Gum analysis is one of the common problems in the elderly, which not only affects the appearance of the smile, but can also reduce the overall health of the mouth and even the quality of life. This condition usually appears as gum receding and exposing the tooth root and if neglected, it increases the risk of loosening or losing teeth.
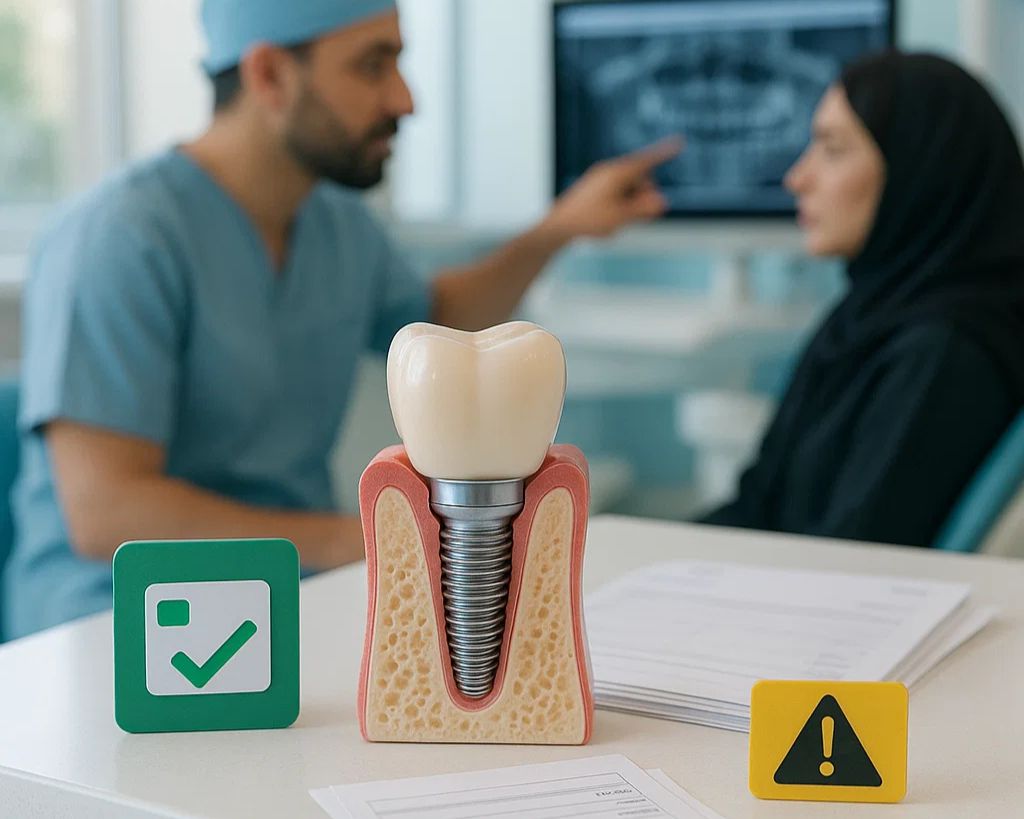
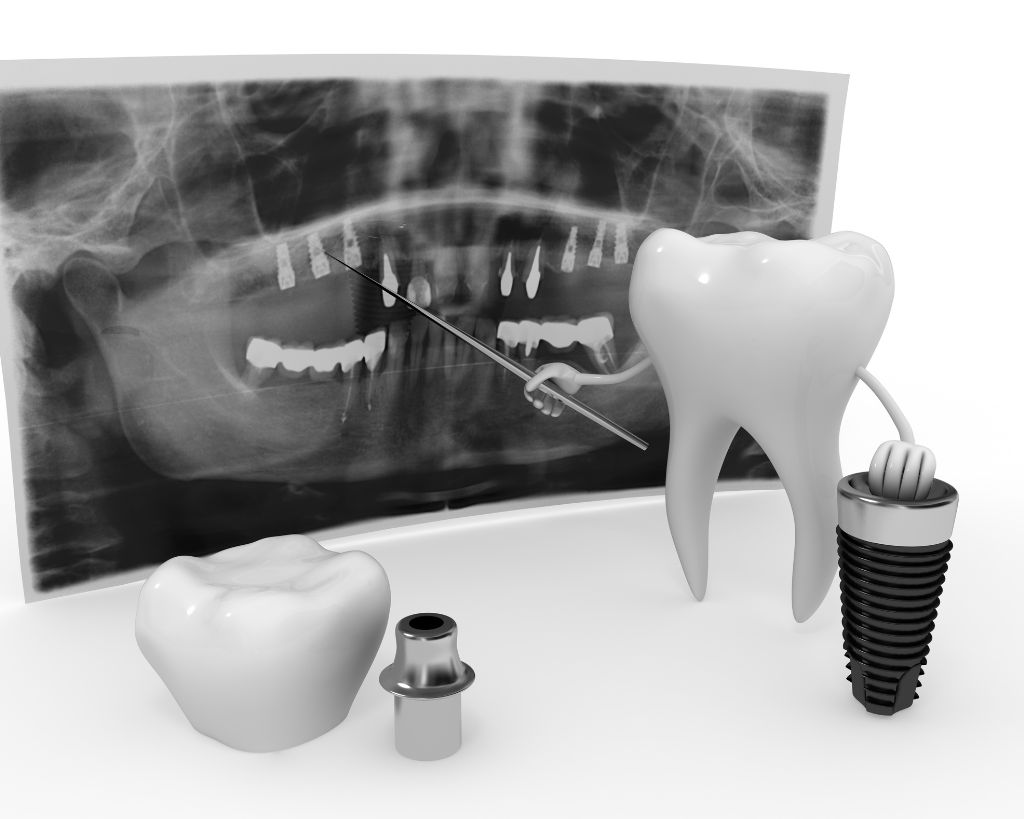
