
Causes of swollen knees and treatment methods - Radin Physiotherapy Clinic

Radin Physiotherapy Center
تهرانMohammad Dehghani - Physiotherapist
The cause of swollen knees and treatment methods
- Category: Knee physiotherapy, articles
- Publication date: May 12, 2025
- Duration of study: 6 minutes

 Study time: 6 minutes
Study time: 6 minutes
Diagnosis of swollen knee
Your health care provider will likely start with a thorough history and physical exam. Then you'll probably need tests to find out what's causing your knee to swell.
Imaging tests
Imaging tests can help show where the problem is. The options are: X-ray. X-rays can rule out broken or displaced bones and determine whether you have arthritis.
Ultrasound. This test uses sound waves to investigate disorders affecting tendons or ligaments.
MRI. Using radio waves and a strong magnetic field, MRI can detect tendon, ligament, and other soft tissue injuries that cannot be seen on X-rays.
Joint aspiration (arthrocentesis)
A needle is used to remove fluid from inside the knee. The fluid is then checked for the following:
Blood that may be from injuries or bleeding disorders
Bacteria that may cause infection
Common problems in gout or pseudogout
The doctor will use the following to get more information:
Arthroscopy
MRI
Ultrasound
X-rays X


Treatment of watery knee
Treatment varies depending on the cause of knee swelling, its severity and your medical history. Physical therapy exercises can improve the function and strength of your knee. In some situations, a knee brace may be helpful.
Knee surgery and other procedures
The primary treatment of a swollen and swollen knee may require:
Arthrocentesis. Removing fluid from the knee can help reduce pressure on the joint. After removing some of the joint fluid, the doctor may inject a corticosteroid into the joint to treat the inflammation.
Arthroscopy. A lighted tube (arthroscope) is inserted into your knee joint through a small incision. Instruments attached to the arthroscope can remove loose tissue or repair damage to your knee.
Self-care and Knee drainage
Self-care for knee swelling includes:
Stopping movement. Avoid weight-bearing activities as much as possible.
Ice and altitude. To control pain and swelling, apply ice to your knee for 15 to 20 minutes every 2 to 4 hours. When you ice your knee, be sure to raise your knee above the level of your heart. For comfort, place pillows under your knees.
Compression. Wrapping the knee with a bandage can help control the swelling.
Relievers. Over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) can help relieve knee pain.
Preparing for a doctor's appointment
See your doctor if self-care measures, such as ice and rest, do not improve symptoms. If one knee becomes red and warm to the touch compared to your other knee, seek medical attention immediately. This could be a sign of an infection inside the joint. You may be referred to a health care provider who specializes in musculoskeletal and joint problems.
What you can do
Write down your symptoms and when they started.
Write down key medical information, including other conditions.
