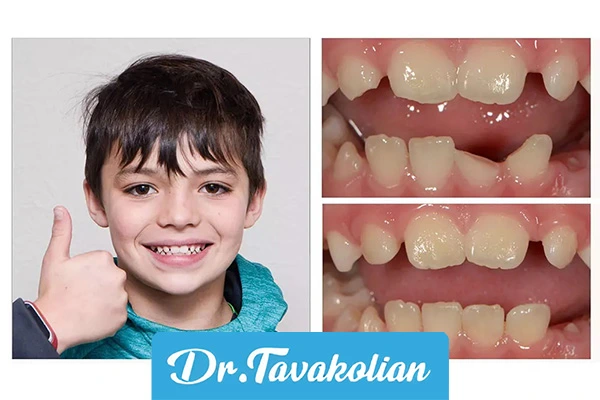
Children's baby teeth trauma is one of the most common incidents between the ages of 1 and 6 years, which often occurs by falling, playing, or having an accident. A blow to a baby tooth can cause a tooth to break, loosen or even fall out, and if not treated quickly, it can lead to permanent problems such as malocclusion or infection. Based on AAPD Guidelines and NIDCR 2025, milk tooth trauma is seen in 30% of preschool children and immediate parental action can save the tooth up to 85%. This article is for mothers who have faced broken baby teeth or lost baby teeth and are looking for practical solutions. class="ez-toc-title ">What you will read in this article:
Trauma of children's milk teeth - Dr. Tavaklian

Dr. Elham Tavaklian
تهرانPediatric dental specialist
Trauma of children's milk teeth
Milk tooth trauma is called injuries caused by trauma, and its types include:
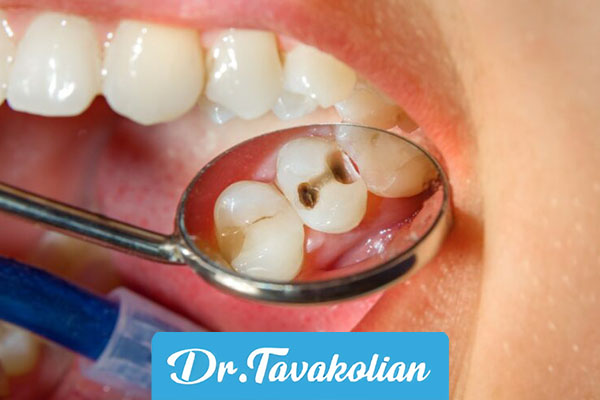
- Enamel fracture: small crack or chip without pain.
- Deep fracture: reaching the dentin or pulp with tenderness or bleeding.
- Looseness (Luxation): tooth loose but still in place.
- Displacement (intrusion/extrusion): tooth pushed in or out.
- Complete falling out (avulsion): tooth completely out of place.
Warning signs of baby tooth impaction include pain, bleeding, discoloration (blackening or graying), and swelling. It is gum. AAPD emphasizes that in 50% of cases, permanent tooth bud damage also occurs.
Baby Teeth: Immediate Actions at Home
When a baby tooth strikes, keeping the mother calm is key. Immediate actions:
- Oral examination: control the bleeding with clean gauze.
- Loose tooth: If the child's tooth is fallen out, pick it up by the crown (not the root), keep it in milk or physiological serum and get to the dentist within 1 hour.
- Loose tooth: prevent the child from chewing and give soft food.
- Teeth Broken: Keep broken piece in milk if found.
- Cooling: Cold compress on face to reduce swelling.