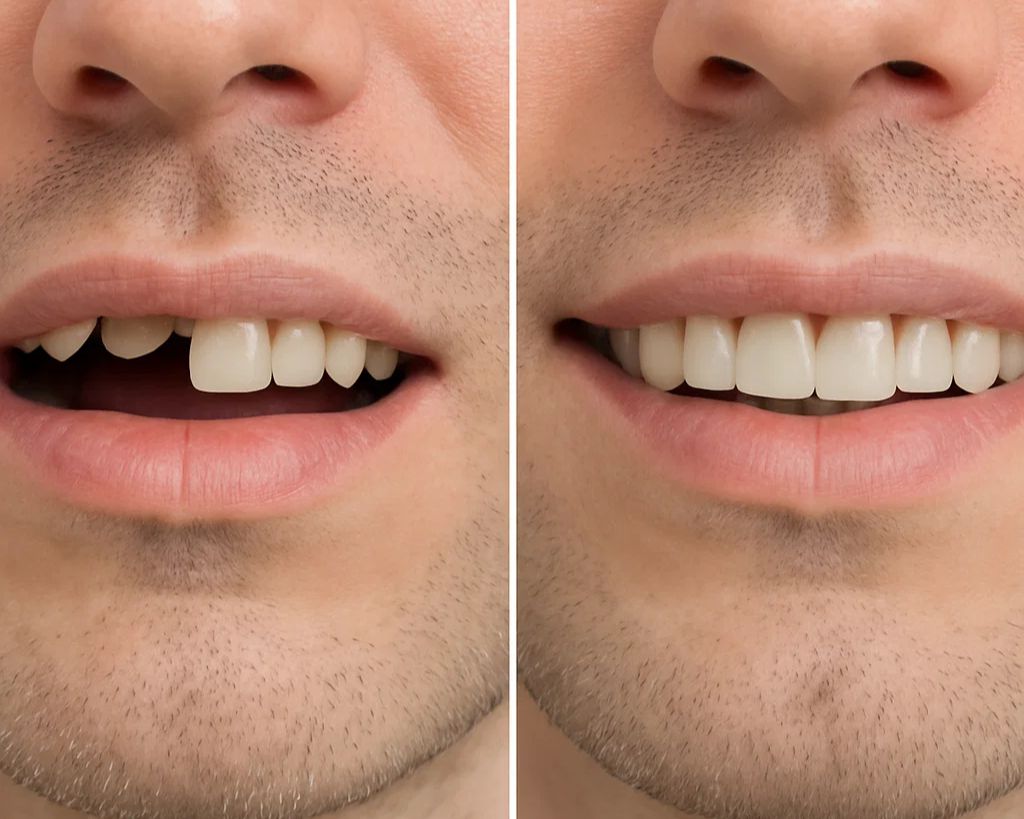
One of the treatment options for people who need replacement due to severe gingivitis and tooth loss is [dental implants in the elderly], which can restore the function of chewing and the beauty of the smile. However, the best approach is to prevent the progression of gingivitis. In this article, we will comprehensively examine the causes, risk factors and prevention methods of gingivitis in old age.
