آیا تابهحال برایتان پیش آمده که با وجود بودن در یک رابطه عاطفی، باز هم احساس تنهایی عمیقی داشته باشید؟ یا هنگامیکه شریک عاطفیتان به شما میگوید «دوستت دارم»، ته دلتان باور نکنید که او واقعا شما را دوست دارد؟ یا شاید ممکن است فردی باشید که بهشدت از صمیمیت و نزدیک شدن به دوست یا شریک عاطفی میترسد و درعینحال، از رها شدن هم وحشت دارد. اگر چنین احساساتی را تجربه کردهاید، باید بدانید که تنها نیستید. شما یکی از بیشمار افرادی روی کره زمین هستید که در چند ماه اول کودکی خود دچار دلبستگی ناایمن بوده است. خبر خوب اینجاست که میتوانید سبک دلبستگی ناایمن خود را به سبک دلبستگی ایمن تغییر دهید. بنابراین، در این مقاله قصد داریم شما را با انواع سبکهای دلبستگی ناایمن، علل بروز آنها و رویکردهای درمانی دلبستگی ناایمن آشنا کنیم. پس اگر میخواهید خودتان را بیشتر بشناسید و روابط باکیفیتتری بسازید، پیشنهاد میکنیم ادامه این مقاله را از دست ندهید.
