Children's azithromycin is one of the common antibiotics prescribed in cases of dental infection. این دارو از گروه ماکرولیدها است و با مهار رشد باکتریها، عفونتهای باکتریایی را کنترل میکند. این مقاله به زبان ساده و بر اساس منابع معتبر، به بررسی کاربرد، دوز و نکات مهم میپردازد.
آزیترومایسین برای عفونت دندان کودکان یکی از آنتیبیوتیکهای رایج است که در موارد عفونتهای باکتریایی دهان و دندان کودکان تجویز میشود. Based on AAPD (American Association of Pediatric Dental) guidelines and CDC in 2025, azithromycin is a suitable option for the treatment of dental infections such as abscess, periodontitis or post-treatment infection due to its broad spectrum, convenient dosing and good tolerance in children. This is a scientific but simple article for parents who are looking for detailed information about Azithromycin dosage for child toothache, side effects and important points.
Is pediatric azithromycin suitable for dental infections?
pediatric azithromycin is effective in bacterial infections of the mouth such as abscesses or infections after root canal treatment. The AAPD emphasizes that antibiotics are only an adjunct to dental treatment, not a substitute for it. Pediatric azithromycin is more convenient for children because of its long half-life (one daily dose).

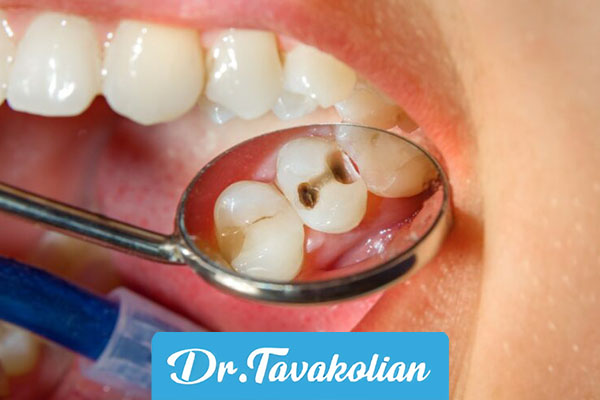
Pediatric azithromycin for dental abscess is prescribed in cases where macrolide-sensitive bacteria (such as streptococcus) are involved. In acute abscesses, azithromycin is combined with pus drainage, the AAPD reports. pediatric azithromycin for tooth abscess is usually taken for 3-5 days to reduce swelling.

Azithromycin syrup for tooth infection in children is a common form for children under 8 years of age. The concentration of 200 mg/5ml or 100 mg/5ml is available. The CDC recommends that the syrup be consumed after meals to reduce gastrointestinal side effects. Azithromycin syrup for baby tooth infection has a fruity taste and increases the child's acceptance.
Azithromycin for children's teeth: important points
The use of azithromycin for children's teeth should be accompanied by these points:
- Complete the course of treatment even if the symptoms have disappeared.
- Take with food to reduce nausea.
- Avoid milk or antacids at the same time (decreases absorption)
- Monitor for complications such as diarrhea or rash.
AAPD says Azithromycin for baby teeth is only proven for bacterial infections.

Azithromycin for dental infection in children
Azithromycin alternative for dental infection in children includes:
- Amoxicillin (AAPD first priority for dental infections).
- Clindamycin (in penicillin allergy).
- Metronidazole (for anaerobic infections).
Alternative to azithromycin for dental infection in children is selected based on sensitivity testing. The AAPD prefers amoxicillin because of its broader coverage.
Azithromycin for children is an antibiotic from the group of macrolides that stops the growth of bacteria by inhibiting protein synthesis. In pediatric dentistry, azithromycin is prescribed for infections caused by streptococcal, staphylococcal, and anaerobes bacteria. The AAPD emphasizes that antibiotics are only necessary in cases of bacterial infection (not viral or simple decay). Pediatric azithromycin is usually taken for 3-5 days due to its long half-life, making it easy for the child to cooperate.

