Laser therapy - Dr. Morteza Tabatabai

Dr. Seyed Morteza Tabatabai
تهرانPhysical medicine and rehabilitation specialist
laser therapy
Laser therapy is a non-invasive method that helps to restore cells, reduce inflammation and pain, and accelerate healing by shining low-power or infrared laser light on tissues. This painless and safe method is used in physiotherapy and rehabilitation to treat muscle and joint problems, sports injuries and speed up the repair of damaged tissues.
What is laser therapy?
Laser therapy (LLLT) is the use of low-power laser light or infrared/red light to help repair tissue, reduce inflammation and pain, and accelerate healing in the body.
Unlike surgical lasers that work with heat or cutting, laser therapy creates chemical reactions in cells (not destruction) by shining low power light into tissues.
Light is absorbed by parts of the cell such as mitochondria, increasing energy production (ATP), activating cell signaling pathways and tissue repair (source).
This method can be used to treat various problems - from wounds and burns to inflammation, muscle and joint pain; It's also often painless and non-invasive, which is why it's used in physical therapy, rehabilitation, and even skin care (source).
In recent years, several meta-analyses have shown that laser treatment can be significantly effective in reducing pain and improving some musculoskeletal disorders. For example, in a study involving 556 patients with "myofascial neck pain syndrome", it was found that those who received laser therapy experienced more improvement (source).
The history of laser therapy and its entry into physiotherapy
Laser therapy gradually entered the medical field after the invention of the first laser in 1960 by "Theodore Maiman", and in the 1960s and 1970s, early studies showed that low-power laser light can increase the speed of tissue repair and wound healing.
These findings laid the foundation for the development of low-power laser therapy (LLLT); A method that was first used in the treatment of wounds and superficial pains, but from the 1980s onwards, it was widely used in physiotherapy and rehabilitation.
During this period, the use of laser therapy in reducing skeletal-muscular pain, inflammation, sports injuries and stimulation of tissue repair was considered, and numerous researches confirmed its cellular and clinical effects.
Today, laser therapy is one of the established and accepted technologies in modern physiotherapy and is used in clinics around the world as a safe, non-invasive and effective method to treat a wide range of muscle-joint problems.
How does laser therapy work?
laser therapy works based on the effect of focused light on body cells; Light that enters tissue with a specific wavelength and stimulates biological processes.
Laser therapy is based on the absorption of light photons by cells, increasing energy at the cellular level and activating repair mechanisms and reducing inflammation. This process makes the process of healing damaged tissues faster and more effective.
main mechanisms of laser therapy
When laser light with the right wavelength and power is irradiated to the skin and the underlying tissues, the photons of light enter the tissue and are absorbed by the cells (source).
cellular stimulation and energy production
Laser light is absorbed by intracellular organelles — especially mitochondria; This absorption leads to an increase in the production of energy (ATP) in the cells. This extra energy helps the cells perform their normal functions better: tissue repair, protein production, cell renewal and damaged tissue regeneration (source).
reducing inflammation and improving blood flow
Laser helps reduce inflammation in the affected area; By reducing inflammatory substances and signaling and increasing tissue repair, swelling and pain are reduced. Laser light also improves blood flow and increases oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, which speeds up the healing process (source).
pain reduction and healing stimulation
The result of light absorption and cellular changes include reducing pain, faster tissue repair, reducing swelling and restoring normal tissue function. Because laser therapy is non-surgical and non-invasive, this process is associated with minimal risk and pain for the patient (source).
types of laser therapy
Laser therapy in physical therapy is not just a single method — it can be done with different types of lasers and based on different light intensities. Choosing the type of laser depends on the treatment needs. In the following, we mention the most important types of laser therapy and the applications of each.
low power laser
Low-level laser therapy is one of the most common types of laser therapy in physiotherapy and is usually known as cold laser or soft laser.
This type of laser works with a power below 500 milliwatts and its light enters the surface layers of the skin and soft tissues without generating heat.
The low-power laser accelerates the tissue repair process by stimulating cells, increasing energy production (ATP), reducing inflammation and improving blood circulation.
This method is used to treat muscle pain, inflammation of tendons, superficial injuries, wounds and chronic problems of mild to moderate severity.
Because it is non-invasive and painless, low-power laser (LLLT) is one of the safest and most widely used methods in physiotherapy clinics (source).
high power laser
High-Power Laser Therapy works with a power higher than 500 milliwatts and is designed to penetrate deep tissues.
This method can penetrate deep layers such as thick muscles, tendons and even joint structures; For this reason, it is suitable for the treatment of severe pain, deep injuries, sports injuries, chronic pain and recovery after surgery.