What is insecure attachment and how is it formed?
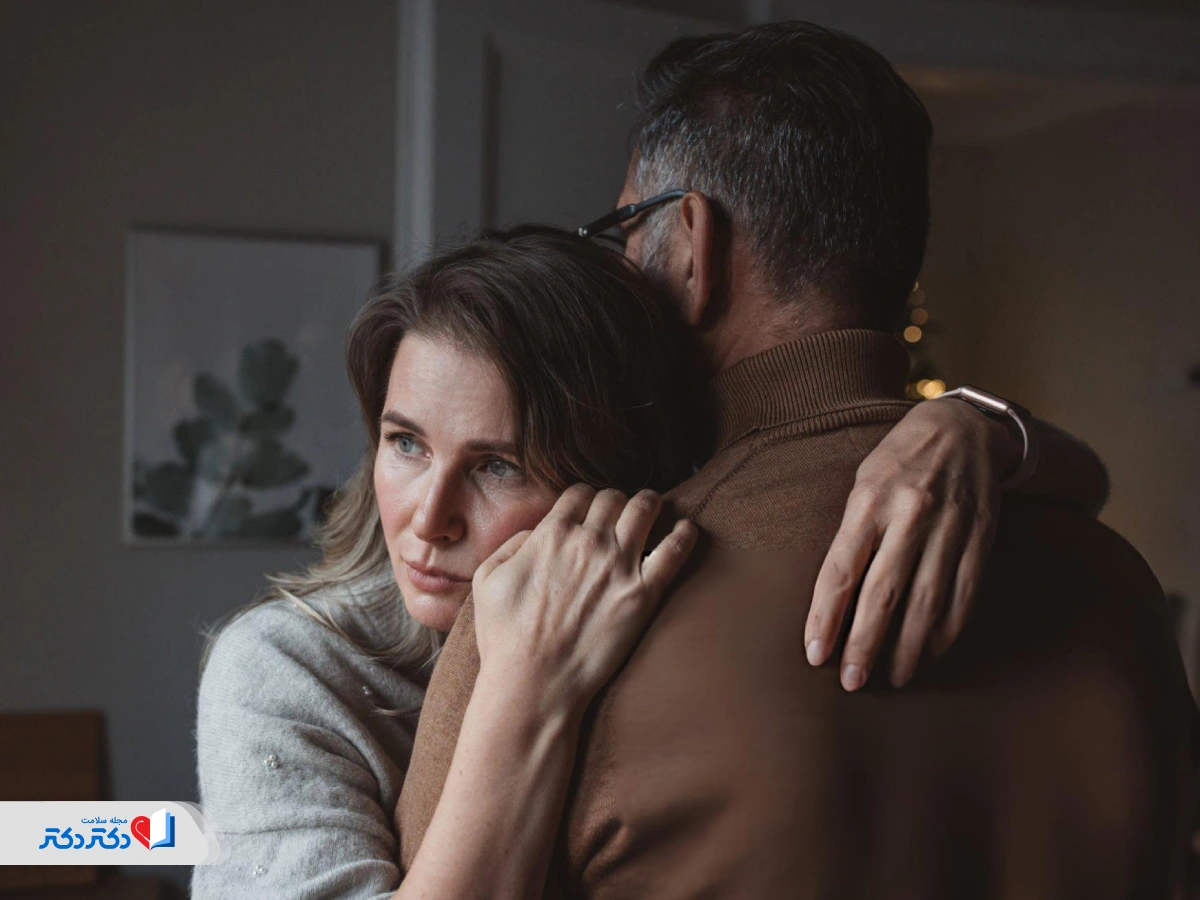
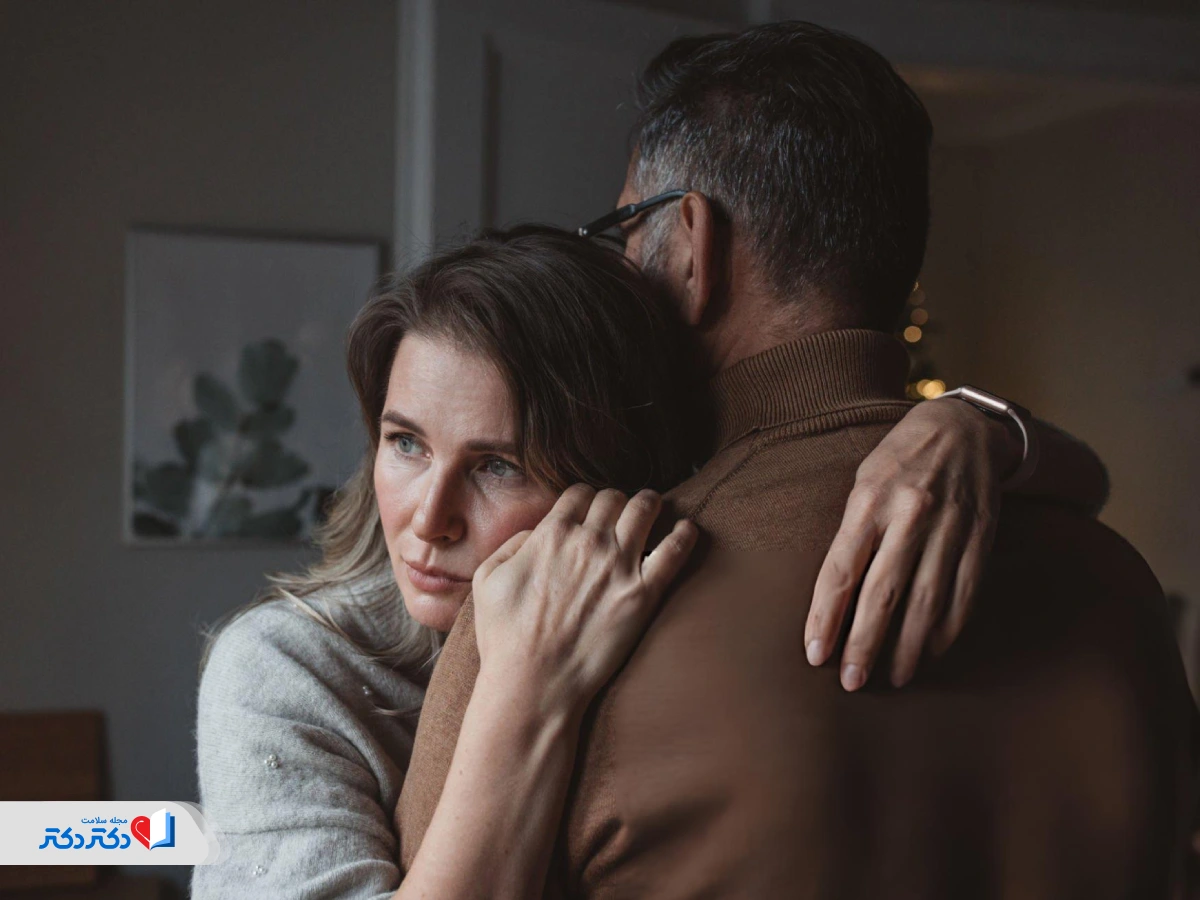
Insecure attachment style (Insecure Attachment Style) is a behavioral and emotional pattern that makes a person feel insecure and mistrustful in their relationships with others. Unlike secure attachment, in which a person can establish healthy, stable and secure relationships, in insecure attachment, a person is constantly afraid of loss, fear of rejection, or overdependence. Some people with this attachment style may become overly clingy and dependent, while others avoid intimacy and closeness.
