مجله پزشکی
Share the article
elementor-widget-table-of-contents" data-id="6e32680" data-element_type="widget" data-settings='{"headings_by_tags":["h2","h3"],"exclude_headings_by_selector":[],"no_headings_message":"No headings were found on this page.","minimized_on":"desktop","container":".postcontent","marker_view":"numbers","minimize_box":"yes","hierarchical_view":"yes","min_height":{"unit":"px","size":"","sizes":[]},"min_height_tablet":{"unit":"px","size":"","sizes":[]},"min_height_mobile":{"unit":"px","size":"","sizes":[]}}' data-widget_type="table-of-contents.default">
In general, the ear is divided into three parts: outer ear, middle ear and inner ear. The outer ear is the outer part of the ear that receives sound. The mechanism of the middle ear is responsible for changing the sound and the inner ear receives and transmits the sound. The eardrum or tympanic membrane is located between the middle ear and the outer ear. This thin membrane separates the middle ear from the outer ear. Finally, the sound vibrations enter the ear canal and cause the earlobe to vibrate. It should be noted that sound stimuli are transferred from the middle ear to the inner ear fluids by three small bones. In this article prepared by Dr. Maryam Yacoubi, we are going to talk about the structure and ear bone surgery.

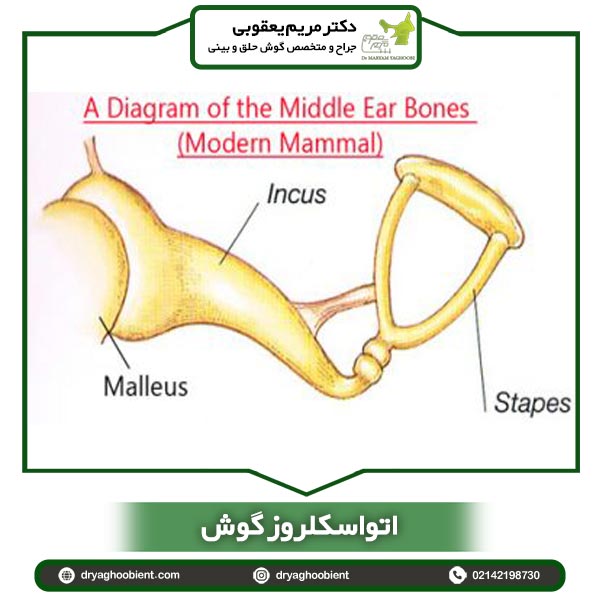
The ossicles of the ear or auditory ossicles are three small bones of the middle ear (hammer, anvil and stapes) that transmit the vibrations of the tympanic membrane to the inner ear. These waves stimulate the fine nerve endings in the auditory canals. Note that electrical impulses are transmitted somewhere from the nerve to the brain, where they are interpreted as intelligible sound. The inner ear is located inside the temporal bone in a bony cavity, which has a central area called vestibule containing two small cavities filled with liquid, the ventricle and the sac, and is connected to the cochlea, which is responsible for the sense of hearing, and the semicircular canals, which are responsible for dynamic balance, and receives vibrations from inside the middle ear.
types of hearing disorders
The outer and middle ear direct the sound. The inner ear receives sound. If there is a problem in the outer or middle ear, a conductive hearing loss occurs. If the problem is in the inner ear, the result is a sensorineural hearing disorder. When there is a problem in the middle ear and the inner ear, a mixed or combined disorder occurs.
ear otosclerosis is a disease of the middle ear bone and sometimes the inner ear. Otosclerosis is a major cause of hearing impairment. ) Any disease that affects the eardrum or ossicles can lead to conductive hearing loss as a result of sound transmission disorder to the inner ear. It should be noted that some hearing damage; It may be caused by the rupture of the eardrum, the partial or total disintegration of one or all three eardrums, scarring of the tissue around the ossicles or the eardrum.

Cochlear bone
When otosclerosis spreads to the inner ear; It may cause sensory-neural hearing disorder due to interference in nerve function. This neurological disorder is called cochlear otosclerosis, which may be permanent if it occurs. Sometimes, otosclerosis may spread to the balance channels and cause periods of instability. Ear hearing may be affected by certain diseases, including infections or traumatic injuries. Ear hearing does not always occur following functional disorders of the ear and diseases, and it can be hereditary and is caused by the accumulation of abnormal bone growth on the tiny stapedoid bone. The tiny bands are the third auditory bone and their movement on the foot plate of the inner ear; It moves the fluid inside the inner ear and allows us to hear. Overgrowth of bone in atherosclerosis may cause the bone to become fixed, thereby limiting its movement. This process may affect one or both ears. This disease usually starts in the late teens or early 20s and progresses slowly.
