Table of contents
Listen to the summary of this article in this podcast
Anemia in women is one of the most common health problems worldwide that can affect their quality of life, productivity and even general health. This problem is especially important during reproductive age, pregnancy and menopause due to hormonal changes and specific nutritional needs. A decrease in the number of red blood cells or a decrease in hemoglobin in the blood leads to a decrease in oxygen delivery to tissues and organs. Women are at a higher risk than men due to menstruation, pregnancy and the need for more iron. A complete understanding of the symptoms, causes, methods of diagnosis, treatment and prevention of anemia can play an important role in improving the general health of women. In this article, we are going to do a comprehensive review of this issue from your doctor.
What is anemia in women?
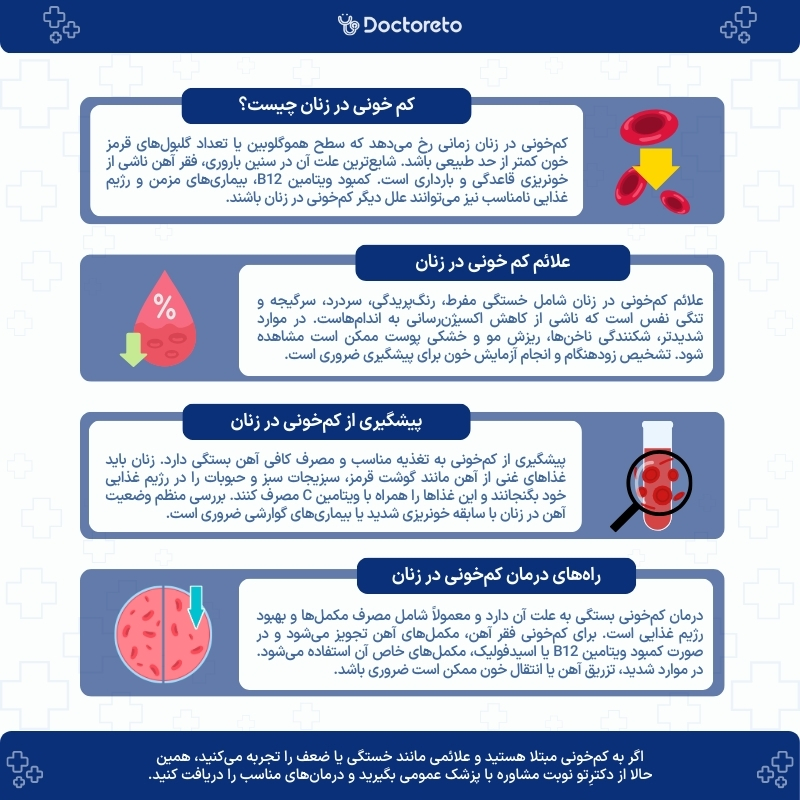
Anemia in women is a condition in which the level of hemoglobin, the number of red blood cells, or the blood's oxygen-carrying capacity is lower than normal, and it has several causes, each of which must be carefully diagnosed. The most common type of this disease, anemia in women of reproductive age is usually due to iron deficiency caused by menstrual bleeding and pregnancy, but other causes such as vitamin B12 deficiency, chronic diseases and absorption problems are also important.
Inappropriate diet, especially in vegetarians, can also be another effective factor in anemia in women. This disease is treatable if diagnosed early, but if ignored, it can lead to muscle weakness, decreased concentration and impaired immune system. Determining which of the types of anemia is the cause of the disease is important for proper treatment.
1. Anemia in postmenopausal women
Anemia in menopausal women is usually less related to menstrual bleeding and more related to problems such as gastrointestinal diseases, improper nutrition, poor absorption of nutrients, reduced absorption of iron and vitamin B12, hidden stomach bleeding, or the use of certain medications. Accurate diagnosis and treatment under the supervision of a doctor, including blood tests and colonoscopy, may be necessary to manage this type of anemia. If a postmenopausal woman suffers from iron deficiency anemia, the standard of care is that, in addition to iron treatment, the cause of iron deficiency should also be taken seriously.

