Side effects in hair transplantation
General effects
Prevention of complications
Hair transplant surgery though by hand done by skilled professionals or even though everything goes according to plan, It is possible that the patient will face its side effects. Doctors should complete history (past, present, family, family and personal medical records) of the referring person Ask the most important questions about the history of allergies, co-morbidities, consumption Medicine now, and complete physical examinations of all patients.
Patient selection
Medical precautions
combined diseases
Before surgery, blood sugar and blood pressure levels should be checked Control the blood of patients with diabetes and high blood pressure. Cardiovascular problems should be To be established with the permission and under the authority of a cardiologist. Although diabetes, high blood pressure or cardiovascular diseases are not considered an absolute contraindication for hair transplantation, but hair transplantation in people Patients with these concomitant diseases should be treated with caution.
Blood disorders, liver and kidney problems And the presence of infectious skin diseases should also be identified before surgery. This is to prevent from excessive bleeding during and after the operation, ensuring proper and timely delivery Drug and its elimination and discharge, avoiding long-term absorption and drug accumulation, and avoiding exacerbation of infection Skin problems, which may affect the growth of transplanted grafts in the implantation or healing of the donor areas (the place of hair removal at the back of the head) has a negative effect, it is done.Patients with alopecia areata should Undergo a scalp biopsy and refer to a dermatologist. After being treated Getting and diagnosing the patient's stable or inactive disease before surgical intervention in these cases, At least 2 years of waiting time is required.
protective drugs
Use of anticoagulants such as aspirin, Warfarin, vitamin E, herbal medicines, etc. should be at least 2 weeks It should be stopped before surgery, and if possible, based on the consent of the patient's cardiologist take Many doctors perform implantation on patients who take baby aspirin They do, while some of them don't. According to personal experience Surgery was performed on patients taking aspirin and severe and excessive bleeding occurred has not given, but patients who cannot stop taking this drug can also With the utmost caution and care, undergo surgery.
Smoking and alcohol consumption
Smoking should be at least 2 weeks before Surgery should be stopped, because it may delay healing due to its vasoconstricting effect Ulcer, poor wound healing and causes wound opening or poor growth of transplanted grafts. substitute Smoking e-cigarettes or nicotine lozenges with cigarettes can help. It is recommended to In order to reduce bleeding and swelling, avoid drinking alcohol at least a few days before the operation.
Previous skin lesions and diseases
Skin diseases such as actinic keratosis (actinic keratosis) or basal cell carcinoma should be treated and removed before surgery. Folliculitis or skin infections should be treated in the same way.
If there is a keloid disease, to Due to the possibility of forming a bigger scar due to hair transplant, it is recommended to act with caution And to prevent poor healing of the wound from techniques such as trichophytic suture, the use of Scar gel or creams or steroid injections, or if possible, PRP (platelet-rich plasma) or Acell injections should also be included in the treatment equipment.
General effects
Hair transplant surgery is generally a B method The risk is that there are relatively few side effects. These side effects can be skin type The highly vascularized head, the techniques used in disinfection, and the continuous improvements in surgical techniques. It is created, attributed.
Complications during surgery
Severe drug sensitivity
If the patients before permission for The surgery has been properly evaluated through the medical history and complete physical examination. Drug reactions during surgery are not common. During the patient's initial consultation, each The patient's history of allergic reactions to local anesthesia and drugs is asked and checked be.
Commonly used drugs for Before and during hair transplant surgery, including anti-anxiety drugs (such as diazepam), painkillers and antibiotics.
Allergic reaction to local anesthesia It is rare. Amide local anesthesia (lidocaine, mepivacaine, bupivacaine, articaine, and prilocaine) statistically less than the types of esters (benzocaine, procaine, tetracaine) It causes allergies. Allergic reaction to local anesthesia including type hypersensitivity reactions IV especially in the group of esters, usually Occurs after topical application of the drug. Immediate allergic IgE (Immunoglobin E) reactions to local anesthetics often occur Hopeful anesthesia is not common; However, case reports show a hypersensitivity reaction type I including urticaria (picture 1), angioedema or skin swelling, wheezing and shortness of breath, sneezing, itching, or anaphylactic shock (allergic attack) Drug injection happens within a few minutes. Anaphylaxis in the form of respiratory symptoms (tightness breath, wheezing, upper respiratory tract obstruction and edema), gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain) and cardiovascular symptoms (dizziness, syncope or fainting, low blood pressure) It shows itself.For patients with a history of reaction Sensitivity to local anesthesia, perform a skin test before surgery as a diagnostic tool It is recommended.