The high-powered laser may generate some heat, which increases blood circulation, reduces inflammation, improves oxygenation, and accelerates tissue repair. High Power Laser (HPLT) is a more powerful and targeted method and is usually used for more severe conditions that require a deeper therapeutic intervention.
What is a low power laser?
Low-power laser (LLLT) is a form of light therapy in which low-intensity light (usually red or near-infrared light, with a wavelength of about 600 to 1,000 nm) is shone into body tissue to stimulate natural cellular repair processes without causing heat or damage (source).
In this process, light photons are absorbed by structures inside the cell (especially mitochondria); Light absorption increases cellular energy production (ATP), activates signaling pathways, improves blood flow and reduces inflammation (source).
In other words, low-power laser (LLLT) helps reduce pain, reduce inflammation, and repair damaged tissue faster by stimulating cell metabolism and tissue repair — without burning or destroying the tissue (source).
What is a high power laser?
High-power laser (HPLT) is a type of laser therapy that uses high-power lasers instead of weak and superficial light so that the light energy penetrates into the deeper tissues of the body (muscles, tendons, joints and deep structures).
Several studies have shown that high-power laser can reduce pain and improve performance in musculoskeletal problems.
For example, a systematic review and meta-analysis including 44 studies showed that high-power laser generally reduces pain and improves functionality (source).
This method works by increasing cellular energy production (ATP), improving blood circulation, reducing inflammation and stimulating tissue repair, which ultimately leads to reduced pain, reduced swelling, faster recovery and better return to function (source).
In some clinical studies, the use of high-power laser (HPLT) for muscle trigger points (such as trapezius muscle involvement) has had significant results in reducing pain (source).
The difference between low power laser and high power laser
Low-power laser (LLLT) and high-power laser (HPLT/HILT) are both used in physiotherapy to reduce pain, reduce inflammation, and repair tissue, but they have important differences in output power, penetration depth, intensity of effect, and clinical application.
Choosing between these two types of laser depends on the type of injury, pain intensity, depth of desired tissue and treatment goal. In the following, we will examine the main differences between these two methods.
light power and intensity
Low-power laser (LLLT) works at low power and its light mainly penetrates superficial tissues, so it is suitable for superficial treatments and mild injuries.
In contrast, high-power laser (HPLT/HILT) has a higher power and is able to transmit light to deeper tissues, thus creating a stronger and wider therapeutic effect.
depth of penetration
The low-power laser is limited to the surface layers of the skin and soft tissues near the surface of the body and is mostly used for superficial pain and inflammation.
But the powerful laser can penetrate deep muscles, joints and thick tendons and is suitable for more severe and chronic injuries.
Generate heat
The low power laser light does not create noticeable heat and the treatment process is completely non-invasive and painless. While the high-power laser may produce some heat, which increases blood circulation and more penetration of light into deep tissues.
Clinical application
Low power laser is used to reduce superficial pain, repair small wounds and mild inflammation and provides a gentle treatment process.
High-powered lasers are used for more serious problems such as chronic pain, severe sports injuries, and post-surgical recovery, and are capable of treating deeper tissues.
speed and intensity of effect
The effect of low power laser is usually slow and gradual and requires several treatment sessions to see the results. High power laser has a faster and more powerful effect and is a more suitable option for conditions that require quick repair or deep treatment.
advantages of laser therapy
Laser therapy, by using focused light and without surgery, is a relatively modern and safe solution to reduce pain, reduce inflammation and accelerate the tissue repair process.
This method can be a good substitute or supplement for drugs and invasive methods. Next, we review the most important benefits of this treatment.
increasing the speed of tissue repair and cell regeneration
Laser therapy accelerates the tissue repair process by stimulating energy production at the cellular level. This helps to regenerate damaged tissues such as muscle, tendon or soft tissue faster and shortens the healing process (source).
reducing inflammation, swelling and pain
One of the biggest benefits of laser therapy is the reduction of inflammation in the damaged tissue. This reduction in inflammation results in less swelling and pain, less muscle cramps and spasms, and faster recovery (source).
improving blood circulation and nutrient supply
Laser therapy improves the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the damaged tissue by stimulating blood vessels and increasing blood flow. This better blood circulation allows proper nutrition of the cells and removal of waste materials and provides conditions for faster healing (source).
Non-invasive, drug-free and with minimal side effects
Unlike surgery or drug treatments that may have side effects and require a recovery period, laser therapy is a non-invasive method. Also, unlike many pain relievers and drugs, it has no risk of addiction or systemic side effects (source).