. Acting in 30 minutes increases chances of saving teeth by 90% NIDCR reports

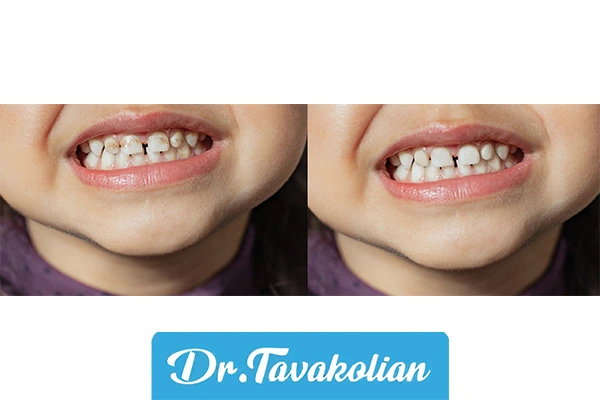
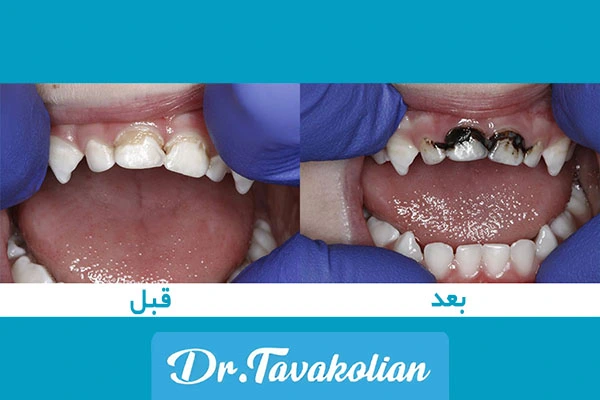
Broken baby tooth: possible treatments
Broken baby tooth is treated depending on the depth of the damage:
- Small fracture: edge smoothing or composite.
- Deep fracture: pulpotomy or veneer SSC.
- Fracture with pulp: root canal treatment or extraction.
AAPD recommends that a fractured baby tooth should always be saved except in severe cases, as premature loss will compromise permanent tooth space.

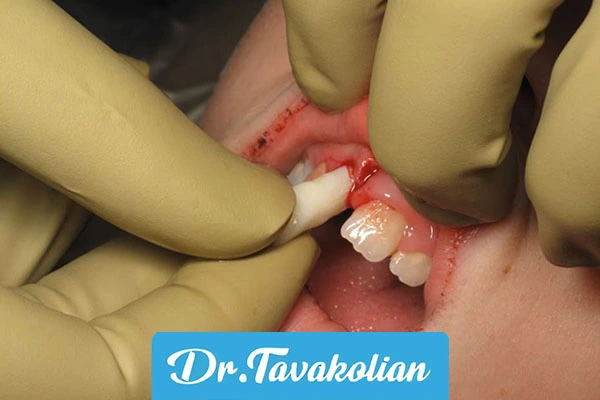
A fallen baby tooth (complete avulsion) in a baby tooth is usually not replanted, as it may damage the permanent bud. AAPD protocol:
- Do not clean the tooth (the root is sensitive).
- Keep in breast milk or saliva.
- See the dentist quickly to install the spacer.
In rare cases, if the root is intact, reimplantation is possible.

Loose baby teeth: care and follow-up
Loose baby teeth often fix spontaneously after an impact. Care:
- Soft food for 1 week
- Avoidance of high-risk games
- Visit 1 week and 3 months later for radiography
NIDCR shows 80% of cases of loosening heal without complication.

Treatment of pediatric dental trauma include:
- Splint: for displaced teeth, wire fixation for 1-2 weeks.
- SSC: for deep fracture.
- Pulpotomy: if pulp damage
- Space: Always after tooth loss.
AAPD emphasizes that treatment in the first 24 hours improves results by 70%.
- Using a mouth guard in sports
- Supervision in high-risk games
- Teaching "hands over the mouth" when falling down
- Regular visit from 1 year old
Questions Frequent mothers
1. Should I put a fallen child's tooth in water? No, in physiological milk or serum.
2. A blow to a baby tooth destroys the permanent one? In 50%, yes, but it can be controlled with early treatment. class="ez-toc-section-end">
Children's milk tooth trauma is completely manageable with prompt action and specialized treatment. Parents can protect the future of their child's smile by knowing impacted baby teeth, broken baby teeth, fallen baby teeth and loose baby teeth. Consult a pediatric dentist for advice.