If despite thorough screening for reactivity Allergic reactions during preoperative counseling, adverse drug reactions during surgery, The use of any suspected stimulants should be discontinued, such as antihistamines such as Diphen Hydramin should be available and used, and emergency care should be administered and implemented to be Inhaled albuterol should be used exclusively in the event of bronchospasm be available In case of anaphylactic shock, epinephrine should be immediately available (please see table 1). Ensure that all staff as well as the clinic for Be well equipped to deal with emergencies such as allergic reactions. Perform surgery Using hospital settings and equipment can be used for patients who are suspected of having a reaction Hypersensitivity is more appropriate.
Poisoning with local anesthesia
Local anesthesia crosses the blood-brain barrier and systemic toxicity can manifest as symptoms of central nervous system (CNS) or cardiovascular system (CVS) toxicity. Nervous system toxicity is dose dependent And with low doses it leads to depression and in high doses it causes irritation and convulsions in the system He gets nervous.
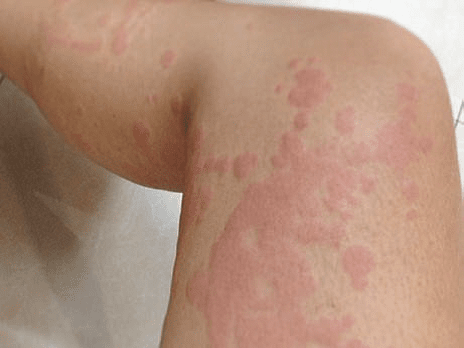
Picture 1 of hives
| Complications | prevent | Management |
| Severe drug sensitivity | Skin test (in case of suspected allergy to local anesthesia) Previous history of the patient's drug allergy | Stop using stimulants Use of antihistamines such as diphenhydramine 50 mg oral tablet, single dose 50 mg/mL Intramuscular injection through the deltoid muscle Inhaled albuterol 2 to 4 times (in cases bronchospasm and laryngitis) Epinephrine 30.0 mg (30.0 mL standard dose mL1 or mg1 vial) injection Muscular to the outer thigh or other deltoid muscle |
| Local anesthetic poisoning | 1. Inject 3-5 mL of anesthesia with a time interval between each injection 2. Vent the needle before each injection 3. For high volumes in anesthesia, the values are 10-15 μg/kg in adults | treatment with intralipid emulsion (ILE) substance injection As opposed to a large amount, up to 20% emulsion Intralipid at 1.5 mL/kg for more than From 1 minute and then inject 15 mL/kg/h, max three boluses Maximum dose Cumulative, 12 mL/kg |
| hiccups | Drink water or ice hold your breath Breathing in brown paper envelopes Oral chlorpromazine 25 mg every 6 hours for 7-10 days | |
| Vasovagal reaction | Avoiding precipitating factors. It means sitting or standing for a long time, emotional stress, pain, heat, venous blood draw, consumption Alcohol, dehydration, and the use of vasodilators and diuretics (diuretics) | The patient should be in a supine position (legs should be straight) or Squat position (in case of initial symptoms of the disease). Aerobic and isometric exercises of the limbs. Hydration or delivering fluid to the patient's body (2-2.5 liters per day and sodium supplement) Use of drugs 1. Fludrocortisone 0.2-0.1 mg / daily for Younger and healthy patients 2. Metoprolol for patients over 40 years or suffering from high blood pressure |
| Excessive bleeding | 1 to 2 weeks before surgery, the use of anticoagulants should be stopped. Daily alcohol consumption should be stopped a few days to a few weeks before surgery. Control blood pressure. | Direct pressure and blood coagulation with a clamp or suture of the bleeding area. injection/wet dressing impregnated with local anesthesia + Epinephrine. Intravenous injection (serum therapy) in conditions of large blood volume loss |
| Severe drop in blood pressure | Avoiding agents that accelerate the vasovagal reflex. Avoid intravenous injection Local anesthesia (with epinephrine) Blood pressure monitoring during surgery | high blood pressure • Management the pain • Medicines Continue antihypertensives (except non-cardioselective beta-blockers). Low blood pressure Bradycardia: Atropine injection Sublingual or intramuscular in doses of 0.5 mg (mL 0.5) • Normal heart rate: ephedrine injection Sublingual or intramuscular injection in doses of 25 mg or (mL 0.5) |
| the pain | Take painkillers before and during the operation | Pain management using local anesthesia and auxiliary maneuvers (ice pack, massage, etc.) |
