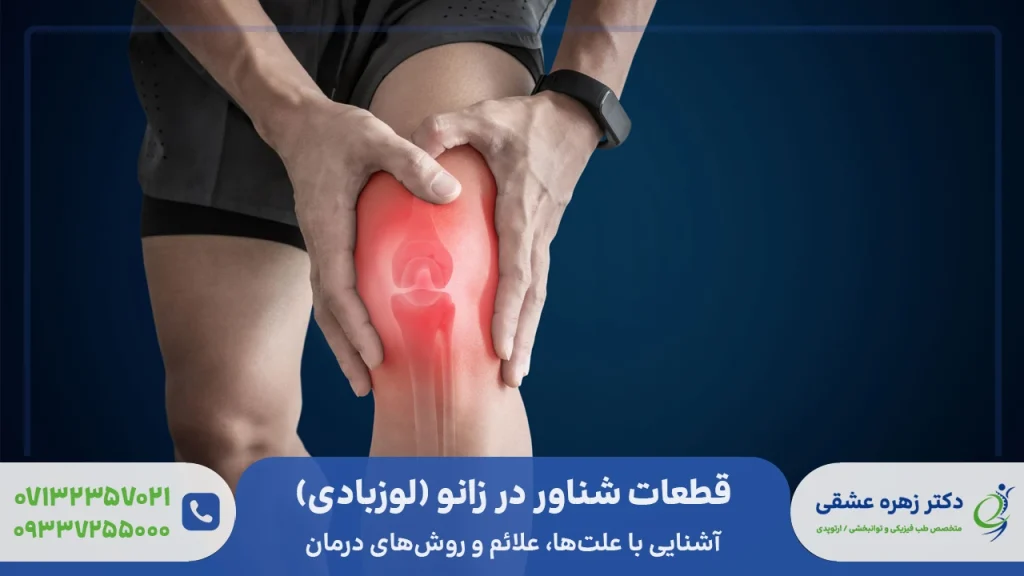
آیا تا به حال اصطلاح لوزبادی (Loose Body) را شنیدهاید؟ If you have this problem or the same floating objects and parts in your knee, you have experienced the following:
- You recently had an X-ray and some floating objects were detected in your knee
- You feel that there is something in your knee and you have searched for any possibilities on Google
- You have pain or problems bending your knee and you do not know whether it is a ligament or No
All of these possibilities are good reasons to find out more about this strange knee problem.
What is a hydrangea?
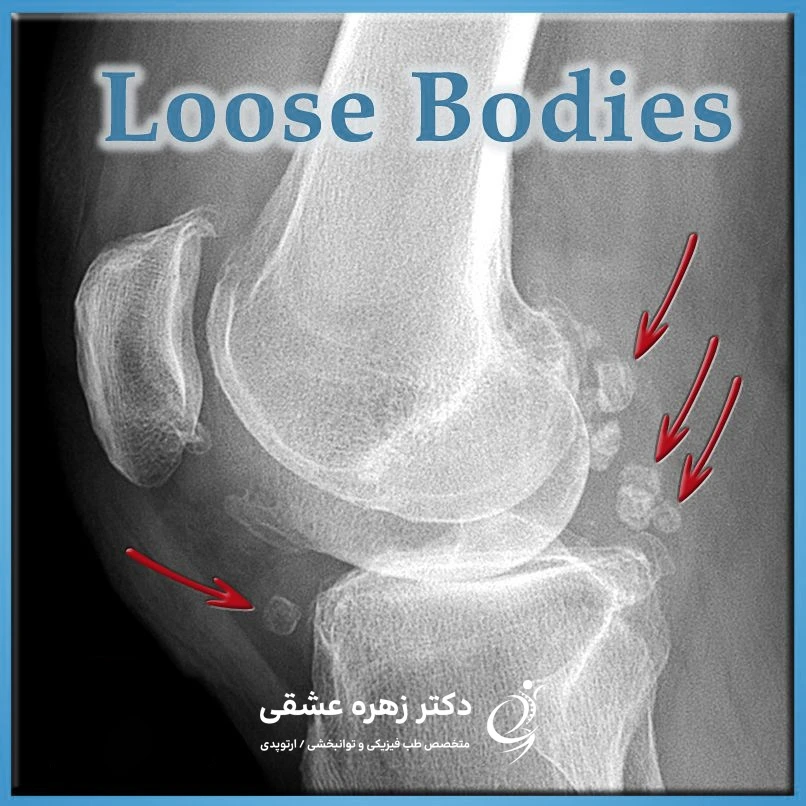
A knee floater is a piece of cartilage or bone that has separated from the joint surface. Sometimes the piece stays in place, loosens, and floats freely in the thick synovial fluid that protects the joint (called unstable synovial fluid).
You may even be able to feel it under the skin!
The cause of floating objects or parts in the knee