2. Anemia in pregnant women
Pregnant women are more susceptible to anemia due to the increased need for iron in the body and the growth of the fetus, especially Anemia in pregnancy severe and untreated can increase the risk of premature birth, low birth weight and maternal immune problems. Proper nutrition, taking iron supplements and following up with regular tests are essential. Also, lack of folic acid or vitamin B12, especially in women with limited diet, can cause anemia. Timely treatment and careful care play an important role in preventing complications.
symptoms of anemia in women
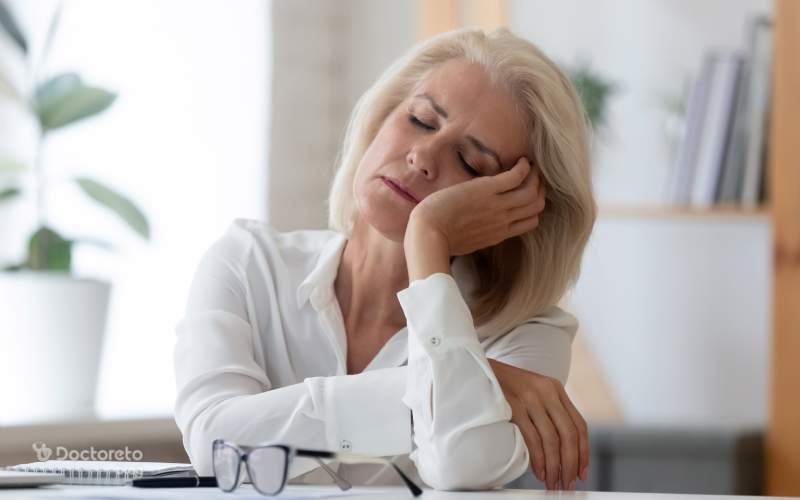
The symptoms of anemia in women may vary depending on the type and severity of the disease, but some symptoms are common in most cases. The most important of them are extreme fatigue, pale skin, headache, dizziness and shortness of breath. These symptoms of severe anemia in women are caused by a decrease in oxygen supply to the organs and may interfere with daily activities. Also, fast heart rate, feeling cold, decreased concentration and irritability are also observed in some affected women.
In more severe or chronic cases, the symptoms of anemia in women include changes such as brittle nails, hair loss, dry skin and cracked lips. Sometimes anemia progresses gradually and a person without knowing it, copes with mild symptoms until the disease reaches a more advanced stage. For this reason, awareness of these symptoms and regular blood tests are essential for early diagnosis and prevention of complications. The most common symptoms of anemia in women are:
- Abnormal fatigue and reduced activity power
- Pale color of the skin or mucous membrane inside the eyelid
- Rapid heart beat
- Dizziness and anemia with black eyes Shortness of breath with activity
- Cold hands and feet
- Nail brittleness, dry skin or hair loss anemia
- Headache or loss of concentration
1. Symptoms of anemia in menopausal women
In menopausal women, anemia is usually associated with weakness, restless sleep, shortness of breath and cold hands and feet. Changes in memory, concentration or mood can also be seen. Heart palpitations, numbness of limbs and fainting are other common symptoms. Many of these symptoms may be confused with normal menopause symptoms. If you notice unexplained weight loss, dark stools or loss of appetite, you should see a doctor immediately. Because anemia at this age may be a sign of diseases such as digestive cancer.
2. Symptoms of anemia in middle-aged women
In middle-aged women, anemia often manifests itself with fatigue, lethargy, decreased energy, and sleepiness, and one may feel that one is not as energetic as before. If the periods are heavy or long, dizziness and heart palpitations become more common on menstrual days, and even exercising or climbing the stairs feels more difficult than before. Some people also experience symptoms such as headache, loss of concentration or restless legs at night, which can coincide with iron deficiency. These symptoms are not specific and are helpful for diagnosis, CBC test and checking iron stores.
3. Symptoms of anemia in adolescent girls
Symptoms of anemia in teenage girls can be manifested by paleness, tiredness at school, sleepiness, loss of concentration and reduced performance in sports. The onset of menstruation, rapid growth and sometimes irregular feeding increase the risk of iron deficiency, especially if the intake of iron sources is low or there are restrictive diets. Some teenagers report cravings for ice or non-food items, which can be a sign of iron deficiency. If the parents have noticed the loss of energy and paleness, it is better to check the blood test and nutritional assessment to make the treatment targeted.
4. Symptoms of severe anemia in women
Severe anemia in women is usually associated with more pronounced symptoms, such as shortness of breath even with little activity, rapid heartbeat, noticeable dizziness and obvious weakness. In some cases, a person may have black eyes or feel close to fainting when standing up suddenly. If severe anemia is due to bleeding, there may be symptoms of bleeding such as dark stools or heavy menstrual bleeding, and this situation requires immediate action.
symptoms of severe anemia in girls
In teenage girls, severe anemia can be accompanied by obvious lethargy, loss of power in daily activities, heart palpitations, dizziness, and sometimes shortness of breath, and the family may think it is just general weakness or low blood pressure. If there is heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, the symptoms will intensify in the same days and the possibility of iron deficiency increases. Because growth is still ongoing during adolescence, severe anemia can seriously affect quality of life and concentration in school. In this situation, it is better to perform a medical evaluation and blood test quickly, and the treatment should not be arbitrarily postponed.