| Nausea and vomiting | Eat a light meal before surgery Avoiding agents that precipitate vasovagal shock Control of diabetes, blood pressure Allergy testing and screening to prevent anaphylactic shock | Anti-nausea drugs (table 2) |
Table 1. Intraoperative complications, prevention and management
Poisoning local anesthesia has two phases It started with the stimulation of the nervous system (restlessness, change in hearing, metallic taste in the mouth). up to convulsions and strokes, depression and reduced activity of the nervous system (drowsiness, coma and respiratory arrest) It progresses and is followed by inflammation of the cardiovascular system (tachycardia, ventricular arrhythmia, hypertension blood) and finally depression and reduction of body activity (bradycardia or slow heartbeat, heart block, arrest). heart, depression or cardiac depression) continues.
Through (1) injecting anesthetics into Gradual face in the amount of 3-5 mL and then pausing with a time interval between each injection. and (2) venting the syringe needle before each injection to avoid intravascular injections and (3) For high volume of anesthesia, for adults, the amounts do not exceed the toxic limit of 10-15 μg/kg, it can be avoided by B poisoning. Local sensation prevented.
In hair transplant surgery, as long as The specialist should not exceed the maximum dose and consider the mentioned preventive measures Be aware that local anesthetic poisoning is rare. In severe poisoning, Treatment with fat emulsion (ILE) is prescribed (Table 1).
Hiccup
During the operation, the patient may be sick get hiccups and this condition can last from 48 hours to a week. The patient can At first, with home treatments and physical maneuvers such as rapid swallowing of water or a thin slice Small ice, holding the breath, or exhaling and breathing in a paper envelope can be treated. Chlorpromazine, one Phenothiazine type is one of the sedative drugs used for hiccups and its side effects such as Confusion, sleepiness, insomnia and blurred vision are prescribed.
Hiccups during surgery due to head movements
They can cause problems when placing grafts. If the surgery continues at night
They find that patients may have trouble sleeping, feeling restless and tired. consumption
A single dose of oral chlorpromazine immediately relieves symptoms. However, side effects
The above mentioned should be considered.
Vasovagal reaction
Syncope or stroke, a medical problem It is common with a frequency between 15 and 39%, which increases equally between men and women It is more likely to occur after the age of 70. Symptoms of syncope include nausea, color Jumping, sweating, muscle contraction, confusion and sensory disturbance, physical injury, heart palpitations, tightness breath, pain in the chest and bruised skin.
Most causes of syncope, nervous reflex with It is a mediator known as neurocardiogenic syncope or vasovagal reflex. Other causes syncope, cardiac origin, orthostatic drop in blood pressure, carotid sinus tenderness, and neurological and endocrine causes Endocrine and psychiatric disorders.
Vasovagal reflex with sitting or standing Long term, emotional stress, pain, heat, venous blood draw, alcohol consumption, dehydration and use Vasodilators and diuretics can stimulate and advance. Its symptoms include nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, sweating, pallor, palpitations and dizziness. That after this Signs, loss of consciousness and short-lived tonic-clonic contractions (less than 15 seconds) It happens.
The mechanism of vasovagal syncope is still unknown It is not fully understood, but it is defined as a reaction (Bozold's current reflex) that with reduction Venous return resulting in insufficient filling of the ventricles and severe cardiac contractions through the action of mechanoreceptors (C receptors) located in the left ventricle, atrium, and beginning pulmonary artery will be Changes in peripheral vascular resistance occur. Function of the autonomic nervous system Disturbed and leading to failure of sympathetic vasomotor pathways to increase environmental resistance The vessels become vertical when the person is in a vertical position. In addition, heart rate response to The intermediary of pressure receptors to low blood pressure through the vagus nerve is also disturbed.
