Table of Contents
- Types of Twin Pregnancy
- Twin Pregnancy Week by Week
- symptoms of twin pregnancy
- necessary care in twin pregnancy
- effect of twin pregnancy on mother's health
- The effect of twin pregnancy on the health of newborns
- What factors increase the probability of twin pregnancy?
- How are twins born?
- How is twin pregnancy diagnosed?
- Necessary tests during twin pregnancy
- Drugs and pills for twin pregnancy
- What supplements should be taken during twin pregnancy Should we take multivitamins?
- Your doctor's final words about twin pregnancy
Twin pregnancy is a special and different experience that, in addition to being exciting, requires more awareness and care than singleton pregnancy. From the very first weeks, the mother's body experiences more changes and the level of hormones increases. Knowing the types of twin pregnancy, symptoms, week-by-week development process, necessary tests and special care will help you to be more prepared. In this article from your doctor, we will review everything about twin pregnancy so that you can better manage your health and that of your babies.
Types of twin pregnancy
Twins are classified into two categories, identical and non-identical. Almost 30% of twins are identical and about 70% are non-identical twins.
- Pregnancy Identical twins (monozygotic). Identical twins are formed when an egg is fertilized and then splits into two. In this case, two embryos will be formed that have completely similar genes. Identical twins are always the same sex, so if you're pregnant with identical twins, you're more likely to have either a boy or a girl.
- Non-identical twins (dizygotic). This twin pregnancy happens when two eggs are fertilized separately and then placed in the uterus. Non-identical twins may have similarities but are not identical. Identical twins can be of two opposite sexes.
English text:
A little more than half of twin pregnancies end in preterm delivery (before 37 weeks). While 40 weeks is the full gestation period of the average pregnancy, most twin pregnancies are delivered at approximately 36 weeks (range 32-38 weeks depending on the type of twin pregnancy). Persian translation: More than half of twin pregnancies end in premature delivery (before 37 weeks). While the normal length of pregnancy is about 40 weeks, most twin pregnancies usually end around 36 weeks (range 32 to 38 weeks depending on the type of twin pregnancy). target="_blank" rel="noreferrer noopener">hopkinsmedicine
Twin pregnancy week by week
Twin pregnancy week by week is usually associated with more severe changes and symptoms than singleton pregnancy. In the first weeks, symptoms such as breast tenderness, morning sickness, fatigue or delayed menstruation may appear. In the first trimester, a home pregnancy test can show a positive result, but the only sure way to diagnose twins is to do an ultrasound. Although the first weeks often pass peacefully, as the pregnancy progresses, more pressure on the mother's body causes new symptoms and different experiences. Next, we will examine the weeks of pregnancy twins and their changes week by week.
first three weeks of twin pregnancy
In the first three weeks of twin pregnancy, usually the mother still does not notice any difference from singleton pregnancy. The main changes at this stage occur inside the uterus, where the fertilized egg implants and begins to grow. Early pregnancy symptoms such as fatigue, breast tenderness or nausea may appear, but are not reliable for diagnosing twins. In this period of time, even an ultrasound cannot show a twin pregnancy, and you usually have to wait a few more weeks for a definite confirmation.
week four
In the fourth week of twin pregnancy, the implantation stage is completed and the sperms are attached to the uterine wall to receive nutrients and oxygen. This process may be accompanied by spotting or light bleeding, which is called implantation bleeding. After that, the placenta begins to form for each embryo to provide a pathway for nutrition and oxygenation. In identical twins, sharing a pair (monochorionic) is relatively common and requires special care; In fraternal twins, each embryo usually has a separate placenta.
5th to 8th week
In the fifth to eighth week of twin pregnancy, important changes occur in the mother's body and the development of the fetuses. During this period, morning sickness begins, which is more intense in twin pregnancy, and many consider it a sign of the normal course of pregnancy. From around the sixth week, the brain and spinal cord of the embryos are forming, and by the eighth week, hand and foot buds appear. Also, the tissues of the heart begin to grow and the basic foundations of all the vital organs of the babies are laid. This stage is one of the most sensitive parts of growth, and medical care and proper nutrition are especially important.
weeks 9 to 13 of twin pregnancy
During the 9th to 13th week of twin pregnancy, you are nearing the end of the first trimester and important changes are taking place in the development of the babies. During this period, fingers and toes appear, and by the twelfth week even small nails begin to form. The facial features of fetuses become more distinct; The eyelids, nose, eyes and upper lip become more clear and the face of the embryos becomes more similar to the real baby. Also, tooth buds are formed in the gums of twins. This stage is a turning point in the development of fetuses and is a sign of entering a more stable period of pregnancy.
weeks 14 to 17 of twin pregnancy
In the 14th to 17th weeks of twin pregnancy, the changes in the mother's body and the growth of the fetuses are quite noticeable. Usually, twin mothers experience belly bulge earlier than singleton pregnancies, and due to feeding two babies at the same time, they are more tired and overweight. However, this period is known as the "golden trimester of pregnancy" due to reduced nausea and increased energy. At the same time, the twins grow rapidly and their organs and features develop more.