Loose body in the knee can be caused by an injury to the knee or wear and tear. The most common cause is trauma such as an accident, fall, twisting the leg during exercise or a tackle. Another possibility is the wear of the cartilage of the joint, which means that the wear has caused the joint to fragment and separate from the bone surface.
Floating bodies in the knee are common in these sports:
- Basketball
- Football
- Rugby
- Volleyball
- Combat sports
Other factors that can lead to formation Lumps in the knee:
Arthritis and joint wear and tear
In people with knee arthritis, the joint surface is destroyed over time. Small pieces of cartilage or bone are separated from the surface and remain in the joint in the form of cartilage.
Osteochondritis Dissecans
It is a disease in which a part of the bone under the cartilage is not well supplied with blood. This area is separated over time and becomes a floating piece.
Injuries to the meniscus
Special tears in the meniscus sometimes lead to the separation of a small part of it and the creation of free parts in the joint.
Previous knee surgeries
After some surgeries such as partial replacement or repairs Cartilage, there is a possibility of remaining or forming small fragments.
Rare tumors or metabolic diseases
In some rare diseases such as synovial chondromatosis, multiple pieces of cartilage are formed in the joint.

What are the symptoms of floating parts in the knee or pelvis?
Signs and symptoms of floating bodies in the knee include:
- Sudden and unpredictable pain in Knee
- Feeling that the joint is stuck when moving
- Locking of the knee due to the part being stuck in the joint
- Swelling and inflammation of the knee due to irritation of joint fluid
- Feeling of a foreign body in the joint
- Decreased range of motion
- Hearing a grinding sound when moving the knee or a clicking sound
What is the size of a lobe?
Floating bodies can be microscopic and tiny, but their average size is about 5 to 10 mm. With the growth of new cells on the surface of the fragment or its calcification and ossification, its dimensions become larger. Doctors often compare this process to the shape of a pearl in an oyster. A lump can grow significantly, even to the size of a golf ball.
How serious is a lumpy knee usually?
As long as it doesn't start causing irritating symptoms, it doesn't cause a problem.
The most obvious symptom is pain, swelling and inflammation. If these parts move into the joint, they can cause mechanical problems such as locking or jamming of the knee. It means that you cannot shake, bend or stretch it. Sometimes it becomes difficult to walk.
What should be done to fix this problem?
The first important step is to check exactly what happened in the knee. A floating body on an X-ray doesn't necessarily tell the whole story.
A floating object may be a sign of deeper damage and needs further investigation, such as cartilage damage or arthritis.
When should floating parts be removed?

Additional and floating parts do not always need to be removed. Some of them are easily fixed without any symptoms, but if they grow and cause problems, surgery is probably recommended.
In this procedure, two very small incisions are made on both sides of the knee, and then the doctor places a small camera in the incision to see what is going on inside.
After examining and finding the part or parts, they will be carefully removed from their place with the device. This operation is performed under general anesthesia and takes about 30 minutes.
Usually the recovery period is 2 to 4 weeks. Removing the cartilage from the knee is simple and in most cases, the problem is solved.
Sometimes a piece of bone or cartilage belonging to a structure in the knee can loosen or separate from its natural place, which is called cartilage.
If these bodies are floating around the knee joint, they are called unstable cartilage. Lumbars have different sizes and inhibit the normal movement of the knee. As a result, the knee joint is locked.
When to see a doctor
If you have experienced symptoms of arthritis in the knee, such as swelling or locking, see an orthopedic specialist.
During the visit, the doctor will ask you to describe the symptoms and then examine the knee for pain and swelling. For a better diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe the following tests:
- X-ray to detect a loose piece of bone in the knee
- MRI to detect a loose piece of cartilage in the knee