Avoidance of accelerating factors and placement The patient is in a supine position or sitting on the floor while squatting Early signs of illness, hydration or fluid Reaching the body, and aerobic and isometric exercises of the limbs are recommended as initial management will be Drug treatments include fludrocortisone and metoprolol (Table 1).
Excessive bleeding
Severe bleeding in hair transplant surgery Especially in cases of surgery with the combination of epinephrine in local anesthesia or tumescent anesthesia with Higher risk in patients taking aspirin, heparin, vitamin E, herbal medicines and other blood thinners. or in patients who had daily alcohol consumption before surgery, it is uncommon. pressure High blood pressure also aggravates bleeding. Blood coagulation tests can be used for screening used by patients to determine the presence of bleeding disorders.
Use of Thomsent anesthesia and care And it is important to avoid cutting the vascular structures when harvesting from the hair bank area and It helps to prevent excessive bleeding.
Decreasing the depth of cut in creating a slot for
Implantation also helps in controlling bleeding, which increases the implantation time and ultimately the entire operation
does This process risks poor growth of transplanted grafts because it takes a long time
They are outside the body.
Bleeding during surgery can be Control bleeding by applying direct pressure and coagulation, ligation, or suturing the area. Injection Additional local anesthesia with epinephrine in the bleeding area can also help control bleeding slow.
Also use wet dressing Local anesthesia containing epinephrine can be useful in controlling bleeding. Intravenous injection (serum therapy) is possible in severe volume loss Blood related blood pressure is required. Careful examination of the donor area (hair bank) should be done first It should be done by closing the wound to reduce the possibility of bleeding after the operation or creating a hematoma. Bleeding After the operation, despite the pressure dressing and the use of an adhesive headband across the forehead and area Hair bank in order to control swelling of the face and also prevent further bleeding from the area wound Hair harvesting (hair bank) rarely happens.
High blood pressure and low blood pressure
In a healthy person, high blood pressure During hair transplant surgery, it is usually caused by pain.
Patients with high blood pressure should Continue antihypertensive medications. To patients who take non-selective beta blockers It should be recommended to combine it with selective cardiac beta blockers (asbutolol, atenolol, betaxolol, bisoprolol, esmolol, metoprolol) because a combination of beta blockers Nonselective and large amounts of systemic epinephrine risk acute hypertension (high systolic 200 mmHg) that can suddenly lead to a stroke to be Epinephrine has both alpha-adrenergic (vasoconstriction) and beta-adrenergic effects (creating vasodilation or widening of blood vessels) non-selective beta blockers by leaving an effect Unhindered epinephrine vasoconstriction causes hypertensive reaction and vasodilation They prevent.
Non-selective beta-blockers may also Can inhibit the reaction to epinephrine in the form of anaphylactic shock, which can lead to death do.
Hypotension is possible with a reflex Vasovagal about to occur or due to the volume of blood lost (in the case of bleeding more than limit) to be related.
If blood pressure drops with bradycardia (Bradycardia), atropine is used sublingually or injected intramuscularly. If blood pressure with normal heart rate, ephedrine is used sublingually or It is injected into the muscle (table 1).
Pain
Surgical pain due to signal disturbance
Painful effects occur from disturbed peripheral nerves and with non-anti-inflammatory drugs
Regular steroids (NSAID) or drugs
Stronger analgesia, preoperative and intraoperative pain can be managed. Some surgeons decide
They decided not to use drugs and alternative methods such as body massage as extraneous
sedation, using ice packs as adjunctive anesthesia, playing music, watching
Video or talk to the staff while the patient is under local anesthesia to keep
It is recommended to have the patient in a comfortable and pain-free position. Injection of local anesthesia every 2 hours
In the area of hair removal and the place of implantation (recipient) through nerve and fiber block until completion
Surgery provides a continuous and continuous anesthetic effect.
Nausea and vomiting
occurrence of nausea and vomiting during surgery can cause problems; Because it may increase the operation time, more bleeding and out Grafts coming out of place and as a result swelling of the face. However, this happens after surgery (immediately afterwards or the next day) is more common. Uncontrollable vomiting though to It happens rarely, but it may be necessary to replace the intravenous injection (serum therapy). Patients experiencing nausea and vomiting may decide to Getting results, they don't want to follow the next meetings.