- Nausea will decrease and mother's energy will increase.
- The bones of the head and the long limbs of the fetuses begin to harden.
- The eyes move behind the eyelids at the 16th week, although they do not yet open.
- Eyebrows and eyelashes begin to grow.
- The twins move their arms and legs, but their movements are still not clearly felt.
Week 18 to 22
In weeks 18 to 22 of twin pregnancy, significant changes occur in the mother's body and the development of the fetuses. Due to the enlargement of the uterus and hormonal changes, the mother may feel more pain and discomfort, but light exercises approved by the doctor can reduce these problems and help improve circulation. During this period, the twins become more active, start the sucking reflex, and their movements and kicks can be clearly felt. Also, their ears begin to form in the 18th week and acquire the ability to hear sounds, while their heads are covered with thin hair called lanogo by the 20th week.
week 23 to 27 of twin pregnancy
In weeks 23 to 27 of twin pregnancy, the mother's body and the fetuses experience significant changes. The mother may feel Braxton Hicks contractions for the first time, or false labor, which is a sign that the body is preparing to give birth. At this time, the twins have significant growth; Their fingerprints are formed and the palms and feet become more distinct. They can also react to environmental sounds and move when they hear the mother's voice. Around the 26th week, the fetus's lungs begin to develop and prepare for breathing outside the womb by producing a substance called surfactant.
week 28 to 32
In weeks 28 to 32 of twin pregnancy, more pressure is placed on the mother's body and symptoms such as back pain and swelling of the hands and feet intensify, so that it becomes more difficult to walk and sleep. During this period, babies are often in the proper position for normal delivery with their heads down, although in some cases one or both fetuses may be in a different position. Also, during these weeks, babies' brains grow significantly, they gain the ability to control their body temperature and can even open and close their eyes. This stage is a sign of entering a sensitive period where the possibility of premature birth or the need for cesarean section increases.
33 weeks to 36 weeks
At 33 weeks pregnancy to 36 twin pregnancies, the babies' lungs reach a stage where they can prepare for breathing outside the womb. During this period, twins begin to store fat and gain weight, although they are usually smaller than singleton babies and their average birth weight is about 2.3 kg. Most twin mothers may have premature births, so in these weeks there is a possibility of giving birth around week 35. For this reason, careful attention to the signs and symptoms of childbirth becomes very important.
symptoms of twin pregnancy
Twin pregnancy usually manifests itself with more severe and earlier symptoms than singleton pregnancy, because the level of hormones is higher and the body tolerates more pressure. These symptoms are not always definitive, but they can be a sign of multiple births. The most common symptoms of twin pregnancy are:
- More severe morning sickness especially in the first trimester
- faster and more weight gain compared to singleton pregnancy
- Extreme fatigue and sleepiness Heart palpitations and shortness of breath due to more pressure on the heart and lungs
- larger belly size compared to gestational age
- More or earlier movements of the fetus in the mother's womb
- Abnormal or higher than expected results in the β-hCG test
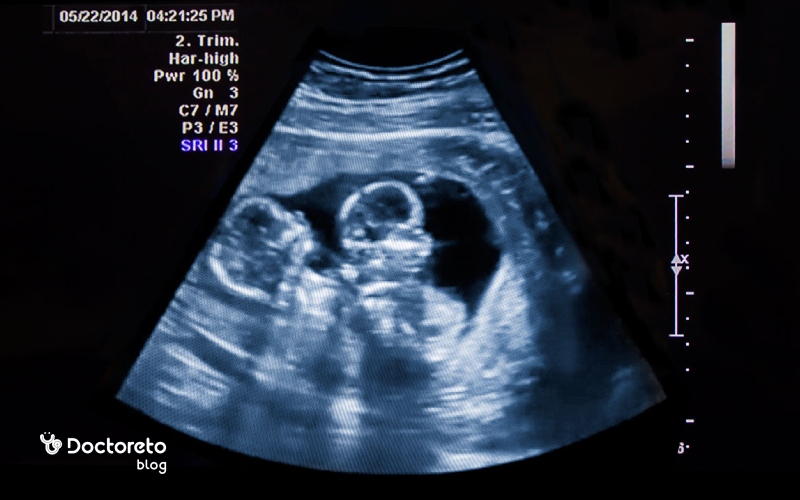
- Observation of two gestational sacs or two fetuses in ultrasound
necessary care in twin pregnancy
Due to more pressure and changes on the mother's body, twin pregnancy requires special and more careful care than singleton pregnancy. This type of pregnancy can increase the possibility of premature birth, anemia, pregnancy blood pressure and other complications; Therefore, paying attention to medical advice and regular follow-up is very important during this period. The most important twin pregnancy cares are:
