آلرژی کودک به شیر گاو یکی از اولین آلرژیهایی است که در کودکان تشخیص داده میشود، زیرا شیر گاو یکی از اولین غذاهای خارجی است که به نوزادان داده میشود. This allergy affects about 2 to 3 percent of children, and although many children outgrow it over time, it can affect a child's growth and nutrition for several years.

What is a child's allergy to cow's milk protein?
Allergy in children Cow's milk is one of the most common food allergies in childhood. It is usually detected in the first years of a child's life. This type of allergy is caused by the abnormal reaction of the body's immune system to the proteins in cow's milk. In fact, the child's immune system considers cow's milk proteins as a threat and produces antibodies to fight them, which lead to allergic symptoms. This allergy is usually caused by the body's incorrect immune response to cow's milk proteins, such as casein and whey.
Symptoms of child allergy to cow's milk
Symptoms of cow's milk allergy in children are diverse and include digestive symptoms, skin sensitivity, respiratory and general symptoms. Below are the usual symptoms of this allergy:
- Vomiting
- diarrhea
- Intestinal inflammation
- Abdominal pain and bloating
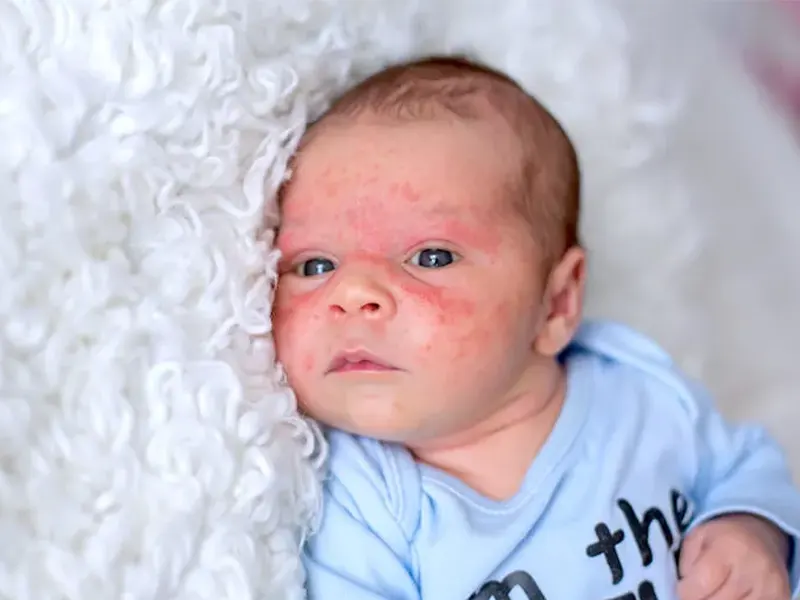
- creating red and itchy pimples on the skin. Sore throat in children
- Eczema and dry skin
- Persistent coughs
- Difficulty in breathing
- fatigue and lethargy
- Weight loss or lack of proper weight gain
Why are some babies and children allergic to cow's milk?
In a normal state, the body's immune system should react appropriately with proteins and foods, but in people with food allergies, the immune system mistakenly overreacts to certain proteins, such as cow's milk proteins. The main causes of cow's milk allergy in children and infants include the following:
- The amount of protein in cow's milk
- The degree of indigestion
- Genetic factors and susceptibility to food allergies
- Immature immune system
- Mother's nutrition during pregnancy and breastfeeding
reflux difference with cow protein allergy
Reflux refers to a condition in which stomach contents, including stomach acid, return upwards into the esophagus. This condition usually occurs due to a weakness or defect in the valve between the esophagus and the stomach (esophageal sphincter). Cow's milk protein allergy refers to the abnormal reaction of the body's immune system to the proteins in cow's milk. This allergy can cause severe immune reactions to cow's milk proteins. In fact, as you know, reflux is related to weakness in the esophageal sphincter, while cow's milk protein allergy is related to the body's immune response to cow's milk proteins.Treatment of children's allergy to cow's milk
Treatment of cow's milk allergy in children includes several steps and solutions to manage and reduce symptoms. In the following, the main methods of treating this sensitivity are given:
The most important step in the treatment of cow's milk protein allergy is to avoid consuming cow's milk and all dairy products. This includes milk, yogurt, cheese, butter and other products containing cow's milk protein. Consultation with a doctor or an allergist is very important to get an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment strategies for your baby's cow's milk protein allergy. Your doctor can help you develop the right treatment plan. Conducting tests to assess the severity of sensitivity and monitor the health status of the child may be needed. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe medications to manage allergy symptoms, such as antihistamines or corticosteroids. By following these methods and following medical advice, you can control the symptoms of cow's milk protein allergy and improve your child's quality of life.
FAQ
Diagnosis of an allergy to cow's milk protein is usually by medical consultation, examination of clinical symptoms and necessary tests including blood tests or tests.
In many cases, sensitivity to cow's milk protein in children decreases over time and may improve with age. However, some children may retain the sensitivity into adulthood. Follow-up and consultation with a doctor is necessary to evaluate the situation.
Completely avoiding the consumption of cow's milk and dairy products, using suitable food substitutes and checking the labels carefully to avoid Contact with cow's milk protein are important measures to prevent allergic reactions.
Conclusion
Allergy to cow's milk protein can bring challenges for babies and children, but with awareness and appropriate measures, this situation can be managed well. Avoiding cow's milk and dairy products, using appropriate food substitutes, and consulting with a doctor or nutritionist to choose treatment and manage symptoms are key measures. Keep in mind that sensitivity to cow's milk protein may change over time, and in some cases, a child may be able to tolerate cow's milk again or recover from it as an adult.