What is gum disease and why is it more common in old age?
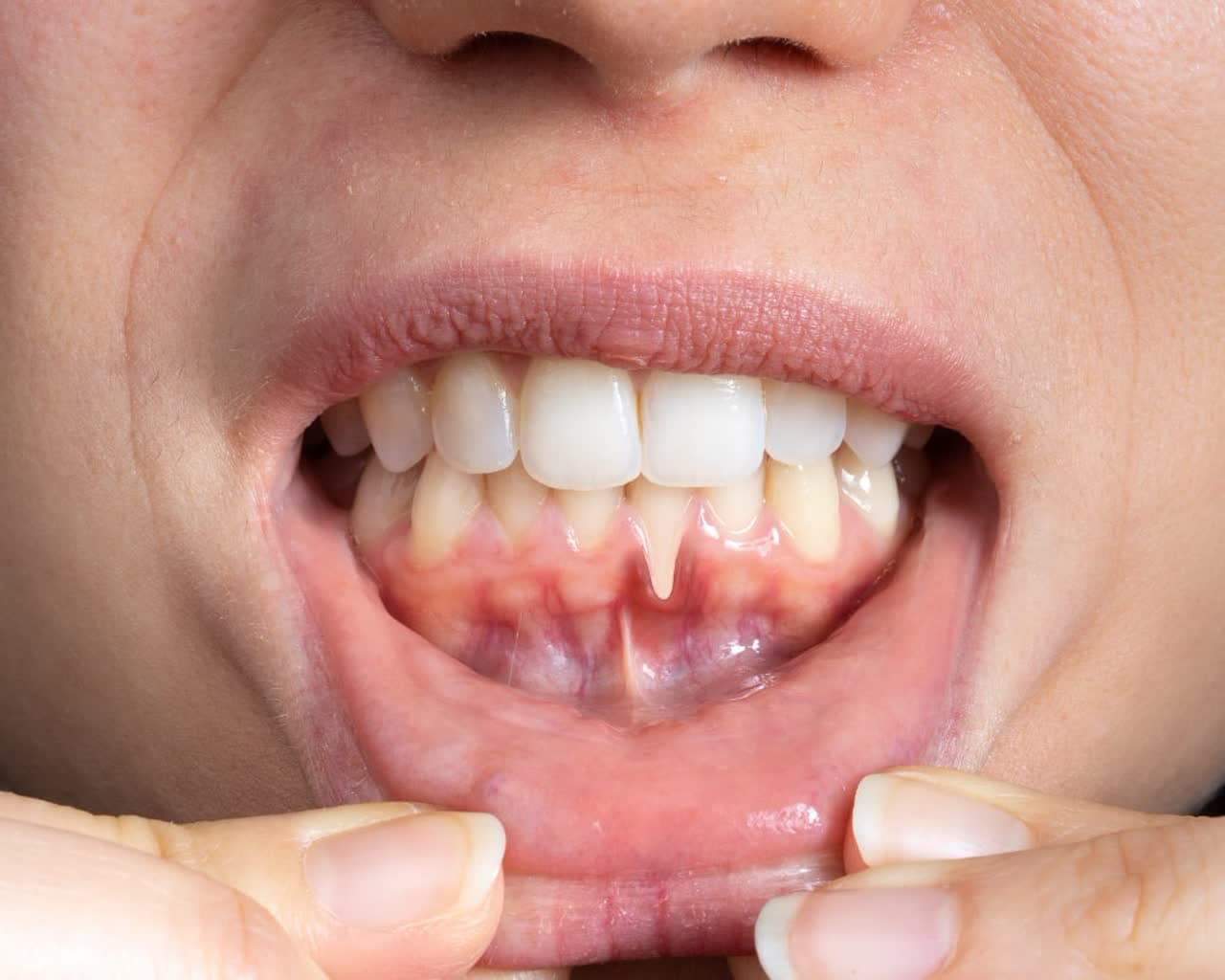
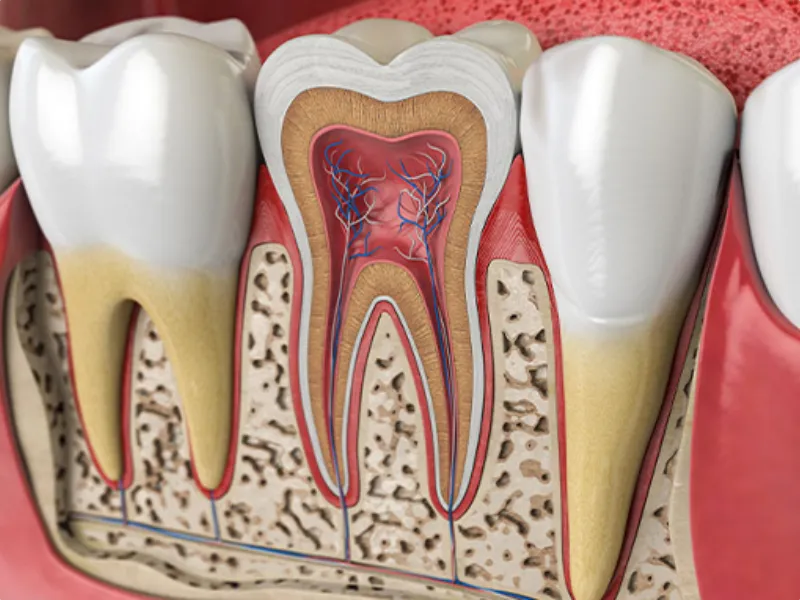
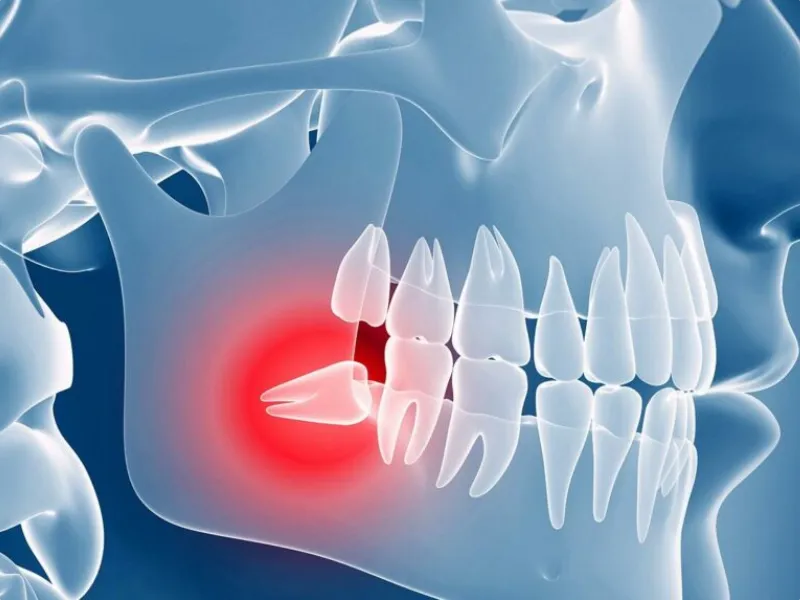
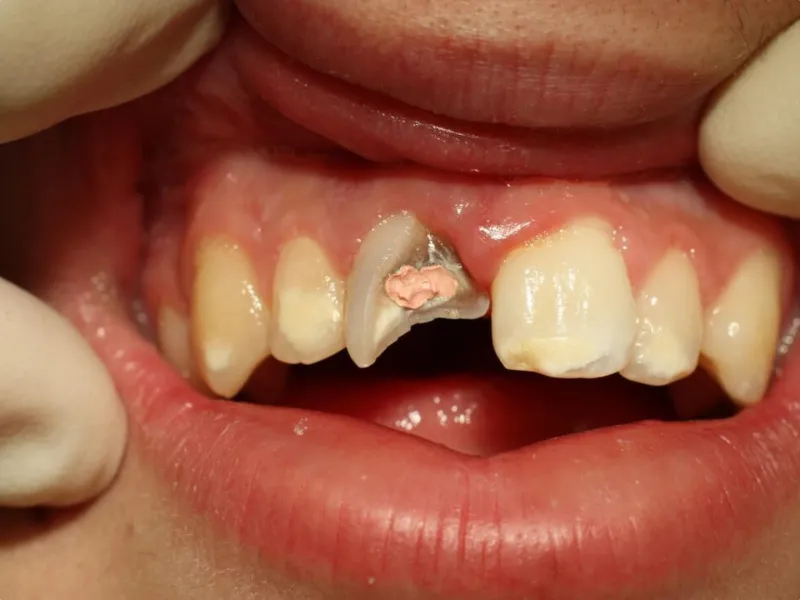
Gum Recession refers to the receding of the gum tissue from the surface of the tooth, which exposes more of the tooth or even its root. In old age, for various reasons, the gum tissue and the bone supporting the teeth are prone to decay, including:
-
Physiological changes associated with aging
- Decreasing the ability to repair tissues
- Longer history of exposure to damaging factors such as plaque and grime
- Systemic diseases that become more common with age (diabetes, osteoporosis, etc.)
The most important risk factors for gingivitis in the elderly
-
Gum diseases (periodontal)
Periodontitis and gingivitis are the main causes of gum recession. With increasing age, the possibility of contracting these diseases increases due to the weakening of the immune system and the reduction of oral health care.
-
Incorrect brushing
Using a toothbrush with a very hard brush or wrong technique can cause mechanical wear of the gum and its retreat. The influence of gum health on the success of dental cosmetic treatments should not be ignored at all.
-
teeth grinding and excessive pressure on the teeth
Habits such as teeth grinding (Bruxism) or clenching the teeth during the day put a lot of pressure on the gums and supporting bone.
-
Hormonal and drug changes
Some blood pressure medications, antidepressants, or heart medications can cause dry mouth or changes in gum tissue, which in the long term increases the risk of decay.
