Corrective movements - Dr. Morteza Tabatabai

Dr. Seyed Morteza Tabatabai
تهرانPhysical medicine and rehabilitation specialist
Corrective Movements
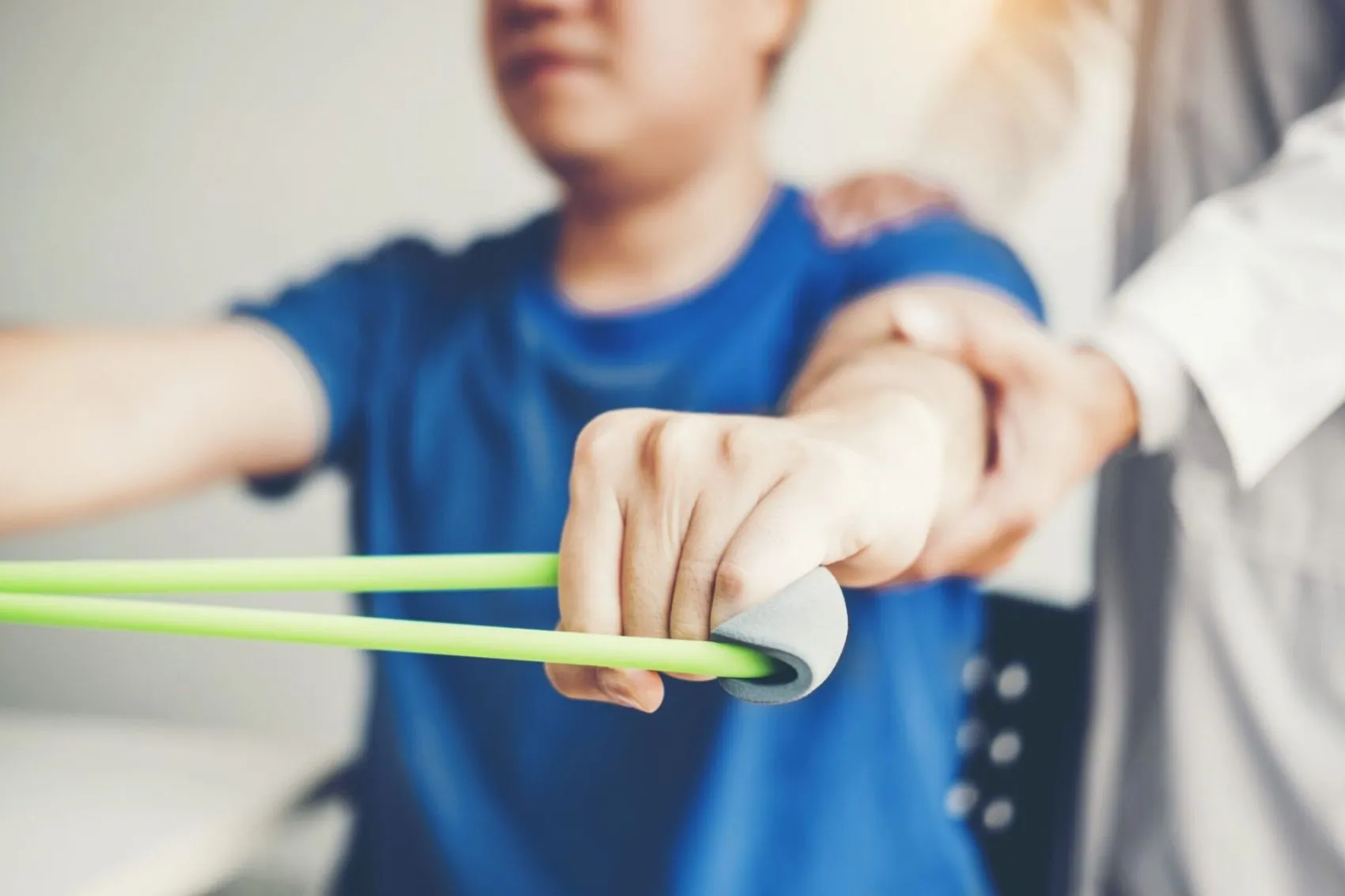
Corrective movements are a set of exercises that are performed to correct body abnormalities, improve movement patterns, muscle balance and body posture. By stretching tight muscles, strengthening weak muscles and correcting movement, these movements return the body to a natural and pain-free pattern.