- Making regular medical visits and more than singleton pregnancy
- Consumption of prescribed supplements such as iron, folic acid and calcium
- Having a balanced and high-calorie diet to meet the needs of two fetuses
- Adequate rest and avoiding heavy activities
- control of weight, blood pressure and blood sugar levels during pregnancy
- Drinking enough water to prevent dehydration
- Pay attention to warning signs such as abdominal pain, bleeding or premature contractions
- Preparation for the possibility of premature birth and advice about the delivery method

The effect of twin pregnancy on mother's health
Twin pregnancy puts more pressure on the body and therefore the risk of some complications in mothers increases. In this situation, hormonal and physical changes can cause problems that require more careful medical care and follow-up. The most common complications of twin pregnancy are:
- Pregnancy blood pressure and increasing the possibility of premature separation of the placenta
- Anemia caused by iron deficiency and increased risk of premature birth Gestational diabetes and high blood sugar levels
- Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) and severe itching caused by the accumulation of bile acids
- Excessive increase of amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios)
- Miscarriage or twin disappearance syndrome in the first trimester
- Postpartum depression (PPD) and related psychological problems
- Postpartum bleeding, although rare but serious
The effect of twin pregnancy on the health of newborns
Twin pregnancy can have different effects on the health of babies and is associated with more challenges than singleton pregnancy. In this situation, premature birth is more likely, and as a result, babies may have a lower birth weight or require special care in the NICU. It also increases the risk of respiratory problems, neonatal jaundice, growth disorders, and in rare cases, birth defects. However, most twins can be born healthy and develop normally with regular medical care and careful pregnancy control.
What factors increase the probability of twin pregnancy?
Twin pregnancy occurs for various reasons and usually depends on factors that cause the release of more than one egg or the division of a fertilized egg. In some women, genetic conditions, hormonal changes, or assisted reproduction methods make this type of pregnancy more likely. Also, environmental factors and individual characteristics of the mother can play a role in the formation of twin pregnancy and increase its chances. The factors that increase the possibility of twin pregnancy are:
- Family history of twins from mother's side
- Age over 30 years old, especially 35 to 40 years old
- Having previous pregnancies and multiple births
- Consumption of fertility drugs or doing IVF
- Race and ethnicity (more in African women and less in Asians)
- Higher height or higher body mass index (BMI) in the mother
How are twins born?
Twins can be born both by natural delivery and by cesarean section. The choice of delivery method depends on the position of the embryos, the condition of the mother and the doctor's opinion. If both fetuses are in a head-down position and there are no special complications, it is possible to give birth naturally. However, if one of the twins is not in a good condition or the pregnancy is high-risk, a cesarean delivery is usually recommended.
How is twin pregnancy diagnosed?
Diagnosis of twin pregnancy is not possible only with home pregnancy test or blood test, because these tests only show the presence of pregnancy hormone (β-hCG) and cannot determine the number of embryos. In twin pregnancy, the level of this hormone is usually higher, and the home test may be positive sooner or more strongly, but this is not certain. A blood test can detect pregnancy earlier than a urine test, but it still cannot detect twins. The accurate and reliable way to understand twin pregnancy is ultrasound in the first weeks of pregnancy, which clearly shows the presence of two gestational sacs or two fetuses.