-
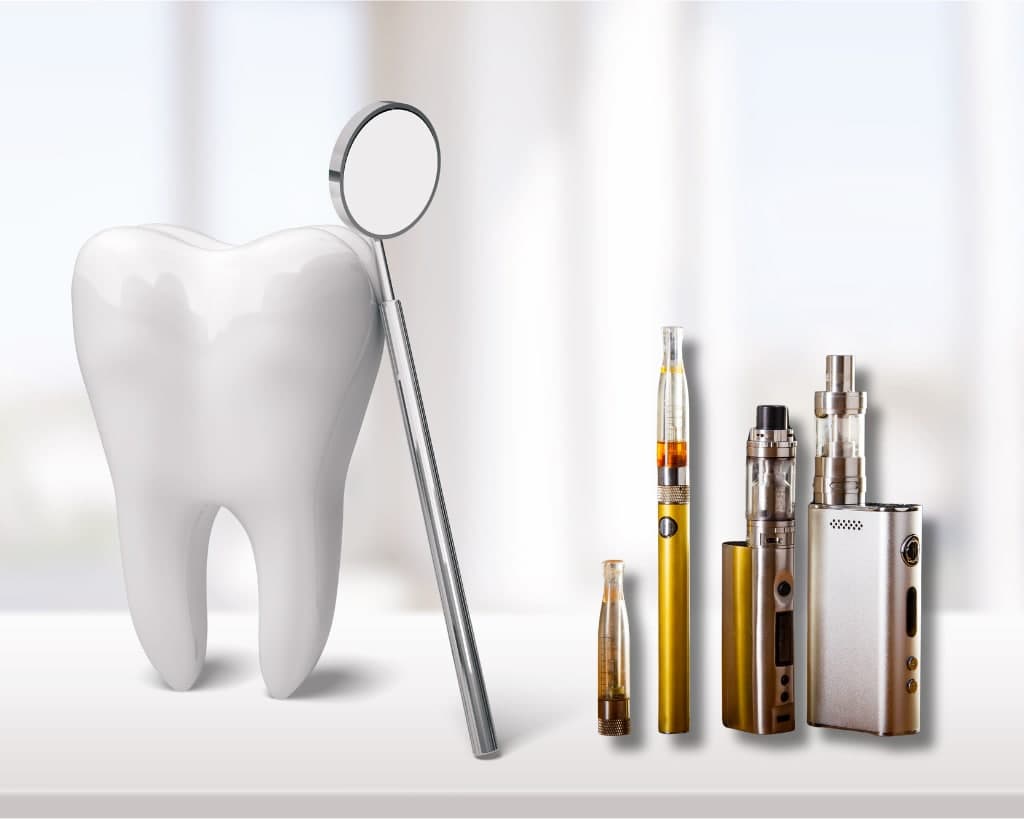
Smoking
Cigarettes and other nicotine-containing products reduce blood flow in the gums, weaken the immune system, and accelerate gum degeneration.
early symptoms of gingivitis
- Increasing sensitivity of teeth to cold and heat
- Longer appearance of teeth than before
- creating a groove or depression near the gum line Bleeding gums while brushing or flossing
- persistent bad breath
Early diagnosis of these symptoms by the dentist can prevent the progress of analysis.
Methods to prevent gingivitis in old age
-
Strict observance of oral and dental hygiene
- brushing twice a day with a soft toothbrush and gentle circular movements
- Using fluoride toothpaste
- dental floss or interdental toothbrush to remove plaque between teeth
- Rinse your mouth with antibacterial mouthwash if recommended by the dentist
Note: The elderly should avoid applying too much pressure when brushing their teeth due to the sensitivity of their gums.
-
Crime and regular dental examinations
With increasing age, the possibility of faster formation of dental plaque increases. crime Once every 6 months can prevent gum inflammation and decay. Also, regular check-up helps to detect problems quickly and prevent them from progressing.
-
Modification of eating habits
- Consumption of foods rich in vitamin C (such as citrus fruits and bell peppers) for healthy gum tissue
- Using foods containing calcium and vitamin D to strengthen the jawbone because The effect of calcium and vitamin D on tooth strength is very high.
- Avoid excessive consumption of sugar and acidic drinks that can weaken tooth enamel
-
Management of systemic diseases
Diseases such as diabetes and osteoporosis in the elderly can accelerate the process of gingivitis. Controlling these diseases with the help of a doctor and following a treatment plan plays an important role in prevention.
-
Quit smoking
Quitting cigarettes and other nicotine-containing products improves blood flow in the gums, increases tissue repair capacity and reduces the risk of gum diseases.
-
Using tooth protection in grinding teeth
For the elderly who suffer from grinding teeth, using a nightguard or a dental protector while sleeping can reduce the pressure on the gum and bone tissue.
-
Correcting inappropriate restorations and prostheses
Dental prostheses or veneers that do not fit well can cause mechanical damage to the gums. In these cases, the repairs must be repaired or replaced.
