.
- Blood thinners (anticoagulants): To prevent clots, the doctor may Prescribe drugs such as warfarin or heparin. These drugs inhibit the action of blood proteins responsible for clotting and can be taken as pills, ampoules, or intravenously.
- Specific drugs for congenital deficiencies: People who have antithrombin III deficiency may receive antithrombin. Also, in people with protein C deficiency, the doctor may prescribe protein C to prevent the formation of clots.
Home methods and lifestyle changes to reduce blood concentration
Doing simple things and lifestyle changes can help reduce blood concentration, including:
- Treating diseases that can cause
- stop smoking;
- lose weight;
- avoid taking estrogen-containing drugs;
- move your legs frequently to increase blood flow during long trips. Taking some other things can help reduce blood concentration. However, remember that the consumption of these natural substances should not replace prescription blood thinners. Some of these substances may interact with blood thinners and increase the risk of bleeding. Always consult your doctor before starting any new supplement or natural substance.
Foods that are useful for blood thinning
Some foods can help improve blood circulation, but be aware that they may interact with blood thinning medications. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor before consuming these substances, including:
- Turmeric: Turmeric contains curcumin, which acts as a natural anticoagulant. Studies have shown that curcumin can prevent the formation of blood clots by inhibiting components of the coagulation pathway.
- Ginger: Ginger contains salicylate, which is found in many plants. Salicylates act as a precursor to aspirin and can prevent blood clots.
- Cinnamon: Cinnamon contains coumarin, which acts as a strong anticoagulant in some medications. However, excessive consumption of cinnamon may cause liver damage.
- Cayenne pepper: Cayenne pepper contains salicylate and can have a more diluting effect than ginger. It can also lower blood pressure and increase blood circulation.
- Vitamin E (E): Vitamin E is known as a mild anticoagulant. Consuming food sources rich in vitamin E such as olive oil, almonds, spinach, and tomatoes can help improve blood circulation.
- Foods rich in flavonoids and phenols: Foods such as grapes, cherries, apples, plums, pears, citrus fruits, whole grains, black or green tea, and nuts may help prevent blood clots.
- Foods containing Phytoestrogens: Foods such as legumes and soy products may prevent heart diseases by reducing the level of bad cholesterol and increasing the level of good cholesterol.
- Organosulfur compounds: Compounds such as onions, garlic and leeks may prevent heart diseases by reducing cholesterol production in the liver.
- Proper hydration: Consuming enough fluids is essential for proper blood circulation. Dehydration causes the blood to thicken, which can lead to blood clots.

Blood Concentration Enemies or Harmful Foods
If you want to reduce the risk of blood clots or if you already have a clot, diet plays a very important role. Some foods can make the problem worse or interfere with your medications. Be sure to consult a doctor or nutritionist at Dr. Dr. about diet management. In the following, some of the ingredients that you should be careful about are mentioned.
1. Processed and refined foods
Avoid processed foods, including:
- white bread;
- sweetened cereals;
- crackers;
- white rice;
- sweets and cakes;
- packaged snacks;
- potatoes. fried;
- fast foods.
These foods can cause chronic inflammation in the body, which damages blood vessels and increases the possibility of clotting. They also cause weight gain, which is one of the risk factors for deep vein thrombosis.
2. Sugary drinks and foods
Consuming too much sugar damages blood vessels and can lead to diabetes and heart problems, both of which increase the risk of blood clots. Therefore, it is better to avoid consuming substances containing sugar, including:
- carbonated drinks;
- energy drinks;
- chocolate and candy;
- sugary desserts.
Use water, herbal teas or fruit juice instead.
3. Trans and saturated fats
These fats raise bad cholesterol, or LDL, and stimulate inflammation, both of which increase the risk of clots. Avoid foods containing trans fats, including:
- margarine;
- vegetable butter;
- packaged baked goods;
- fried foods;
- red meat;
- processed meats such as bacon, sausage, and hot dogs.