Write down key personal information, including major changes or stressors in your life.
A list of all medications, vitamins or Get your supplements.
Find out if anyone in your family has had an autoimmune disease.
Ask a relative or friend to accompany you to help you remember what your health care provider says.
Write down questions to ask your provider.
Questions to ask your doctor
Most likely cause of my symptoms What is it?
What kinds of tests do I need?
What treatments are available?
I have other health conditions. How can I manage them together?
What to expect from your doctor
Your healthcare provider will likely ask you a number of questions. Being prepared to answer them may leave you time to explore the points you want to discuss in depth. You may be asked:
Have you recently injured your knee? If so, describe the injury in detail.
Does your knee lock or feel unstable? Does it?
Is your knee warm or red? Do you have a fever?
Do you do recreational sports? If yes, what sports?
Do you have any form of arthritis?
Do you have a family history of autoimmune disease?
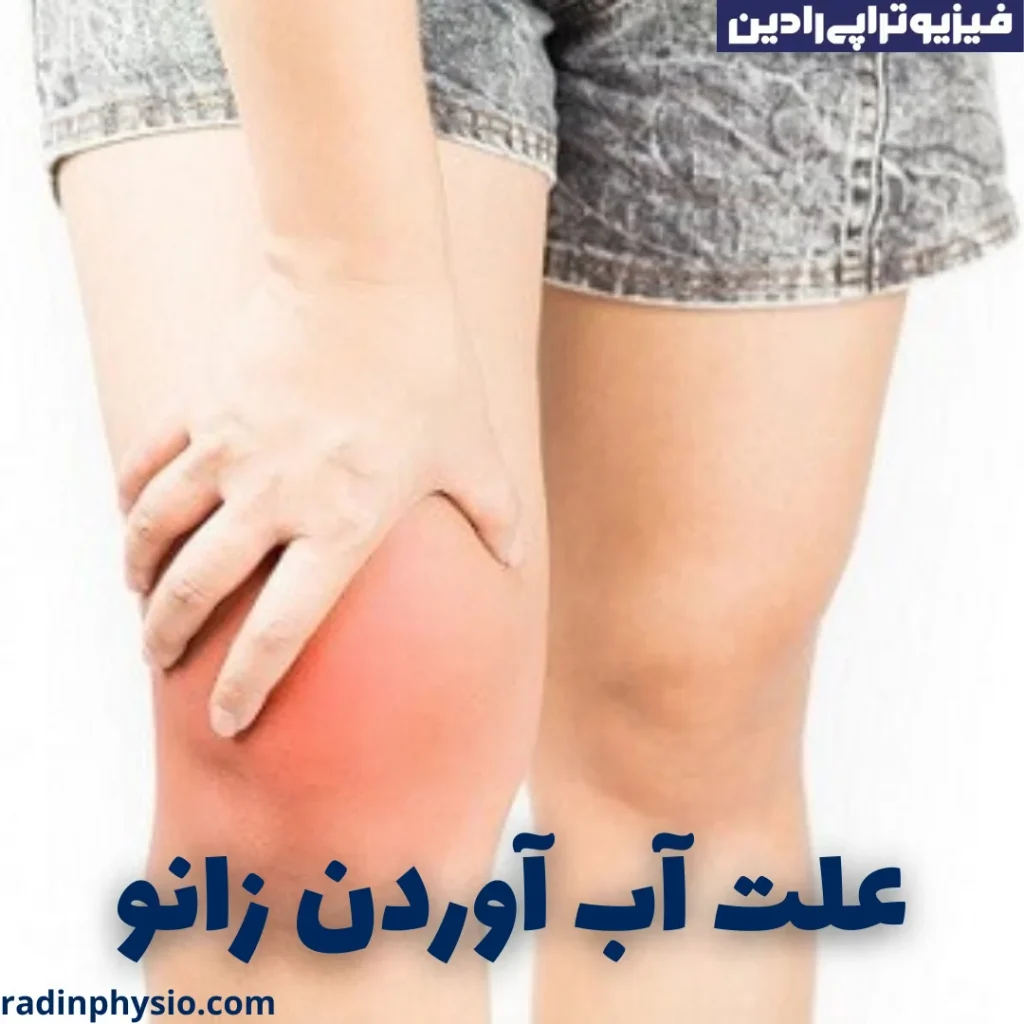
Swollen kneeIt happens when excess fluid builds up in or around your knee joint. Healthcare providers may refer to this condition as an effusion (uh-FU-zhun) of the knee joint.
A swollenknee may be the result of trauma, overuse injuries, or an underlying disease or condition. To find the cause of the swelling, your doctor may need to test a sample of the fluid for infection, disease, or blood from an injury.
Removing some of the fluid may help reduce the pain and stiffness associated with the swelling. Once the underlying cause is known, treatment can begin.
Symptoms of watery knee
Symptoms and signs usually include:
Swelling. The skin around your kneecap can swell significantly, especially when you compare the affected knee to your other knee.
Stiffness, stiffness. When the knee joint contains excess fluid, you may not be able to fully bend or straighten your leg.
Pain. Depending on the cause of the fluid build-up, your knee may be so painful that it becomes impossible to bear weight on it.
Many problems, from traumatic injuries to diseases and other conditions, can cause knee swelling.
The role of injuries in knee swelling
Injury to any part of your knee can cause excess joint fluid to build up. Injuries that can cause fluid to build up in and around the knee joint include:
Ligament tears, especially the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
Cartilage (meniscus) tears.
Overuse irritation
Broken bones
Anterior cruciate ligament
ACL injury
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one It is one of the key ligaments that helps stabilize the knee joint. Connects the thigh bone (femur) to the leg bone (tibia). It is usually torn during sports that involve sudden stops and changes of direction, such as basketball, soccer, tennis, and volleyball.
Torn Meniscus
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of tough, rubbery cartilage that acts as a shock absorber between the leg bone and thigh bone. If you twist your knee suddenly while bearing weight on it, it can tear.