Improve movement, flexibility and joint/tissue function
Many who have laser therapy report reduced stiffness, improved joint range of motion, reduced muscle stiffness, and an easier return to daily activities after just a few sessions. This is a huge bonus for those who are injured or have chronic problems (source).
Applications of laser therapy in physiotherapy and medicine
Laser therapy, as a non-invasive and light-based treatment method, allows to accelerate the healing process by naturally stimulating the cellular and tissue processes of the body, while reducing pain and inflammation.
This flexibility has made laser therapy used in a wide range of musculoskeletal problems, sports injuries, joint problems, wounds, and even neurological problems. In the following, we will examine some of its most important uses.
Treatment of musculoskeletal pain
laser therapy can reduce muscle and joint pain; By shining light on the damaged tissue, cellular energy production is increased, inflammation is reduced, and blood circulation is improved, all of which help reduce pain.
This feature makes laser therapy a suitable option especially for people with chronic pain or pain caused by muscle and joint work (source).
Use of laser therapy in sports injuries
In sports injuries – such as muscle strains, tendon or ligament injuries, sprains and soft tissue tears – laser therapy accelerates the healing process by increasing the rate of tissue repair, increasing blood flow and reducing inflammation (source).
Especially in athletes or people who want to return to activity soon, laser therapy can be very useful as a supplement to rehabilitation.
The use of laser therapy in the treatment of inflammations
Laser light can reduce the inflammatory process by affecting cells and tissues — reducing inflammatory substances, improving blood flow, and increasing fluid (lymphatic/blood) drainage helps reduce swelling and redness.
This feature makes laser therapy a good choice in conditions where there is joint, tendon or soft tissue inflammation.
The use of laser therapy in the treatment of arthritis
For arthritis (wear and tear or inflammation of the joints), laser therapy can also be helpful: by reducing pain, reducing inflammation, improving circulation in the joint, and promoting tissue repair — it can help reduce symptoms and improve joint function (source 400;">).
Although it should be emphasized that laser therapy is often used as part of combined treatment (physiotherapy + exercises + care) and not alone.
laser therapy in the treatment of back and neck disc
Many disc problems or back/neck pain originating from inflammation or pressure on soft tissue may be improved with laser therapy; Because laser can help reduce pain and improve performance by reducing inflammation and increasing blood circulation and tissue repair.
In physiotherapy and rehabilitation, especially when the patient wants to be treated without surgery and with a non-invasive method, laser therapy is a common option (source).
laser therapy in wound healing and tissue repair
Laser therapy — especially the low-power type — is effective in healing wounds (acute or chronic), repairing skin, reducing scarring, and accelerating recovery after surgery ( 400;">source).
Such an effect is based on stimulating collagen production, increasing blood circulation, reducing inflammation and activating fibroblast cells — that is, it enhances the natural process of tissue repair (source).
laser therapy in neuralgia and nerve pain
Laser, by affecting the function of cells and nerves, can be useful in reducing nerve pain, numbness, burning or tingling; It also speeds up the healing process by repairing nerve tissue and improving blood circulation.
This application has made laser therapy to be considered as a complementary treatment after nerve surgery or nerve damage, along with neuropathy treatments.
laser therapy in physiotherapy after surgery
After surgery — be it joint, muscle, or soft tissue surgery — laser therapy can help reduce inflammation, reduce pain, accelerate wound healing, reduce scar tissue formation, and return function more quickly.
This feature helps with shorter recovery times and faster return to normal activity (source).
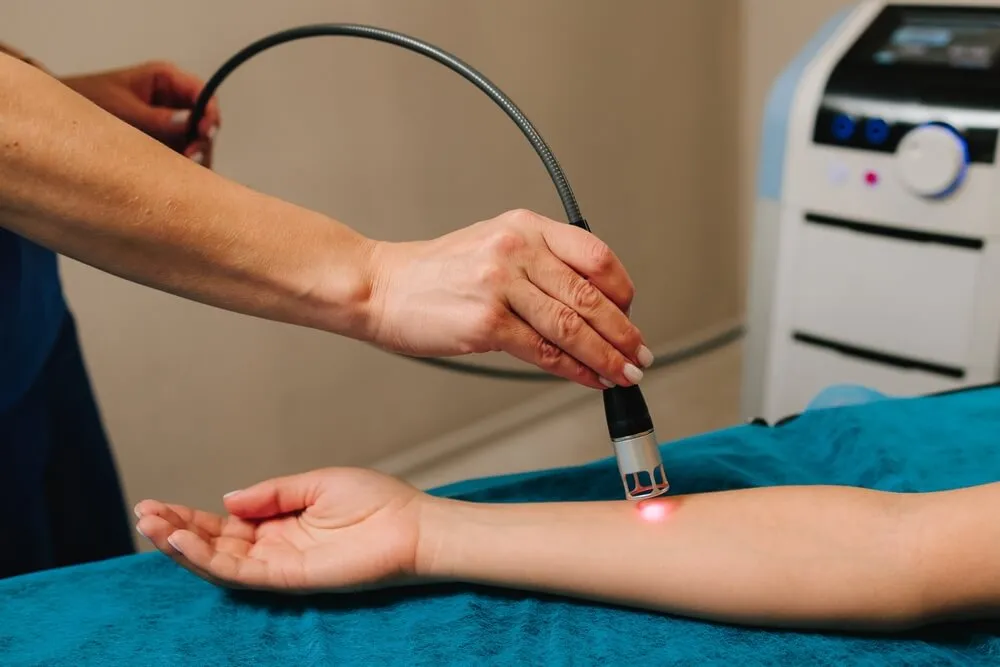
How is laser therapy performed?