This concept was first introduced by John Bowlby, a British psychiatrist, and Mary Ainsworth, an American psychologist in the mid-20th century. Attachment theory shows how the quality of the child's relationship with the primary caregiver in the first 18 months of life affects his ability to establish and maintain relationships in adulthood. Factors such as not meeting the child's basic needs, the cold or distracted behavior of the primary caregiver, emotional abuse or parental neglect can create a deep sense of insecurity in the child and make his mind pessimistic and cautious towards the world and others. Also, the experience of trauma, emotional neglect, physical and sexual abuse, changing and moving a lot between primary caregivers (such as moving between kindergartens) and depression or addiction of parents are some of the factors that play a role in the formation of insecure attachment style. These experiences can cause the formation of fear of rejection, anxiety in relationships and inability to trust others, and finally establish an insecure attachment style in a person. 
Types of insecure attachment: avoidant, anxious and disturbed
Insecure attachment style may appear in three ways in people. These three types of insecure attachment are different patterns of behavior that are formed from early experiences with the primary caregiver. Some people avoid intimacy and others become overly attached and clingy.
Also, some people may avoid any type of intimate relationship despite having a deep inner desire for closeness and intimacy. All three categories are included in the group of people who have an insecure attachment style, while showing different characteristics of this style. In the following, we examine each of the three attachment styles: avoidant, anxious, and disturbed.
1. Avoidant insecure attachment
Avoidant insecure attachment style is characterized by a severe inability to tolerate closeness and intimacy in adult relationships. People with insecure avoidant attachment avoid intimacy and have a strong desire to be independent. These people usually claim that they do not need anyone and deliberately suppress their feelings in relationships.
The main characteristics of insecure avoidant attachment in a relationship
Avoidant people have a deep fear of emotional vulnerability and it is difficult for them to establish real relationships. For this reason, these people spend most of their energy, time and focus on work and personal success and prefer to live in isolation.
People with avoidant insecure attachment usually:
They see intimacy as suffocating and uncomfortable;
They don't allow their friend or romantic partner to get close;
Tend to short-term or superficial relationships;
Ignore the feelings of the emotional partner.
The roots of the formation of insecure attachment Avoidant
The root of the avoidant insecure attachment style usually goes back to the absence or rejection of the primary caregiver during infancy. If a child's emotional needs are rejected or ignored in the first few months of life, the child learns to avoid intimacy in order to protect himself and develop a strong and pathological desire for independence. and lead to emotional suppression.

2. Anxious insecure attachment
Anxious insecure attachment style makes a person constantly feel worried and insecure. People with this style become attached to others with a deep fear of rejection and abandonment. These people are too much looking for a relationship and are thirsty for emotional intimacy, while they cannot fully trust their emotional partner. This behavioral conflict usually leads to excessive attachment or confirmation-seeking and reassurance-seeking behaviors in the relationship.
The main characteristics of insecure attachment anxiety in the relationship
A person who has an insecure attachment anxiety is very sensitive and waits for the smallest signs of danger in the relationship. is Such a person usually has low self-confidence and measures his worth solely based on the behavior of his emotional partner.
These people:
react to the slightest sign of rejection. They show extreme fear, anger or anxiety;
It is difficult for them to respect the boundaries of their emotional partner;
Constantly seeking to be "loved" are.
Common reactions and behavioral patterns
High anxiety makes it difficult for these people to control their emotions. For this reason, they may use methods like the following to maintain the relationship:
Creating guilt
Controlling behaviors
Extreme attention seeking
These reactions often come from a deep fear of abandonment and aim to ensure The commitment of the emotional partner to the relationship; However, sometimes it backfires and puts more pressure on the relationship.
The roots of the formation of anxious insecure attachment
The root of this style usually goes back to the first few months of childhood; When the primary caregiver responded irregularly to the child's emotional needs. That is, the caregiver was sometimes responsive and sympathetic and sometimes absent, cold or distracted.
This instability in meeting needs causes the child to experience extreme anxiety, mistrust and insecurity and not know when his needs are going to be met.
The consequences of this experience in Adulthood
In such a situation, the child learns to constantly watch the behavior of the parent or primary caregiver in order to receive love and attention. The child learns that he must always be alert and ready to react to any possible sign of rejection.
These early experiences eventually create a pattern of constant worry, emotional dependence, and anxiety about future relationships and form an anxious insecure attachment style in adulthood.

3. Disorganized insecure attachment
Disorganized insecure attachment style is the third type of insecure attachment. This style is a combination of high anxiety and avoidance. Adults with disturbed or disorganized insecure attachment often feel that the world is a dangerous place and that they will not benefit from relationships and intimacy.