When otosclerosis occurs due to poor movement of the auditory bones; It creates the type of "conductive hearing loss" and can be corrected. Otosclerosis can cause sensorineural hearing loss. This disorder may cause an increase in ringing in the ears, which is known as tinnitus, which unfortunately cannot be corrected. #000080; border-collapse: center; height: 287px;">border: 3px solid #000080; 10px;">Description
| Improving hearing | Increasing the quality and clarity of sound for patients with bone problems. |
| Increasing the quality of life | establishing better communication with others and reducing the feeling of isolation. |
lasting results | In many cases, the result of surgery is long-term and stable. | Improve the person's hearing limitations | Medical treatment (ear bone surgery)
There is no medicine that can correct the hearing loss caused by conductive type otosclerosis or prevent its progression. However, it is possible in patients who have hearing loss of the neurological type of otosclerosis; Treatment with fluoride drugs should be used. Fluoride in moderate doses has been shown to inactivate abnormal otosclerotic bone toxic chemicals that are toxic to the auditory nerve. However, it should be used in moderate doses for at least one to two years until the progression of nerve loss stops, and then in lower doses indefinitely. This drug should not be used in anyone of childbearing age because of the potential risks involved. Hearing aids can be effective in treating hearing loss related to otosclerosis in most patients. Whether a hearing aid is the best option or not is a personal decision between you and your doctor.

What is middle ear surgery?
Middle ear surgery is a surgical intervention to treat eardrum problems in the chain of small interconnected bones (hammer, anvil and stirrup) and mastoid cells (temporal bone cavities). There are two main surgical methods: tympanoplasty and mastoidectomy. Tympanoplasty includes ossification (repair of bones) and myringoplasty (closing the hole in the earlobe).
Middle ear surgery in children
Middle ear ossicles surgery in children requires greater precision and experience due to anatomical and physiological differences compared to adults. Children's middle ear is still growing, and the ossicles are smaller and more delicate, so their reconstruction or replacement should be done according to future growth. The use of flexible prostheses or restorative techniques with natural materials usually produces better long-term results. Early diagnosis of middle ear disorders such as cholesteatoma, chronic infections or ossicular damage plays a vital role in the success of surgery. Delay in treatment can cause permanent hearing loss, so it is especially important for parents and doctors to pay attention to the symptoms of hearing loss or frequent infections. Minimally invasive techniques, especially endoscopic surgery, are preferred in children due to better visibility and less damage to healthy tissues. The main goal of surgeons is to preserve the normal ear structure and hearing function during the child's development. Post-operative care is also an important part of the treatment process. Infection control, ear hygiene and regular follow-up of hearing are essential. In some cases, hearing rehabilitation helps the child to process the restored hearing well.
In general, middle ear surgery in children has important differences from adults, and its success depends on timely diagnosis, choosing the right method and careful post-operative care. The use of modern techniques and accurate planning can guarantee long-term favorable results and improve the quality of life of the child.
Why middle ear surgery is performed?
Medical interventions in the treatment of middle ear problems or ear bone surgery are recommended.
- Tympanoplasty: It is recommended for a large perforation of the earlobe or a middle ear infection such as acute or chronic otitis media, which cannot be treated with antibiotics.
- Mastoidectomy: An operation to remove the flat air cavities of the skull behind the ear (temporal bone) in order to treat infections in the mastoid part of that part of the skull, to treat the complications of otitis media, abnormal bone growth, Cholesteatoma (cell cyst skin in the middle ear), or for placing cochlear implants.
The surgeon accesses the middle ear by making an incision behind the ear or through the ear canal to perform the necessary measures depending on the person's injury. This procedure may include removing any infection or dead tissue in the earlobe, placing a graft to reconstruct the tympanic membrane, or placing a prosthesis to replace the damaged bone in ear bone surgery.
Improving hearing after ossicle surgery
One of the main goals of middle ear ossicle surgery is to restore or improve hearing. The success of this surgery depends on several factors, including the type of damage to the ossicles, the surgical technique, and the condition of the middle ear before the operation.