Azithromycin dose for child toothache is determined based on the weight and severity of the infection. The following table is based on AAPD and CDC 2025 guidelines:
| Child's weight (kg) | First day dose (mg/kg) | Day 2-5 dose (mg/kg) | Recommended pharmaceutical form | Duration of treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-15 | 10 | 5 | Syrup 200 mg/5 ml | 3-5 days |
| 15-25 | 10 | 5 | syrup or capsule | 3-5 days |
| 25-35 | 10 | 5 | 250 mg capsules | 3-5 days |
| above 35 | 500 mg fixed | 250 mg fixed | capsule 500 mg | 3-5 days |
Note Important: The exact dosage should be determined by a pediatric dentist. Azithromycin should be taken with food to reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
Azithromycin in pediatric dentistry side effects are usually mild. Most common side effects:
- Indigestion (nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain) in 5-10% of cases.
- Rare allergy (skin rash).
- Temporary taste or smell disturbance.
CDC reports that serious side effects (such as cardiac arrhythmia) are very rare (<0.01%) in children. The side effects of azithromycin in the treatment of children's teeth are reduced with the simultaneous use of probiotics.
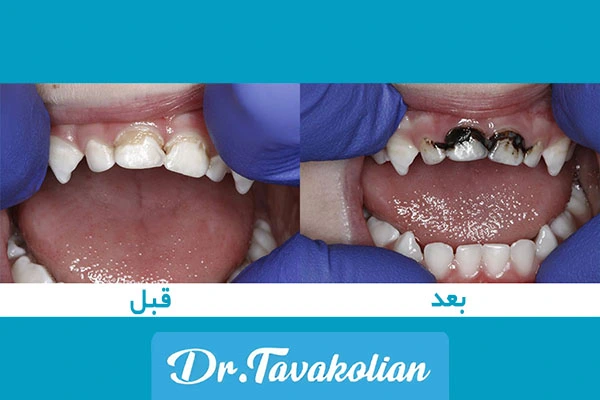
Treatment of baby tooth infection with azithromycin is recommended in the following cases:
- Dental abscess with facial swelling
- Infection after pulpotomy or Dragging
- Juvenile periodontitis
AAPD emphasizes that antibiotics are complementary to mechanical treatment (cleaning or drainage) and do not cure caries alone.
Azithromycin or amoxicillin for children's teeth depends on the situation:
- Azithromycin: for children allergic to penicillin, lower dose, spectrum Broader.
- Amoxicillin: first-line AAPD, cheaper, better strep coverage.
A 2024 study found both to be 90% effective in treating dental infections in children.
value Azithromycin consumption for dental infection in children
Azithromycin consumption for dental infection in children should be accurate and based on the child's weight. Azithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic prescribed for bacterial infections of the mouth and teeth (such as abscesses or post-treatment infections). According to the AAPD and CDC 2025 guidelines, this drug is a suitable option due to its convenient dosage and low side effects. Always determine the dose by a pediatric dentist - self-medication is dangerous.
Azithromycin dosage for tooth infection is usually 3-5 days.
Important point: The exact dosage should be determined by a pediatric dentist. The drug should be taken with food to reduce digestive side effects.
Important tips for parents
- Take the full course even if the symptoms disappear.
- In case of severe diarrhea or rash, inform the doctor immediately.
- Probiotic (yogurt) should be taken at the same time to maintain the balance of intestinal flora.
- Azithromycin is not a substitute for mechanical treatment (dental cleaning).
Possible side effects
Common side effects are mild: Nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain. Serious complications are rare. class="ez-toc-section-end">
Azithromycin for pediatric dental infection is a safe and effective option, but should only be taken with a prescription from a pediatric dentist. Parents can better manage the treatment by knowing Azithromycin dose for child toothache and Azithromycin side effects in children's dental treatment. Pediatric Azithromycin is effective in certain cases of dental infection, but always combined with dental treatment. Parents should not give medicine arbitrarily. For accurate diagnosis and proper prescription, see a pediatric dentist.