In relationships, the behavior of people with disturbed or disorganized insecure attachment is often confusing, unpredictable, and unstable. These people are very hungry for love and connection, but at the same time, they are afraid of being hurt by their lover. This conflict causes people with a disturbed attachment style to constantly engage in attraction and repulsion behaviors, that is, sometimes they seek intimacy and sometimes withdraw without warning.
People with a disturbed attachment style are unable to manage and control their emotions and often have a negative view of themselves. These people do not trust anyone and often behave aggressively, controlling or abusive. Unorganized insecure attachment style has a significant relationship with the possibility of personality disorders in a person.
This insecure attachment style is formed when the child's primary caregiver has been both a source of comfort and a source of fear for the child, for example, consider the behavior of a mother who is both a source of nourishment and comfort for the child and punishes and reprimands her child for crying. Thus, the child does not know how to react to the primary caregiver and shows confusing behaviors. Also, people who were the target of trauma, neglect or abuse in childhood, often have disturbed insecure attachment.
These early experiences in adulthood make a person stuck between the desire for intimacy and the fear of being hurt. As a result, the relationships of these people are often full of tension, misunderstandings and frequent disconnections. Such people hardly receive a sense of love and emotional security.
What is the difference between disturbed and ambivalent insecure attachment?
Ambidextrous insecure attachment style (anxious) and disturbed insecure attachment style (disorganized) are both associated with anxiety and insecurity in relationships, but in the roots and pattern behavior in adulthood is different.
In ambivalent insecure attachment or anxiety (Anxious/Ambivalent), a person is afraid of being rejected and abandoned, and for this reason he clings to others. Such a person wants constant attention and approval and shows behaviors such as excessive worry, clinginess, control or dependence in his relationships. This style is often formed as a result of the primary caregiver's unstable and unpredictable responses to the child's needs, that is, when the parent is sometimes kind and available and sometimes indifferent or cold.
On the other hand, the lack of a sense of security in disorganized attachment is more complex and deeper. In this style, the child receives a feeling of fear and security from his caregiver at the same time, that is, the person who should be sheltered is sometimes a source of threat or pain. For this reason, in adulthood, a person is stuck between a strong desire for intimacy and fear of harm, and shows contradictory behaviors such as anger and frequent reconciliations. Such a person cannot have a regular and fixed solution to deal with problems and behaves unpredictably.
Simply put: an ambivalent person is afraid of "abandonment", but a disturbed person is both afraid of "abandonment" and has anxiety about "being in a relationship", because he learned in his childhood that love and danger come from the same source. 
Insecure attachment in children
Insecure attachment styles are formed from the first months of life and indicate the type of emotional relationship a child has with his main caregiver. According to the attachment theory of John Balby and Mary Ainworth, when the caregiver cannot provide the correct response to the physical and emotional needs of the child in a consistent and stable manner, the child is likely to have an insecure attachment style. Insecure attachment styles are formed from early childhood and if not treated, they will stay with the person for the rest of their lives. Therefore, children may also show three insecure attachment styles.
- Anxious-Dependent attachment style: This style is formed when the caregiver is sometimes responsive and sometimes absent. In this situation, the child feels insecure and anxious and sees his caregiver as unreliable. Such a child becomes sad and anxious when separated from its caregiver. But when the caregiver returns, the child does not calm down and shows contradictory behaviors towards the parent. Such a child anxiously clings to the parent and searches his environment with difficulty. Also, children who have an anxious-dependent attachment style have trouble controlling their emotions and may show behaviors that indicate excessive anger or frustration.
- Avoidant-neglecting attachment style: When a child feels that their emotional needs are ignored or rejected by the primary caregiver, the avoidant-neglecting attachment style is formed. The caregiver has shamed or reprimanded such a child for expressing his feelings. Therefore, the child takes the approach of avoidance and emotional coldness and tries to be extremely aloof and independent. When a child with an avoidant attachment style is afraid or feels hurt, he does not return to his parent for comfort, and if he is separated from the parent, he does not show distress. Also, the avoidant child often rejects contact with the parent when the parent turns to him. Such a child does not differentiate between a primary caregiver and a stranger.
- Disturbed attachment style: A child with a disturbed attachment style usually has experienced roots such as extreme fear, neglect, trauma, or abuse. Such a child is confused about the primary caregiver, seeing him as both a source of comfort and a source of punishment and fear. The behavior of a child with a disturbed attachment style is inconsistent and unpredictable. This child may go to his parent for moments to calm down, but suddenly distance himself from him or even show fearful and defensive behaviors. These conflicting reactions are because the child does not know whether the parent is supposed to calm him down or be aggressive towards him.
If the right interventions are not made to help children with insecure attachment, insecure attachment patterns can continue into adulthood and have a serious impact on their future relationships.