What are corrective actions?
Corrective Exercises are exercises and movements designed to correct abnormalities and disorders in movement patterns, muscle balance and body posture (source).
In effect, corrective exercise attempts to restore the body's natural state by analyzing and identifying muscle imbalances, muscle tightness or shortening, joint weakness, or incorrect movement patterns — which may lead to pain, decreased performance, or injury (source).
The program of these exercises usually includes a combination of stretching, strengthening weak muscles, stability exercises and modifying movement patterns so that the body can function with correct movements, without pain and with better efficiency (source).
Overall, the goal of corrective exercise is to adjust the body so that muscles and joints are coordinated and balanced, movement becomes natural and healthy, and the risk of injury or chronic pain is reduced (source).
According to the World Health Organization, more than 1.71 billion people in the world live with musculoskeletal disorders, and back pain alone affected 619 million people in 2020. These statistics show that the use of corrective movements to reduce pain and improve physical performance is a serious and global need (source).
What is the purpose of emotional movements?
The purpose of corrective movements is to restore the body's normal function by correcting abnormalities, muscle imbalances and incorrect movement patterns.
These exercises try to release tight and overactive muscles, strengthen weak muscles and increase coordination between muscles and joints.
The result of this process is reducing pain, preventing injury, improving the quality of movement and increasing the body's efficiency in daily and sports activities. Corrective movements actually lead the body to move correctly, without pain and with more stability.
History of corrective actions
The roots of remedial movements go back centuries, in the late 18th century, the French doctor Clément Joseph Tissot tried to replace the traditional methods of immobilization after surgery by introducing remedial gymnastics.
Continuing and over time, the idea of exercise therapy and targeted exercises to improve the body was formed in broader frameworks such as sports and rehabilitation systems; برای مثال سیستم پیلاتز (Pilates) نیز — که بعدها بهعنوان پیشزمینهای از تفکر اصلاحی تلقی شد — در اوایل قرن بیستم توسعه یافت.
اما مفهومی که امروزه با عنوان حرکات اصلاحی شناخته میشود، در میانهٔ قرن بیستم و پس از جنگ جهانی دوم جدیتر شد.
هنگامی که در نیروی نظامی آمریکا برای بازتوانی سربازان مجروح، واحدهای فیزیکال ریکاندیشنینگ (physical reconditioning) تأسیس گشت تا با تمرینات هدفمند، سلامت و توان حرکتی نظامیان بهبود یابد (منبع).
آنگاه در سال ۱۹۴۹ اولین مقالات علمی درباره کینزیولوژی حرکات اصلاحی منتشر شدند و با گذشت دههها، این رشته به شکل امروزی — ترکیبی از ارزیابی بدن، اصلاح ناهنجاریها، کشش، تقویت و بهبود الگوهای حرکتی — تبدیل گردید (منبع).
فواید حرکات اصلاحی
حرکات اصلاحی نه تنها برای افرادی که دچار درد یا ناهنجاریهای بدنی هستند مفید است، بلکه میتواند سلامت کلی بدن، عملکرد روزمره و پیشگیری از آسیبها را برای همه افراد بهبود ببخشد.
این تمرینها با تمرکز بر تقویت عضلات ضعیف، کشش عضلات کوتاه و اصلاح الگوهای حرکتی باعث میشوند بدن بتواند حرکات خود را به شکل طبیعی و بدون درد انجام دهد.
- اصلاح وضعیت بدنی (Posture): کمک به صاف شدن ستون فقرات، شانهها و لگن.
- کاهش دردهای مزمن: کاهش دردهای شایع مانند کمر، گردن، شانه و زانو.