Laser therapy is a non-invasive and safe method that stimulates healing and pain reduction processes by irradiating laser light to damaged or painful body tissues.
Depending on the type of laser (low-power or high-power) and the depth of the target tissue, the method and duration of light irradiation is different. The treatment is usually performed in a clinic or physiotherapy center by a trained physiotherapist or specialist and does not require surgery or special drugs.
Preparation and determination of treatment area
At first, the physiotherapist examines the desired area and determines the appropriate laser wavelength and power. The skin may be cleaned and, if needed, a special gel is used to increase light penetration. This step helps to ensure a better effect of the treatment.
Placing the device and lighting
The laser device is placed directly on the injured or painful area and the light is emitted with a specific intensity and duration.
Treatment is usually painless, and the patient may only experience a slight warmth or tingling sensation. The intensity, duration and number of sessions vary depending on the type of injury and the body's response.
duration and number of sessions
Laser therapy sessions usually last between a few minutes and about 20 minutes, and the number of sessions varies from a few sessions to more than ten sessions depending on the severity of the injury, the type of tissue and the goal of the treatment. Sessions can be scheduled daily or several times a week for best results.
monitoring and follow-up treatment
During the treatment, the physiotherapist evaluates the effects of previous sessions and adjusts the intensity or wavelength of the laser if needed. This supervision makes laser therapy to be maximally effective and possible complications are minimized.
Comparison of laser therapy with other methods
Laser therapy is often compared with other physical therapy methods such as ultrasound and electrical stimulation of the cutaneous nerve (TENS) due to its non-invasive effect, reducing pain and accelerating the tissue repair process.
Each method has its own mechanism and may provide different effects depending on the type of injury, pain intensity and target tissue. Next, we examine two common comparisons.
Comparison of low power laser with ultrasound waves
Low power laser (LLLT) and ultrasound waves are both used to reduce pain and stimulate tissue repair, but they have different mechanisms.
Low power laser light stimulates cells and increases the production of cellular energy (ATP), which reduces inflammation and accelerates tissue regeneration (source).
Ultrasound creates deep heat and mechanical vibration using sound waves to increase blood flow and tissue flexibility.
This method is more suitable for warming the tissue, reducing spasm and stimulating local metabolism. Low-power lasers are usually heat-free and non-invasive, while ultrasound may cause some heat and sensitivity.
Comparison of high power laser with electrical stimulation of cutaneous nerve
High-power laser (HPLT/HILT) is used to reduce chronic pain and deep injuries, and by penetrating the tissue, it reduces inflammation and stimulates cell repair. Its effect is usually quick and noticeable and is suitable for deeper tissues (source).
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) by sending electrical pulses to peripheral nerves, blocks pain signals and increases the release of endorphins to reduce pain.
This method is effective for superficial and chronic pain, but its effect is mostly limited to pain control and has no direct effect on tissue repair (source).
possible side effects of laser therapy
Laser therapy is generally a safe and non-invasive procedure, but like any other treatment, mild or temporary side effects may occur in some people or in certain conditions. Most of these effects are short-term and can be prevented or controlled by adjusting the intensity, duration of radiation and expert supervision.
dangers of high power laser therapy
High power laser (HPLT/HILT) may cause mild heat in the treatment area due to deep penetration and higher power. Some people may experience burning, redness, or sensitivity of the skin, which is usually short-lived.
In rare cases, non-professional use can lead to minor burns or eye damage, so the use of protective glasses and the presence of a specialist is required (source).