The role of diseases and conditions in knee swelling
Diseases and conditions that can cause fluid accumulation in and around the knee joint include:
Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Infection
Gout
Gout False
Bursitis
Cysts
Tumors
Risk factors in knee swelling
Factors that may increase the risk of knee swelling include:
Age. The likelihood of developing swollen knees associated with osteoarthritis increases with age. Exercises. People who participate in sports that involve rolling the knee, such as basketball, are more likely to experience a variety of knee injuries that cause swelling.
Obesity. Excess weight puts additional pressure on the knee joint and contributes to tissue and joint overload and knee atrophy, which can lead to knee swelling. The fluid in the knee can damage the function of your muscles and cause weakness and atrophy of the thigh muscles. A build-up of fluid in your knee can lead to the formation of a Baker's cyst on the back of your knee. A swollen Baker's cyst can be painful, but usually improves with ice and compression. If the swelling is severe, it may be necessary to remove the fluid with a needle.
Prevention of knee sprains
A swollen and swollen knee is usually the result of an injury or chronic illness. To manage overall health and prevent injuries:Strengthen the muscles around your knee. Strong muscles around the joint can help reduce pressure on the joint.
Choose light exercise. Some activities, such as water aerobics and swimming, do not put constant weight-bearing stress on the knee joints.
Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight contributes to wear-and-tear injuries that can lead to knee swelling.
Conclusion
To improve and treat swollen knees, Best Physiotherapy specialist in Tehran Please contact us to book an appointment with the cooperation of the experienced staff of the complex to speed up your recovery with techniques and the most equipped equipment.
Contact the clinic Get appointment InstagramPhysiotherapy with insurance Supplemental
Physiotherapy with Asia Insurance Physiotherapy with social security insurance Physiotherapy with armed forces insurance Physiotherapy with Kausar Insurance Physiotherapy with teacher insurance Physiotherapy with entrepreneur insurance Physiotherapy with Sepeh Bank Insurance Physiotherapy with cooperative insurance Physiotherapy with Mellat Insurance Physiotherapy with Refah Bank Insurance Physiotherapy with SOS insurance Physiotherapy with Sarmad insurance Physiotherapy with Saman Insurance Physiotherapy with new business insurance Physiotherapy with Razi Insurance Physiotherapy with Salem city insurance Physiotherapy with Arman Insurance Physiotherapy with Bank Melli Insurance Physiotherapy with modern insurance Physiotherapy with Dana Insurance Physiotherapy with Parsian Insurance Physiotherapy with Sina Insurance Physiotherapy with Alborz InsuranceYou can contact Radin Physiotherapy Clinic for more information and to get an appointment
5 3 votes The score of this article 0 comments The most votes Newest Oldest Feedback (Feedback) View all commentsTable of contents




everything in The case of spine surgery, spine physiotherapy
Read more 

Ankle physiotherapy, 7 methods of treatment
read more

Whiplash Physiotherapy
Read more href="https://radinphysio.com/%d9%81%db%8c%d8%b2%db%8c%d9%88%d8%aa%d8%b1%d8%a7%d9%be%db%8c-% d8%aa%d9%86%da%af%db%8c-%da%a9%d8%a7%d9%86%d8%a7%d9%84-%d9%86%d8%ae%d8%a7%d8%b9%db%8c/">

What is spinal stenosis? Physiotherapy for spinal stenosis
Read more

How is varicose vein physiotherapy done?
Read more

What is flexor tendonitis? Physiotherapy of flexor tendonitis
Read more

What is physiotherapy? What are the benefits?
Read moreOther educational articles
Physiotherapy for muscle cramps or spasmsStudy time: 10 minutes Physiotherapy for muscle cramps or muscle spasm is done with what methods and how effective is it? Muscle spasm or muscle cramp refers to a condition in which muscles are involuntarily cramped and have intermittent and unwanted tension. This condition can be temporary or chronic and can occur in any part of the body. The causes of muscle spasm can include physical, nervous, chronic, stress and psychological factors.
What are degenerative diseases? Physiotherapy of degenerative diseases
Study time: 13 minutes What are degenerative diseases and how is the physiotherapy of degenerative diseases? Degenerative diseases of the nervous system are a group of neurological disorders that cause changes in the body caused by the gradual destruction of nerve cells. These diseases weaken and damage the nervous function and may gradually have a wide impact on memory, movement, alertness and other nervous functions of people.
What is hydrotherapy? What are the benefits?
Study time: 4 minutes Hydrotherapy or in English (Hydrotherapy) is a set of physical therapy movements, exercises and techniques that are performed in water to reduce the patient's pain, strengthen muscles, and increase the intensity of blood circulation. Water therapy includes exercises that are performed in a water pool with a temperature between 33 and 36 degrees. Hydrotherapy focuses more on slow and continuous movements.
Foot Physiotherapy - 6 Multiple Injuries and Treatment Methods
Study time: 5 minutes. Feet and its different areas are among the parts of the body that are very vulnerable to injury. For this reason, many people are looking for the best way to treat various foot injuries. Next, we will talk more about foot physiotherapy...




















