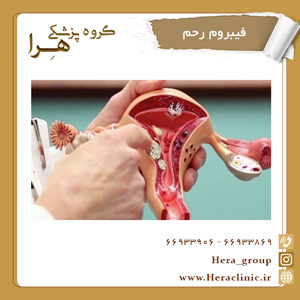
Uterine fibroid
Uterine fibroid is the growth of non-cancerous masses of the uterus that often appear during the reproductive years. Uterine fibroids are not associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer and almost never develop into cancer.
Fibroids range in size from very small lumps that cannot be seen by the eye to large lumps that can distort and enlarge the uterus. You can have one uterine fibroid or multiple lumps. In severe cases, multiple fibroids can enlarge the uterus so much.
Many women will have uterine fibroids at some point in their lives. But maybe you don't know about their existence. Because most of them do not cause symptoms. A doctor may accidentally see a fibroid during a pelvic exam or ultrasound.
Uterine fibroid symptoms
Many women with fibroids have no symptoms. When present, symptoms can be influenced by the location, size, and number of fibroids.
In women who have symptoms, the most common signs and symptoms of uterine fibroids are:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Menstrual periods last more than a week
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Urine frequency
- Difficulty emptying the bladder
- Constipation
- Back pain or leg pain
When to see a doctor Do it?
See a doctor if you have the following problems:
pelvic pain that does not go away
- very heavy, long and painful periods
- spotting or bleeding between periods
- Difficulty emptying your bladder
- Severe anemia
Seek emergency care if you have heavy vaginal bleeding or sudden severe pelvic pain.
Causes of problems with uterine fibroids
Doctors do not know the cause of uterine fibroids, but research and clinical experience They point to these factors:
Genetic changes Many fibroids contain changes in genes that are different from normal uterine muscle cells.
The hormones estrogen and progesterone, two hormones that stimulate the growth of the uterine lining during each menstrual cycle in preparation for pregnancy, appear to promote the growth of fibroids.
Fibroids contain more estrogen and progesterone receptors than normal uterine muscle cells. Due to the decrease in hormone production, fibroids shrink after menopause.
Other growth factors. Substances that help the body maintain tissues, such as growth factors such as insulin, may affect fibroid growth.
Doctors believe that uterine fibroids develop from a stem cell in the smooth muscle tissue of the uterus (myometrium). A single cell divides repeatedly, eventually forming a lump of firm rubber distinct from the surrounding tissue.
Uterine fibroids have different growth patterns – they may grow slowly or quickly, or they may stay the same size. Some fibroids are located in growth cavities, and some may shrink on their own.
Many fibroids present during pregnancy will shrink or disappear after pregnancy, as the uterus returns to its normal size.
Risk factors uterine fibroids
There are known risk factors for uterine fibroids, apart from That the woman is of reproductive age. Factors that can affect the development of fibroids include:
- Heredity If your mother or sister had fibroids, you are at risk of developing them.
- Other factors. Starting menstruation at a young age
- Obesity
- Vitamin D deficiency
- A diet with more red meat and less green vegetables, fruits and dairy products.
- Drinking alcohol, including beer
- Increases the risk of fibroids
Complications of uterine fibroids
Although uterine fibroids are usually not dangerous, they can cause discomfort and complications such as a drop in red blood cells (anemia) that causes fatigue, heavy blood loss. Rarely, a blood transfusion is required due to blood loss.
Hera medical group includes:
Surgeon and specialist in obstetrics and gynecology for the treatment of various gynecological diseases, gynecological cosmetic surgery including vaginal tightening, vaginal whitening, etc., all kinds of delivery methods such as Cesarean delivery, natural childbirth and ...
Nutritionist for Role of nutrition before marriage, The importance of nutrition in women's beauty, The role of nutrition in determining gender and...
Breast surgery fellowship is for performing many things such as breast cosmetic surgery, breast cancer treatment, abdominal cosmetic surgery, general surgeries, etc.
ways of communication with Hera Medical Group
Contact number: 66933906
Pregnancy and uterine fibroids
This problem usually does not interfere with pregnancy. However, it is possible that fibroids can cause infertility or make pregnancy less likely.
Fibroids may also increase the risk of some pregnancy complications, such as placental abruption, fetal growth restriction, and premature birth.
Uterine fibroid prevention
Although researchers continue to investigate the causes of fibroid tumors, the evidence Little science is available on how to prevent them. It may not be possible to prevent uterine fibroids, but only a small percentage of these tumors require treatment.
However, by making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a normal weight and eating fruits and vegetables, you can reduce the risk of developing fibroids.
Some research also suggests that the use of hormonal contraceptives may be associated with a lower risk of fibroids.
Other contents
causes of infertility in women