5. Symptoms of minor anemia in women
Anemia or thalassemia minor in women usually causes mild and stable anemia that may remain asymptomatic for years. Some people just have a little fatigue or paleness and it shows up on a CBC with a low MCV, but it's important not to confuse thalassemia minor with iron deficiency. In thalassemia minor, iron intake is useful only when there is a real iron deficiency, and this should be determined by ferritin and additional investigations. If you have a family history of anemia or consanguineous marriage, you should check more carefully.

6. Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia in women
Anemia caused by iron deficiency in women usually starts with fatigue, paleness, weakness, heart palpitations and reduced activity tolerance, and may also lead to brittle nails, dry skin or hair loss. Some people experience cravings for ice or non-food items, which can be an important sign of iron deficiency. If there is heavy menstrual bleeding, the symptoms worsen during menstruation and the person feels that their energy drops rapidly.
cause of anemia in women
Anemia in women is often due to iron deficiency caused by menstruation and poor nutrition. Heavy menstrual bleeding and consecutive pregnancies are also among the most important causes of anemia in women. A vegetarian or unbalanced diet and diseases such as stomach ulcers or celiac disease interfere with iron absorption. Drinking too much tea or coffee can also reduce iron absorption. Some chronic diseases such as kidney failure and cancers play a role in causing anemia. Anemia is sometimes genetic in origin, such as thalassemia. Accurate investigation of the cause of anemia is essential for effective treatment. In summary, some of the most important causes of anemia in women are:
-
Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding and irregular bleeding
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding and increasing the body's need for iron and folate
- Iron deficiency due to insufficient intake or insufficient absorption
- Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency
- Hidden gastrointestinal bleeding such as ulcers or polyps
- Chronic diseases such as kidney disease or prolonged inflammation Hereditary anemias such as thalassemia minor or sickle cell
cause of severe anemia in women
Severe anemia in women usually occurs due to heavy menstrual bleeding or uterine problems, such as fibroids, which cause severe depletion of iron stores. Sometimes hidden bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, especially in the elderly or aspirin users, is the cause of severe anemia in women. Autoimmune diseases, chronic infections and bone marrow failure can also cause a severe drop in red blood cells. Malnutrition or strict and incorrect diets are also other factors. For accurate diagnosis, complete blood tests are required.
| Causes of anemia in women | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Severe or prolonged menstrual bleeding and irregular bleeding | One of the most important causes of anemia in women; can reduce iron stores |
| Pregnancy and lactation | Increase the body's need for iron and folate |
| Iron deficiency due to inadequate intake or inadequate absorption | Unbalanced/plant-based diet; Diseases such as peptic ulcer or celiac disease impair iron absorption |
| vitamin B12 or folate deficiency | important causes of anemia (especially in restricted diets) |
| hidden gastrointestinal bleeding | such as ulcers or polyps |
| chronic diseases | such as Chronic kidney or inflammation |
| Hereditary anemias | such as thalassemia minor or sickle cell |
| High consumption of tea or coffee | Can reduce iron absorption |
| Cancers | contribute to anemia |
cause of anemia in menopausal women
Anemia in menopausal women is often caused by hidden gastrointestinal bleeding, chronic diseases, insufficient absorption of nutrients, and the use of certain medications. Deficiency of iron and vitamins is also common at this age. Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs can increase the risk of internal bleeding. Also, chronic diseases such as kidney failure may decrease red blood cell production. Due to the greater possibility of underlying diseases, treatment at this age requires more comprehensive and detailed investigations.
cause of anemia in elderly women
In elderly women, anemia can have several reasons, and sometimes a combination of iron deficiency, B12 deficiency, kidney disease and chronic inflammation is seen. Some elderly people reduce their intake of iron and vitamins due to decreased appetite or dietary restrictions, and others have decreased absorption due to medications or digestive problems. Also, chronic diseases are more common at this age and can cause anemia of the chronic disease type in which the body does not use iron in an optimal way. Because anemia in the elderly can be a sign of a hidden problem, a systematic and step-by-step examination is very important.
Ways to diagnose anemia in women
Diagnosing anemia in the anemia test begins with a CBC test, which checks the amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells. If anemia is confirmed, ferritin, vitamin B12 and folic acid levels are also measured. In some cases, a stool test, endoscopy, or colonoscopy is done to find the source of internal bleeding. Reviewing medical history and diet is also important. Also, if necessary, the doctor may prescribe tests such as hemoglobin electrophoresis to diagnose hereditary anemia.