- پیشگیری از آسیبهای ورزشی و روزمره: کاهش خطر آسیبهای ناشی از ضعف عضلانی یا ناهماهنگی حرکتی.
- بهبود تعادل و هماهنگی حرکتی: افزایش پایداری بدن و کاهش احتمال افتادن یا زمین خوردن.
- افزایش انعطافپذیری و دامنه حرکتی: بهبود حرکت مفاصل و کاهش سفتی عضلات.
- تقویت عضلات ضعیف و رفع عدم تعادل عضلانی: ایجاد تعادل میان عضلات مقابل و موازی برای حرکت صحیح.
- افزایش عملکرد ورزشی و روزمره: کمک به اجرای حرکات با کارایی بالاتر و انرژی کمتر.
- بهبود کیفیت زندگی و فعالیتهای روزمره: کاهش خستگی و افزایش راحتی در فعالیتهای معمول مانند نشستن، ایستادن و راه رفتن.
مشکلات و ناهنجاریهایی که حرکات اصلاحی درمان میکند
حرکات اصلاحی با تمرکز بر تشخیص و اصلاح عدم تعادلهای عضلانی، ضعف مفاصل و الگوهای حرکتی نادرست، به بهبود مشکلات اسکلتی و عضلانی کمک میکند.
این تمرینها برای افرادی که دچار درد مزمن، محدودیت حرکتی یا ناهنجاریهای بدن هستند بسیار مؤثرند و میتوانند کیفیت حرکت و سلامت عمومی بدن را بهبود بخشند.
- گودی کمر (Lordosis): تقویت عضلات شکم و کشش عضلات کمر برای کاهش فشار روی ستون فقرات.
- قوز پشت (Kyphosis): تقویت عضلات پشت فوقانی و اصلاح وضعیت شانهها.
- گردن رو به جلو (Forward Head Posture): کشش و تقویت عضلات گردن و پشت شانهها.
- زانوی ضربدری یا پرانتزی: تقویت عضلات پا و اصلاح الگوی راه رفتن.
- شانه افتاده یا نامتقارن: تقویت عضلات سرشانه و پشت برای بهبود تعادل.
- کمردرد و درد مزمن ستون فقرات: با اصلاح وضعیت بدنی و تقویت عضلات مرکزی.
- کوتاهی یا ضعف عضلات خاص (مثل عضلات همسترینگ یا پسواس): با کشش و تقویت هدفمند.
- عدم تعادل و ضعف عمومی عضلانی: افزایش پایداری بدن و هماهنگی عضلات.
انواع حرکات اصلاحی
حرکات اصلاحی تمریناتی هدفمند هستند که با اصلاح ناهنجاریها، بهبود وضعیت بدن و افزایش عملکرد عضلانی و مفصلی طراحی میشوند. These movements are adjusted according to the needs of each part of the body and can reduce pain, muscle weakness and imbalance.
Corrective movements for the spine
These exercises aim to increase flexibility, reduce tension and restore the natural curvature of the spine. Movements such as Cat-Cow and Williams Flexion Exercises help improve vertebral mobility, reduce pressure on discs, and prevent back pain (source).
Corrective movements for the neck and shoulders
These exercises are designed to correct problems such as forward head, slouched shoulders, and neck and shoulder muscle spasms. Movements such as Wall Angel, Chin Tuck, and Chest Opener strengthen the back and interscapular muscles, reduce pressure on the cervical vertebrae, and improve posture. noopener" target="_blank">source).
corrective movements for the back and pelvis
Back and pelvis exercises are performed with the aim of strengthening the central, gluteal and hamstring muscles to reduce the pressure on the spine and put the pelvis in the correct position. These movements help to reduce the hollow of the back and improve the balance of the muscles in the front and back of the body.