Complications of low power laser
Low power laser (LLLT) is usually painless and has minimal side effects, but some patients may experience mild skin sensitivity or redness after treatment sessions.
Also, in some sensitive parts of the body, a short-term pain or mild burning sensation may occur, which usually resolves after rest or continued sessions (source).
Which people should not do laser therapy?
Laser therapy is safe for most people and is considered a non-invasive and low-risk procedure, but some people should not or should use this treatment with caution.
People who are pregnant or may be pregnant, people who are near active cancerous tumors, people who have electronic implants such as pacemakers, and people who have severe photosensitivity or active skin diseases are generally not recommended to undergo laser therapy.
It is also dangerous to treat areas near the eyes without proper protection. In any case, before starting laser therapy, it is necessary to consult with a doctor or a specialist physiotherapist to assess the conditions and risks.
care before laser therapy
Before starting laser therapy, following some precautions can increase the effectiveness of the treatment and reduce the risk of complications.
First, the target area should be clean and dry, and if necessary, suitable clothes should be worn for easy access to the affected area.
The use of anti-inflammatory drugs or painkillers should be checked with the doctor's advice, because some drugs may change the effect of laser therapy.
It is also better not to use unnecessary creams or lotions on the treatment area before the sessions, unless prescribed by the specialist.
Evaluation of physical conditions, history of diseases and skin sensitivities by a physiotherapist or doctor is also necessary to start the treatment safely and effectively.
care after laser therapy
After performing laser therapy, observing some precautions helps to increase the effectiveness of the treatment and reduce the possibility of complications. It is better to keep the treatment area clean and dry for a few hours after the session and avoid rubbing or pressing it.
Drinking enough water and taking a short rest after the treatment can improve the cell repair process. Also, perform light sports or physical therapy exercises prescribed by the specialist and avoid intense activities or excessive pressure on the treatment area to maximize the effects of laser therapy.
If redness, tenderness or mild pain occurs, it usually resolves on its own within a few hours to a day, but if symptoms are severe or prolonged, a physical therapist or doctor should be consulted.
tips to increase the effectiveness of treatment
In order for laser therapy to have the greatest effect in reducing pain, reducing inflammation and accelerating tissue repair, it is very important to observe some points before, during and after treatment sessions. These tips help improve the body's response to laser light and prevent possible side effects.
- Following the prescribed treatment plan: Do the sessions according to the physiotherapist's order and in specific time intervals so that the cumulative effect of laser therapy is complete.
- Pre- and post-treatment care: Keep the treatment area clean and dry and avoid rubbing or putting too much pressure on it after the session.
- Doing recommended physical therapy exercises: combining laser therapy with appropriate exercises increases the effectiveness of the treatment in reducing pain and returning function.
- Keeping the body hydrated: Adequate water intake helps cellular function and tissue repair and improves the healing process.
- Avoid intense activities or excessive pressure: Avoid putting pressure on the treatment area or heavy sports until the sessions are completed.
- Report abnormal changes or symptoms to the specialist: Any unusual redness, burning or pain should be reported to the physiotherapist so that treatment settings can be adjusted.
These simple but effective tips will help you get the maximum result from laser therapy sessions and make the recovery period faster and safer.
factors affecting the cost of laser therapy
The cost of laser therapy depends on several factors, including the type of treatment, the quality and equipment of the center, and the individual's condition.
One of the most important factors is the type of laser; A low-power laser is usually less expensive than a high-power laser because the equipment and power required are less.
The intensity and number of treatment sessions also have a great impact on the cost; The more the number of sessions and the longer the duration of the treatment, the higher the total cost.
In addition, the expertise and experience of the physical therapist, the location and equipment of the clinic, and the type of injury or disease being treated can determine the final cost.
Some insurances may cover part of the cost, which also affects the patient's payable cost.
How to choose the best laser therapy center or specialist?
To choose the best laser therapy center or specialist, several key points should be considered in order to perform safe and effective treatment.
First, make sure that the physiotherapist or specialist has a valid degree and sufficient experience in the field of laser therapy and is familiar with various types of low-power and high-power lasers.
Also, the quality and up-to-dateness of the equipment of the treatment center is very important, because modern lasers provide precision and appropriate penetration into the tissue. Examining treatment records and satisfaction of previous patients can also show the skill and efficiency of the specialist.
Access to pre-treatment consultation and transparency in the treatment plan, the number of sessions and care after laser therapy are also important criteria.
Finally, choosing a center that guarantees compliance with safety and health standards will be a guarantee of receiving effective and low-risk treatment.


