Instead They use healthy fats such as olive oil, nuts and seeds.
4. Salty foods or high consumption of salt
Salt increases blood pressure by increasing blood volume and causes the body to retain more water. This extra pressure damages the veins and disrupts blood flow. Therefore, avoid consuming foods that contain a lot of salt, including:
- canned soups;
- instant noodles;
- chips;
- pickles;
- frozen foods;
- prepared meats;
- fast food.
Most adults should consume less than 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day. do Read the food label and choose low-salt or no-salt options if possible.
5. Too much alcohol
Using too much alcohol increases the number of blood platelets and thickens the blood, making it more likely to clot. It may also interfere with blood thinning medications.
6. Foods rich in vitamin K (K) along with blood thinners
Vitamin K helps blood coagulation and its high consumption can reduce the effect of thinners such as warfarin. Therefore, if you are taking thinner drugs, it is better to be careful in consuming foods containing vitamin K, including:
- Cabbage;
- Spinach;
- Broccoli;
- Green tea;
- Mayonnaise.
It is not necessary to eliminate these foods completely, but they must be consumed regularly and in constant amounts to change the effect of the drug. should not.
7. Fish oil and omega-3 supplements Fish oil can thin the blood. If you are taking blood thinners, it may increase your risk of bleeding. Do not stop eating fish, but be sure to consult your doctor before taking supplements.
8. Excessive caffeine consumption
Caffeine in moderate amounts is usually not a problem, but excessive consumption causes dehydration, which thickens the blood and increases the chance of clotting. Too much caffeine may cause heart problems in some people. Therefore, it is better to consume 1 to 2 cups of coffee a day and avoid energy drinks with a lot of caffeine.
9. Red meat and processed meats
These meats are full of saturated fat. On the other hand, they are also related to inflammation and damage of blood vessels; Especially processed meats such as salami and ham are harmful. Limit the consumption of red meat to once or twice a week and if possible, completely eliminate processed meat.
10. Excessive consumption of calories
Excessive weight increases the risk of venous thrombosis. Eating too much food, regardless of its type, causes weight gain and thus increases the possibility of clot formation. Be careful about the size of the portions and avoid eating large meals at night or consuming a lot of snacks.
Diseases related to blood concentration
Blood concentration can be hereditary or genetic and can happen over time. Next, we introduce the diseases related to blood concentration.
1. Polycythemia vera
Polycythemia vera (PV) is a blood disorder that begins in the bone marrow (the central, soft part of the bone where new blood cells are produced). In this disease, the bone marrow produces more red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets than usual, which causes the blood to thicken. In these conditions, blood clots sometimes form, but the slowing down of blood flow can also cause other symptoms, including:
- fatigue;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- sweating, especially at night;
- skin itching;
- blurred vision and tinnitus. ear;
- Feeling of fullness or bloating in the abdomen due to enlarged spleen.
According to experts, polycythemia vera is caused by genetic changes that occur after conception. This disease is not usually inherited, but genetic changes happen gradually over the years. According to the National Organization for Rare Diseases, polycythemia vera affects between 44 and 57 people per 100,000 people and usually appears after the age of 60.
2. Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia is a rare type of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. In this disease, the body produces a large amount of antibody protein called immunoglobulin M (M), which can cause blood to concentrate and cause various symptoms, including: nosebleeds, bleeding in the gums and retina due to damage to small vessels, anemia, tingling and numbness in the fingers. and foot.
According to the statistics of the American Cancer Society, about 1000 to 1500 new cases of Waldenström's macroglobulinemia are diagnosed in the United States every year.
3. Deficiency of proteins C, S and antithrombin The human body helps prevent blood clotting by producing some natural anticoagulants such as proteins C, S and antithrombin. The level of these items is low in some people. This increases the risk of blood clots. These deficiencies may be hereditary or develop over time. Usually, the formation of a blood clot is an early sign of the disease, which may be discovered by performing various tests. If a clot forms in a deep vein, your doctor will diagnose it as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). If this clot breaks off and reaches the lungs and causes blockage, it is called pulmonary embolism (PE), which is very dangerous.The prevalence of protein C deficiency is about 1 person per 200 to 500 people, protein S deficiency is about 1 person per 500 people, and antithrombin deficiency is about 1 person per 2000 to 5000 people. 