Corrective movements for knees and lower body joints
Exercises that strengthen the muscles around the knee and thigh increase joint stability, reduce knee pain, and improve movement coordination. These movements also increase the range of motion of the lower body joints and prevent injuries caused by muscle weakness.
corrective movements for the soles of the feet and ankles
Foot and ankle exercises are performed with the aim of strengthening supporting muscles, improving balance and joint stabilization. These movements are useful for people who have flat feet, wrist instability or poor balance and can prevent new injuries.
How do corrective movements affect the body?
Remedial movements are designed with the aim of correcting muscle balance, improving movement and coordination of joints and muscles, so that the body can function with a natural structure and more efficiently, and avoid injuries, pain and movement abnormalities.
restoring muscle balance and optimizing muscle length-tension
Many movement problems are caused by muscle imbalance; That is, some muscles become overactive (tight/short) and others become underactive (weak or stretched).
In this condition, the normal length-tension ratio of the muscle changes and the muscle cannot function effectively. Corrective exercises attempt to bring this ratio back to optimal by stretching tight muscles and strengthening weak muscles (source).
Improving joint mobility and range of motion
When the muscles around a joint become stiff or imbalanced, the range of motion of that joint is reduced and the natural movement of the body is limited.
Corrective movements with controlled stretching exercises increase muscle and joint flexibility, relieve tension, and loosen joints — so a person can move with greater freedom of movement and with proper form (source).
Retraining movement patterns and improving neuromuscular control
An important part of the effect of corrective movements is retraining the body — that is, the brain and nervous system learn to perform movements in a better and more correct pattern.
When weak muscles are activated and stiff muscles are relaxed, the body learns to perform the movement with proper muscle coordination, better and with less stress.
This retraining can lead to reduced misalignment, reduced stress on joints and discs, and reduced risk of injury (source).
pain reduction, performance improvement and injury prevention
Studies have shown that regular implementation of corrective movement programs can reduce the severity of musculoskeletal pain, improve quality of life and daily functioning, and reduce the likelihood of sports injuries or poor posture (source).
Optimizing movement efficiency and sports performance
For athletes or people who are physically active, corrective exercises activate the right muscles at the right time and optimize movement patterns — this means maximum training efficiency, reduced muscle compensation, and better and safer performance (source).
How to design a corrective exercise program?
Designing a corrective movement program requires accurate assessment of body condition, identification of incorrect movement patterns, and selection of exercises that can correct muscle imbalances and improve the quality of a person's movement. Following the standard steps in this process helps to create an effective, safe and workable program.
- Postural Assessment: check the alignment of the spine, shoulders, hips, knees and feet to identify abnormalities.
- Analysis of movement patterns: Performing tests such as Overhead Squat, range of motion test and performance tests to find limitations and weaknesses.
- Identifying overactive and underactive muscles: Determining which muscles are short/tight and which muscles have functional weakness.
- Setting program goals: The goal can be to reduce pain, improve posture, increase range of motion, or increase joint stability.
- Inhibition training design: Using techniques such as foam roller to reduce the tension of hyperactive muscles.
- Design of stretching exercises (Lengthening): Static or dynamic stretching for tight muscles, to restore their natural length.
- Design of activation exercises: Strengthen weak muscles with exercises such as Wall Angel, Chin Tuck, Glute Bridge.
- Improving movement patterns (Integration): Using combined exercises such as squat, lunge or hip hinge with a modified form.
- Compilation of the implementation and progress plan: Determining the number of sessions, sets, training intensity and how to increase the volume of training over several weeks.
- Periodic monitoring and evaluation: Recheck posture and movement to modify the program and ensure progress.
Dangers of corrective movements
Although corrective movements are generally designed to improve posture, reduce pain and increase the quality of movement, their incorrect implementation or failure to follow specialized principles can lead to complications. Awareness of these risks helps to choose the right exercises and perform them safely.
- Incorrect execution and increased pressure on the joints: Incorrect technique can cause excessive pressure on the back, neck, knees or ankles.
- Aggravation of existing abnormalities:Choosing the wrong exercise for the wrong problem may worsen the abnormality (such as strengthening an already overactive muscle).