A careful preoperative evaluation using advanced imaging and hearing tests helps the surgeon determine the appropriate method and the expected amount of hearing improvement. The use of artificial prostheses or bone reconstruction with natural materials can significantly increase hearing performance. Minimally invasive techniques and preserving the natural structures of the middle ear increase the chances of long-term success. Also, post-surgical care, including infection control, ear hygiene and regular hearing follow-up, plays a key role in stabilizing the results.
In some patients, post-operative auditory rehabilitation also helps the brain to process reconstructed sounds better and improve hearing quality. Therefore, the combination of precise surgery, appropriate prosthesis and post-operative follow-up is the key to achieving the best hearing results for patients.
Otosclerosis disease
Sound is first guided by the earlobe into the ear canal and then causes movement of the eardrum. When the sound is made, the eardrum will vibrate. These vibrations cause the movement of 3 stapes, anvil and hammer bones of the ear. The movement of these bones causes the movement of fluid into the cochlea, and the movement of this fluid causes the hair cells located at the end of the cochlea to send sound information to the auditory nerves. Finally, the auditory nerves transmit these signals to the brain and the sound will be heard. This is how the auditory system works, and a disturbance in any of these processes can cause problems in hearing.
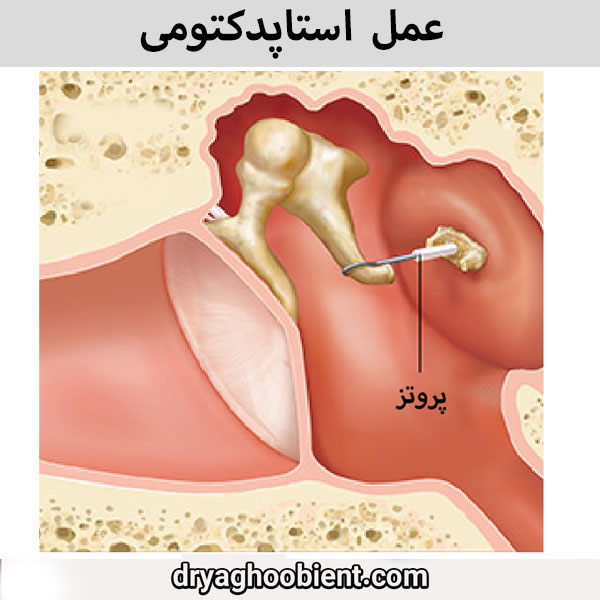
Otosclerosis occurs as a result of stiffening of the stapes bone or disruption of its movement, and prevents the proper movement of this bone, which ultimately impairs a person's hearing. In stapedectomy surgery, incomplete bones are removed and replaced with a prosthesis, as a result, the patient's hearing will improve. Patients who experience dizziness are advised not to undergo otosclerosis surgery. These people must first treat their vertigo 1 year before and then undergo otosclerosis surgery.
Otosclerosis surgery aimed at improving hearing can reduce or increase tinnitus. In some cases, this tinnitus can be cured by surgery. In performing this surgery, the goal is not to eliminate tinnitus, for this reason, in some cases, this problem may be solved, or in rare cases, it may get worse. Ear bone surgery needs to be performed under a microscope and requires high precision and sensitivity. For this reason, it is necessary to be careful in choosing a surgeon.
What is the cause of autosclerosis?
As we mentioned, one of the reasons for the need for ear bone surgery is to get autosclerosis. Offensive factors play a role in causing this disease, which we will examine below.
- Age: Usually people who are over 30 years old are more susceptible to this disease. Age is one of the main factors in the development of autosclerosis. And this disease has been seen in the age range between 10 years old and 45 years old.
- Genetics: It has been seen in many people that this disease is caused by its genetics in the family. Usually, people who have this disease, half of their families also have this disease. But there is no need to worry because the occurrence of otosclerosis is not necessarily caused by the presence of its gene.
- Gender: It has been seen that women are more affected by otosclerosis than men. Gender is also one of the main causes of this disease. An important point for women is that pregnant women are more susceptible to otosclerosis due to hormonal changes. Environmental and ethnic factors: This disease is relatively common in different ethnicities. For example, in the Caucasian ethnic groups, most other ethnic groups such as Americans and Africans are affected by this disease.
- Medical history: People who have various diseases in the past such as measles, ear infections, bone tissue fractures around the ear, etc. are also more likely to get otosclerosis.
- Disorders in the immune system: In some people Disruption between different cells of the immune system (cytokines) that play an important role in bone regeneration has caused the creation of cytokines. elementor-element-72f24028 e-con-full e-flex e-con e-child" data-id="72f24028" data-element_type="container" data-settings='{"background_background":"classic"}'>