Non-surgical treatments of floating parts in the knee or lozenge
These methods are mostly for Mild cases or when the symptoms are not severe are used:
- Rest and reduce pressure on the knee
- Anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers (such as ibuprofen)
- Physiotherapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve movement
- Intra-articular injection (such as coronet or hyaluronic acid gel) to reduce inflammation and pain
- Using a brace or knee brace Supportive
⚠️ Note: Non-surgical treatment usually does not remove the mucus, but helps control symptoms.
Surgical and invasive treatment
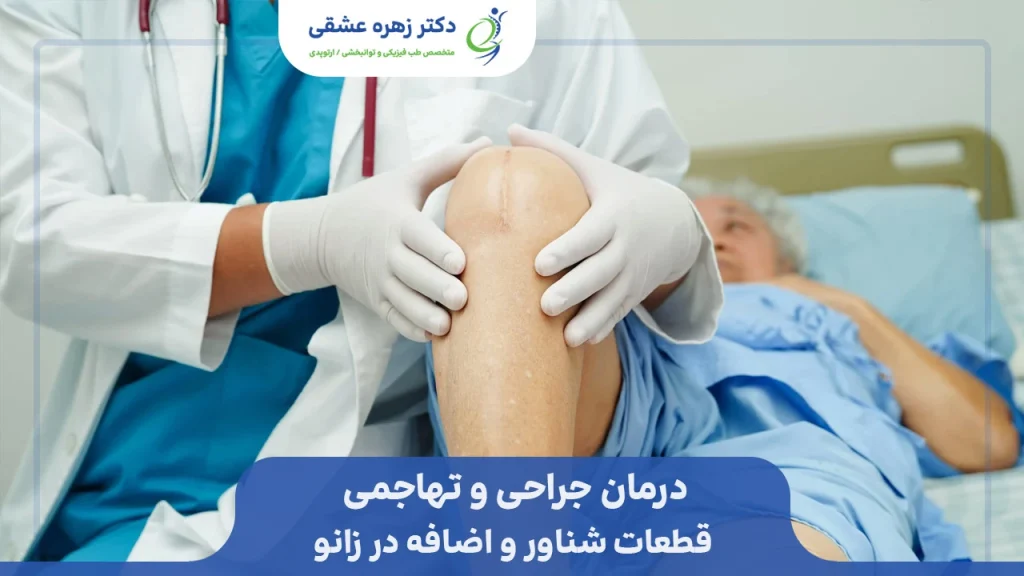
If loose body causes symptoms, it should be surgically removed. In this case, the floating piece in the knee will be removed with arthroscopic surgery as the most common surgical method and treatment of this condition.
Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical method in which the doctor uses several small incisions approximately one centimeter long.
Through this incision, a special camera connected to a thin and flexible tube called an arthroscope is inserted. This camera allows the surgeon to find the soft tissue.

recovery period after surgery
Recovery after hysterectomy usually takes 2 to 4 weeks. Once you regain full range of motion and strength without pain, you will return to normal life. Follow all post-surgery instructions given by your doctor.
Answers to frequently asked questions
No. Unlike inflammation or swelling that may resolve with medical treatment, floating fragments usually remain in the joint permanently. Only if the piece is very small, it may remain asymptomatic.
No. If the fragment is small and does not cause severe symptoms such as frequent locking or severe pain, symptoms can be controlled with conservative treatments such as physical therapy and medication. class="schema-faq-answer">In the early stages, no. But if Lusbody is left without treatment for a long time, it can cause damage to the joint surface and the development of arthritis, which in the long term causes movement restrictions and even the need for joint replacement. Conclusion
Floating parts in the knee or glomerulus are one of the most common joint problems that can cause symptoms such as pain, locking, and limited range of motion. This problem usually occurs due to sports injuries, arthritis, or joint diseases. Accurate diagnosis is possible through examination and imaging, and depending on the severity of the problem, treatment can include medication, physical therapy, and in many cases, knee arthroscopy. Paying attention to symptoms and seeing a doctor quickly can prevent more serious complications such as joint surface destruction and advanced arthritis. Also, by following the correct principles in sports and daily life, this problem can be prevented to a large extent.