Ways to treat anemia in women
Treatment of anemia depends on the cause, but usually involves taking supplements and improving diet. The most common treatment method is to use iron supplements for iron deficiency anemia. If there is a deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid, specific supplements are prescribed. If there is an underlying disease, its treatment is also necessary. Also, food containing iron such as red meat, lentils, spinach and eggs is effective in recovery. In more severe cases, iron injection or even blood transfusion may be necessary.
In pregnant women, anemia treatment should be more accurate and timed, because the body's needs are higher and the goal is to make the mother healthier and reduce the risks of anemia in pregnancy. Gynecology and obstetrics specialist guidelines usually consider oral iron as the first line treatment for iron deficiency anemia in pregnancy and suggest injectable iron for cases of intolerance, lack of response or severe deficiency in late pregnancy. In special cases, such as severe anemia with symptoms or bleeding, a more urgent treatment decision may be necessary, and this part must be done with the doctor's opinion.
quick treatment of anemia in women
To quickly treat anemia, if the cause is iron deficiency and it is not an emergency, starting with oral iron and correcting nutrition, hemoglobin will gradually increase, and it usually takes a few weeks for measurable changes to be seen. But if you're severely anemic, have severe symptoms, or have a low tolerance for oral iron, your doctor may turn to faster options like injectable iron. More important than the speed is the right course of treatment, because the wrong treatment may only take away the chance of treatment.
Treatment of severe anemia in women
If severe anemia is caused by bleeding, controlling the source of bleeding is a priority and sometimes more urgent treatments are needed. In severe iron deficiency anemia, oral iron may not be enough or have a long-lasting effect, and in some cases, injectable iron or taking pills for severe anemia in women is suggested by the doctor's opinion. If you have danger symptoms such as shortness of breath at rest, fainting or chest pain, you should be evaluated quickly.

treatment of anemia in menopausal women
If iron deficiency is confirmed in postmenopausal women, treatment with iron tablets is done, but at the same time, the cause of iron deficiency must be determined, because at this age the possibility of hidden gastrointestinal bleeding is more prominent. Also, anemia may be related to chronic disease or B12 deficiency, which has different treatment. So the best way is to carry out the treatment at the same time as a complete examination so that the anemia does not repeat and the main cause is not lost.
best medicine for anemia in women
For the treatment of anemia in women, iron supplements such as ferrous sulfate, fumarate or iron gluconate are usually prescribed, which are better taken together with vitamin C for better absorption. In some cases, supplements containing iron, vitamin B12 and folic acid are also used. If the person does not respond to gynecological anemia medication, the doctor may order intravenous iron. In patients with kidney failure, drugs are prescribed to stimulate the production of red blood cells. The use of pills for anemia in women should be under the supervision of a doctor and with regular follow-up of tests.
complications of anemia in women
Untreated anemia can cause chronic fatigue, decrease concentration, and interfere with daily activities and affect heart function. In pregnant women, this problem increases risks such as premature birth and low birth weight. In old age, anemia can cause general weakness and risk of falling. complications of severe anemia in women starts with a decrease in the quality of life and can lead to more serious problems such as heart palpitations, shortness of breath and loss of activity. In pregnancy, untreated anemia can increase the risk of some adverse outcomes, and for this reason, timely screening and treatment are important.
English text:
who
In severe cases, anemia can cause poor cognitive and motor development in children. It can also cause problems for pregnant women and their babies. Text translation: In severe cases, anemia can cause problems in the mental and motor development of children. It may also cause problems for pregnant women and their babies.
prevention of anemia in women
Prevention of anemia depends on a balanced diet and adequate intake of iron. Eating iron-rich foods, such as red meat, green vegetables, and legumes, should be included in the daily diet of people with anemia. For better absorption of iron, it is recommended to consume these foods together with sources of vitamin C such as citrus fruits. Also, pregnant and lactating women should take appropriate supplements under the supervision of a doctor. Reducing the consumption of tea and coffee with meals can also help increase iron absorption.
In women with a history of heavy menstrual bleeding or gastrointestinal diseases, it is very important to check the iron status regularly. Also, being aware of the symptoms of anemia and seeing a doctor in the early stages of the disease prevents the development of problems and helps in more effective treatment. Monitoring blood status regularly can prevent serious problems caused by anemia.
Conclusion
Anemia in women is a common but preventable and treatable problem that requires attention to symptoms, proper nutrition and regular medical examinations. Women should monitor their iron status at every stage of life. In postmenopausal and elderly women, anemia, especially iron deficiency, should be investigated more seriously so that important causes such as hidden bleeding are not missed. Symptoms such as fatigue, paleness or shortness of breath should be seen by a doctor and a CBC test should be performed. Early diagnosis enables rapid treatment and prevention of serious complications. Regular follow-up and modification of lifestyle is necessary to maintain blood health and energy.
Your doctor takes care of your health!