4. Prothrombin 20210A gene mutation
People with this genetic problem have too much protein factor 2 (II) or prothrombin. Prothrombin is one of the blood coagulation factors, but its high amount can increase the risk of clot formation, including clots that cause deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
5. Factor 5 (V) Leiden
This disorder is caused by a genetic change that increases the risk of blood clotting, especially in the deep veins. In healthy people, a protein called active protein C controls the activity of factor V. In people with this disorder, protein C cannot control factor V. This causes blood concentration and increases the risk of blood clotting.
6. Other diseases
Other diseases can also cause blood concentration, including:
- types of cancer;
- lupus, causes the production of additional antiphospholipid antibodies in the body. These antibodies can cause blood clotting;
- Protein C deficiency;
- Protein S deficiency.
Blood thickening and cancer
Polycythemia vera is a type of blood cancer called myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN). Myeloproliferative neoplasms are a group of diseases, some of which cause excessive production of various blood cells. Polycythemia vera is caused by a gene mutation that occurs for unknown reasons and usually occurs during a person's lifetime. This disease progresses very slowly and is usually not diagnosed until after the age of 60. This type of cancer is usually not fatal by itself, but its main risk is due to the complications related to blood clotting or the possibility of turning into other types of blood cancer. Blood clots can cause serious health problems, which we will discuss below.
1. Deep vein thrombosis
When a blood clot forms in one of the deep veins, the doctor may diagnose deep vein thrombosis. These clots usually form in the large veins of the legs, but may also form in the thighs, arms, abdomen, or pelvis. Pain and blood circulation problems are usually seen in the area where the clot is formed. This issue is also associated with various symptoms, including:
- Swelling, redness and heat in the target area;
- Sudden or gradual onset of pain;
- Pain in the leg when bending or stretching;
- Camp in the leg muscles;
- Change in skin color in the form of bruising or paleness in other parts of the body.

2. Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism occurs when part of a blood clot breaks off and travels to the heart or lungs. This piece can cause a new clot to form, blocking blood flow and disrupting lung gas exchange. Pulmonary embolism is an emergency and life-threatening condition and is associated with various symptoms, including:
- shortness of breath and rapid breathing;
- rapid heartbeat;
- pain when breathing deeply;
- blood when coughing;
- chest pain.
3. Other complications of blood clots
Blood clots may have other complications, including:
- stroke;
- heart attack;
- kidney damage;
- pregnancy problems;
- peripheral artery disease.
Doctor's Last Word
Many people with high blood concentration usually do not experience any complications, but in some people, treatment can effectively prevent the occurrence of serious conditions such as heart attack, stroke, deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. However, the use of these drugs may be associated with side effects. For example, people who take blood thinners are at increased risk of bleeding. Consult your doctor about the blood concentration and necessary tests. If for any reason the doctor's explanation was not enough for you or if you have any other questions, you can get help from the professional team of Dr. You can also use Dr.Doctor's home test service to perform a blood concentration test at home.
Frequently Asked Questions
What numbers are used to determine blood concentration in a CBC test?Blood concentration in a CBC test is determined by the hematocrit index and with the abbreviation HCT or Hct and as a percentage of red blood cell volume in the whole blood.Can high blood concentration cause a stroke or blood clot? The best What is the quick treatment for blood concentration at home?Do you have Is blood concentration dangerous? How Can blood concentration be treated?Is Can polycythemia be treated? Resources
verywellhealth healthline medicalnewstoday clevelandclinic clevelandclinic mayoclinic mayoclinic healthline bloodclot starhealth
Tags: The content of this article is for your general information only and does not constitute medical prescription.