- Increased muscle pain or inflammation: Exercising too hard or without proper warm-up can cause unwanted muscle pain.
- Injuries from overstretching: Improper or prolonged stretching can cause ligaments and muscles to stretch.
- Balance imbalance and risk of falling: Some corrective exercises related to balance and lower body joints, without expert supervision, can create a risk of falling.
- Exercise mismatch with the person's medical conditions: People with back disc, arthritis or chronic injuries may experience aggravation of symptoms with certain movements.
- Not following up with a specialist: Not having a specialist evaluation (physiotherapist or kinesiotherapy specialist) makes the root of the problem not recognized and the exercises not effective.
The difference between corrective movements and exercise therapy
Although both are designed with the aim of improving the body's performance, corrective movements and sports therapy have important differences in terms of targeting, therapeutic approach and implementation. Knowing these differences helps to choose the right method for skeletal-muscular problems.
Difference in the main goal
Corrective movements focus on correcting physical abnormalities, improving movement patterns, and correcting muscle imbalances; While sports therapy focuses more on treating injuries, reducing pain, and rehabilitating the normal function of the joint or muscle.
difference in the field of application
Corrective movements are mostly used for prevention, correcting posture and improving movement quality. But exercise therapy is usually used in the treatment process after injury, surgery or chronic disorders.
Difference in intensity and type of exercises
In corrective movements, the focus is on light, slow and controlled movements; But in sports therapy, depending on the patient's condition, resistance, functional or more specialized exercises may also be performed.
Difference in assessment and starting point
Corrective movements begin with the assessment of posture, range of motion and movement pattern; However, sports therapy based on medical diagnosis, injury assessment, detailed performance tests, and injury severity assessment begins.
Difference in Executor and Monitor
corrective movements can be designed by trainers specializing in exercise therapy or sports physiology; But sports therapy is usually performed under the supervision of physiotherapists, sports doctors or rehabilitation specialists.
How many times a week should corrective movements be done?
The appropriate number of times to perform corrective movements depends on the severity of the abnormality, the purpose of the exercise and the physical strength of the person, but most reliable sources of physical therapy suggest that these movements be performed daily or almost daily at first so that the body has the opportunity to retrain movement and correct wrong patterns.
Reputable clinics recommend that in the early stages of rehabilitation, corrective exercises can be performed daily to achieve faster results. After reducing symptoms and reaching relative muscle balance, many experts suggest exercises 2-3 times a week (source).
A recommendation that is also proposed in NumberAnalytics to maintain muscle performance and balance. In the maintenance phase, the same pattern (2-3 sessions per week) is sufficient (source).
However, if the exercise causes abnormal pain or extreme fatigue, the number of sessions should be reduced. An issue that is also mentioned in the official guidelines as an important safety criterion.
How long do corrective actions take to see effects?
The effects of corrective movements are usually seen gradually and depending on the severity of the abnormality, the level of commitment to training and the physical condition of the person.
Some initial changes such as reduced muscle tension and improved flexibility may be seen after 2 to 4 weeks of regular exercise, while modification of movement patterns and lasting improvement in posture usually takes 6 to 12 weeks.
Also, to achieve long-term results and stabilize the effects, it is recommended to continue the program 2-3 times a week after the initial stage. In fact, the continuity and correct implementation of corrective movements play a key role in observing noticeable and stable effects.
Can everyone do corrective movements?
Almost most people can perform corrective movements, but the method of execution and the intensity of the exercise should be adapted to the physical condition, ability level and presence of any medical problems.
People with chronic pain, joint injuries, musculoskeletal diseases, or mobility limitations should consult a physical therapist or kinesiotherapy specialist before starting to get a safe and effective program.
Also, the elderly, people with severe muscle weakness, or those just recovering from surgery, need low-intensity corrective exercises and expert supervision.
In general, with proper design and following safety principles, corrective movements are applicable to a wide range of people and can help improve posture, reduce pain, and increase movement efficiency.