Insecure attachment symptoms and impact in adulthood
Insecure attachment styles begin with childhood experiences and often continue into adulthood. These styles create serious problems in starting and maintaining relationships by fueling a person's sense of distrust and worthlessness. People with insecure attachment may have difficulty establishing intimacy or, conversely, become overly dependent on the other person due to childhood issues. In the following, according to the types of insecure attachment, we point out some of the symptoms and patterns of these styles in adulthood.
Features of anxious attachment
- People in anxious attachment are very afraid of being abandoned or rejected.
- These people strongly seek They are intimate, but they worry that others will not want to be intimate with them.
- People with anxious attachment are always looking for reassurance and approval and seem very needy or clingy to others.
- It is difficult for these people to respect boundaries and they do not give personal space to their emotional partner.
- They have a negative view of themselves, but they are able to idolize others.
Characteristics of avoidant attachment
- They tend to avoid intimacy and value independence too much.
- They do not express their emotional needs and suppress their feelings even when they are under extreme anxiety and stress.
- Relationships They end early so as not to become attached to anyone.
- The emotional partner of these people often describes them as closed, dry, cold and emotionless.
Read more: Symptoms What is depression?
Characteristics of disturbed attachment
- These people have confusing, unpredictable, and unstable behaviors.
- Adults with disturbed attachment are always looking for love but are also afraid of getting hurt.
- These people are constantly torn between closeness and Distance (attraction and repulsion) fluctuate.
- People with disturbed attachment cannot manage their feelings and emotions and may show aggressive, controlling or irrational behaviors.
- These people find it difficult to trust others and have a negative image of themselves and others.
- People with disturbed attachment are prone to personality disorders such as borderline personality disorder.

How to treat insecure attachment in adulthood
Although attachment styles are formed from infancy, adults do not need to remain captive to these patterns for the rest of their lives. The brain is always capable of change. With effort and awareness, a person can change his insecure attachment style to a secure attachment style, which is called "earned security". This often happens through healthy adult relationships such as good friends or getting help from a psychotherapist.
A professional therapist can create a safe environment to recognize childhood traumas, reprocess past emotional experiences, and gain a more positive and realistic view of yourself and the world around you. In this regard, you can take advantage of the professional help of Dr. Doctor's psychotherapists through an online visit or an in-person appointment and give yourself and your relationships more security.
Psychotherapists use various treatments to treat insecure attachment in adulthood. We introduce some of these approaches below.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): In cognitive behavioral therapy, the therapist helps the person to identify negative thoughts and distorted thought patterns that cause anxiety, fear of rejection or avoidance behaviors. The therapist then helps the person replace these thoughts with more realistic and healthy beliefs. The goal of CBT is to change the way of thinking and behavior in relationships so that a person can manage his emotions and show a more balanced behavior.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): Dialectical Behavior Therapy is especially useful for people who have difficulty regulating their emotions. This approach focuses on accepting emotions, learning ways to control anger and anxiety, and improving communication skills. In DBT, the therapist teaches the person how to maintain a balance between self-acceptance and trying to change and reduce extreme behaviors or strong emotional reactions in close relationships. Psychodynamic Therapy: In this type of therapy, the focus is on discovering the unconscious roots of problems in current relationships. The therapist helps the individual understand the connection between childhood experiences, relationship with parents, and current attachment style. By increasing insight into these unconscious patterns, a person can correct unhealthy behaviors and build safer and more mature relationships.
In general, a person is halfway through the treatment by being aware of the effects of childhood experiences on unconscious decisions and recognizing the insecure attachment style. A person who has knowledge and insight about his attachment style can take effective steps to correct ineffective thoughts and self-destructive behaviors. Other methods that can help increase a person's psychological security are increasing interpersonal skills, understanding non-verbal communication, increasing emotional intelligence and managing emotions. Establishing a relationship with friends and a healthy and supportive emotional partner can play an important role in repairing past emotional wounds and forming a sense of trust and security.

DoctorDoctor's Last Word
Insecure attachment is like an invisible thread that has been tied to us since childhood and causes us to feel fear, anxiety and intense mistrust in our relationships. However, the way back is open and there are many treatments available to bring people back to safety. The first step is to recognize attachment styles and the next step is to seek help from a mental health professional. Fortunately, the online visit of Dr.Doctor has made it easy for you to find the most experienced psychotherapists in Iran and build more meaningful and stable relationships with your friends and loved ones by repairing the emotional wounds of the past. data-toggle="collapse">How does insecure attachment affect our emotional relationships?