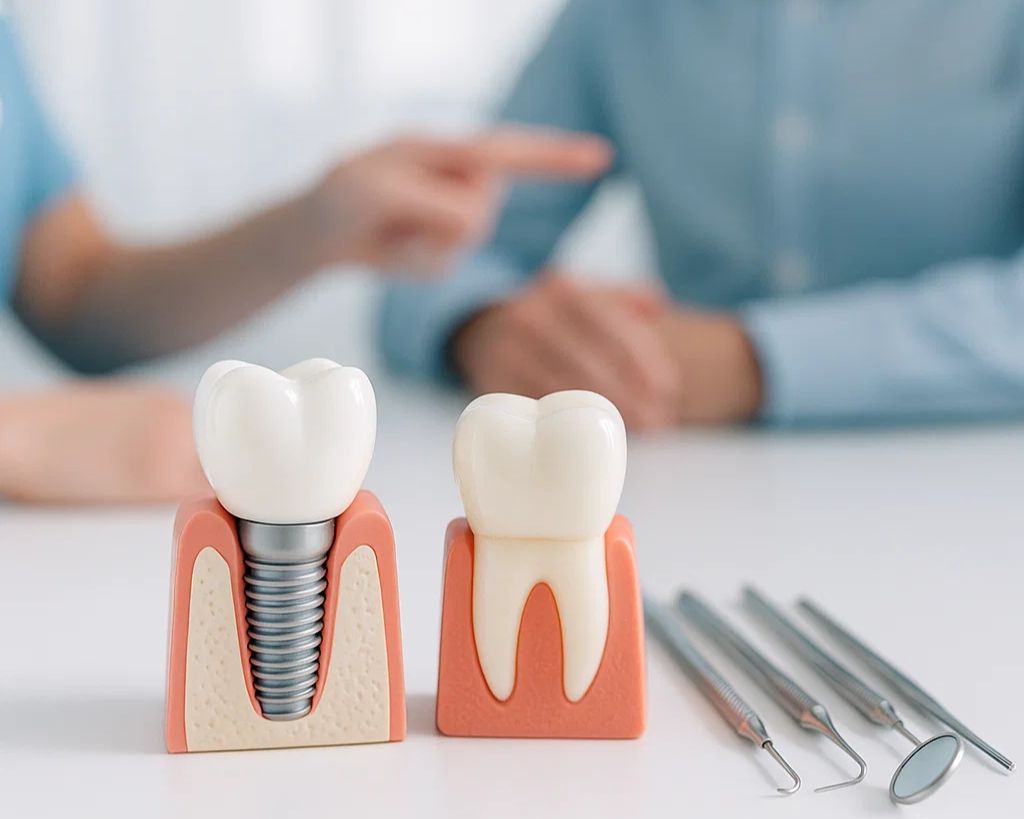
The relationship between gingivitis and dental implants in the elderly
When gum and bone loss reach the point where teeth are loose or missing, seniors may need to replace them with Dental implant in elderly people do By maintaining the volume of the jaw bone, the implant can prevent further erosion and restore chewing function and beauty. However, for the success of the implant, gum diseases must be controlled and oral hygiene must be well observed.
The role of nutrition in preventing gingivitis in the elderly
- Sufficient protein: It is necessary for gum tissue repair.
- Minerals: calcium, phosphorus and magnesium are important for maintaining jaw bone health.
- Antioxidants: such as vitamin E and polyphenols that can reduce gum inflammation.
The importance of education and awareness of the elderly
Many elderly people do not follow oral hygiene properly due to vision, movement problems or even lack of information. Practical training and the use of appropriate tools (such as an electric toothbrush or a toothbrush with a handle) can be very helpful.
When should you see a dentist?
- When observing gum recession
- In case of continuous bleeding gums
- When the teeth are extremely sensitive to cold or heat
- permanent bad breath
- Loose or displacement of teeth
Summary
Gum analysis in old age is a common but preventable problem. The risk of this problem can be reduced to a great extent by observing oral hygiene, visiting the dentist regularly, correcting eating habits and quitting smoking. In cases where gingivitis leads to loss of teeth,