table of beta number in twin pregnancy (beta number in twin pregnancy)
The level of beta-hCG (β-hCG) in twin pregnancies is usually higher than in singleton pregnancies, but the exact amount can vary greatly in different people. Below is an approximate table of the level of this hormone in different weeks of twin pregnancy. These values are only common ranges and for accurate interpretation one should consult a doctor and individual blood test:
| Week of pregnancy | Approximate range of β-hCG in single pregnancy (mIU/ml) | Approximate range of β-hCG in twin pregnancy (mIU/ml) |
|---|---|---|
| 3 weeks | 5 – 50 - 100 - 100 - 4 weeks - 5 - 426 - 50 - 840 - 5 weeks - 18 - 7,340 - 200 - 15,000 - 6 weeks - 1,080 56,500 | 2,000 – 100,000 |
| 7-8 weeks | 7,650 – 229,000 | 15,000 – 450,000 |
| 9-12 weeks | 25,700 – 288,000 | 50,000 – 600,000 |
| 13-16 weeks | 13,300 – 254,000 | 25,000 – 500,000 |
| 17-24 weeks | 4,060 – 165,400 | 8,000 – 300,000 |
| 25-40 week | 3,640 – 117,000 | 7,000 – 200,000 |
urine color in twin pregnancy
The color of urine in a twin pregnancy is usually not significantly different from a singleton pregnancy, but changes may be seen due to the increased level of hormones and the body's need for more fluids. Many women experience darker or more yellow urine in early twin pregnancy due to more severe nausea and dehydration. Conversely, if enough fluids are consumed, urine can be clearer and pale yellow. In general, the color of urine in pregnancy depends more on the state of body water, diet and the use of supplements (especially pregnancy vitamins) than on the number of fetuses.
BB-check in twin pregnancy
BBcheck in twin pregnancy works the same as in singleton pregnancy and shows a positive or negative result based on the detection of β-hCG hormone in the urine. Since the level of this hormone is usually higher in a twin pregnancy, the home test can be positive earlier than normal or the second line can be seen bolder. However, the intensity or boldness of the BB check line alone is not a definitive criterion for diagnosing twins, because factors such as ovulation time, gestational age, dilute or concentrated urine, and the sensitivity of the test are also effective. To ensure twin pregnancy, only more accurate methods such as serial β-hCG blood tests and ultrasound are reliable.
Necessary tests during twin pregnancy
During twin pregnancy, screenings and pregnancy tests should be done more carefully and regularly to check both the health of the mother and the development of the two fetuses. These tests help the doctor to diagnose any possible problems early and provide the necessary care. The most important tests include the following:
- Genetic screening: to investigate the possibility of hereditary and genetic disorders before birth.
- First trimester tests: including ultrasound and blood tests for early detection of birth defects.
- Second trimester tests: screening with multiple blood markers to assess the risk of fetal defects.
- Periodic ultrasounds: to check the growth, structure of fetuses and estimate the date of delivery.
- Amniocentesis or CVS: if needed for more accurate diagnosis of genetic problems.
- Glucose test: to check gestational diabetes.
- Group B streptococcus culture: usually in late pregnancy to prevent infection of the baby after birth.

Drugs and pills for twin pregnancy
For twin pregnancy, special pills or drugs are usually not prescribed to increase the probability of two fetuses, unless the couple is infertile or undergoing fertility treatments. Some ovulation stimulation drugs such as clomiphene citrate (Clomid) or gonadotropins can increase the possibility of simultaneous ovulation of multiple eggs, resulting in a twin or multiple pregnancy. These drugs must be taken under the supervision of a gynecologist and infertility specialist and after careful examination of the hormonal and ovarian status. Arbitrary use of these drugs increases the risk of side effects such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, high-risk pregnancy, and serious problems for the mother and fetuses.
What supplements and multivitamins should we take during twin pregnancy?
During twin pregnancy, the mother's nutritional needs are greater than that of singleton pregnancy due to the simultaneous growth of two fetuses, and pregnancy supplements play an important role in providing these needs. Folic acid consumption from before pregnancy to the end of the first trimester is necessary to prevent neural tube defects. Iodine is important for the development of the brain and nervous system of fetuses, iron for preventing anemia and reducing the risk of premature birth, and vitamins B12 and D for the health of the nervous system and bones. Also, vitamin C helps in better absorption of iron. Of course, no supplement can replace a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, protein and dairy products, and all of these should be taken under the supervision of a doctor.
Your doctor's final words about twin pregnancy
Twin pregnancy is an amazing but challenging experience that requires more attention, awareness and special care than singleton pregnancy. From the very first weeks to the end of pregnancy, the mother's body endures more pressure and the possibility of complications such as premature birth, anemia or gestational diabetes is higher. However, regular follow-up of medical visits, periodic tests and ultrasounds, taking essential supplements and following nutritional and self-care tips can help manage this path better. Finally, with the planning and support of the treatment team, you can spend your twin pregnancy more calmly and confidently and hold the babies safely.
Your doctor takes care of your health!