Medicines such as metoclopramide (Plazil) or domperidone (Motilium) do not seem to help. Ondansetron (Zofran) with Existence of being expensive, an effective drug in my practice for the treatment of emesis after chemotherapy It has been and can be an excellent choice for the treatment of severe vomiting after surgery. other Antinausea drugs can also be used (Table 2).Nausea and vomiting can also be symptoms Anaphylaxis or hypoglycemic shock by giving sweet drinks or thick solution Diabetes is treated for severe cases. Nausea and vomiting with hyperglycemia (increase blood sugar) in diabetic patients can be controlled by continuing the patients' prescription drugs Even during surgery and keeping a glucometer (blood sugar measuring device) and insulin available controlled
Table 2. Antinausea drugs, mechanism of action and some side effects
| Anti-nausea drugs | Mechanism of action | side effects |
| Intravenous injection of promethazine mg25-12.5 Oral 25 mg | Antagonistic effects of dopamine receptors | EPS (extrapyramidal syndromes, including symptoms of akathisia, parkinsonism, tardive dyskinesia) |
| Intravenous injection of prochlorperazine 10-2.5 mg Oral 5-10 mg | Antagonistic effects of dopamine receptors | EPS (extrapyramidal syndromes, including symptoms of akathisia, parkinsonism, tardive dyskinesia) |
| Intravenous injection of metoclopramide 10-20 mg Oral 10-20 mg | Antagonistic effects of dopamine receptors (for patients with gastric reflux or GERD is useful) | Confusion and impaired senses, fainting or under the influence of drowsiness |
| Intravenous droperidol injection mg 0.625 | Antagonistic effects of dopamine receptors | Chronic QT syndrome (QT interval) and cardiac arrest trigger |
| Intravenous injection of ondansetron 1 mg to get rid of nausea and vomiting. 4 mg to prevent / Oral 6 mg | Antagonistic effects of serotonin (HT3-5) | Anxiety, restlessness, irritability, nervous shock or deep and rapid breathing lead to dizziness |
| Oral hydroxyzine mg 25-100 | Antihistaminic effects › Antimuscarinic | Unconscious or under the influence of drowsiness |
| Intravenous injection of diphenhydramine mg 25-50 Oral 25-50 mg | Antihistaminic effects › Antimuscarinic | Unconscious or under the influence of drowsiness |
| Scopolamine 1.5 mg as a skin patch (transdermal) | Antimuscarinic effects › Antihistaminic |
Post-operative complications
General side effects after the operation that are mild and Temporary is considered as part of the postoperative period and includes cases They are as follows:
Persistent hiccups
Possible reasons for hiccups after surgery Hair transplants include: (1) use of diazepam or its discontinuation, (2) nerve contractions Phrenic, which itself causes the irritation of the area behind the ear during the removal of the skin strip under are affected (3) Laying the patient on his back during surgery (4) Breathing too much air Because of the stimulation of the diaphragm muscle movements in excited patients!
Hiccup (Bouts) period lasts about one to two days, in While long hiccups last more than 48 hours and duration of uncontrollable hiccups more than It's been two months.
High sensitivity (pain, skin stiffness) and tingling (numbness and falling asleep in different parts of the body)
Pain after surgery usually at night Surgery takes place and after a few days it is fixed. Patients undergoing hair transplantation with the FUT method compared to FUE method and because of stitches, hard The inflexibility of the scalp and wide incisions for hair transplantation experience more pain do In the FUE method, the pain after the operation is less severe It subsides a few hours after the operation or you will feel a slight discomfort on the night of the operation.
Table 3. Postoperative complications and management It
| Complications | Management |
| Persistent hiccups | Chlorpromazine 25 mg orally each 6 hours for 7 to 10 days |
| Hypersensitivity/tingling and murmur | Hypersensitivity (pain) Medicines Painkillers (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, paracetamol, opioids) ice pack Tingling and murmuring after It resolves itself in a few months |
| facial swelling | The use of triamcinolone acetonide in anesthesia oral steroid Ice bag Elevating the head position (with a small pillow) to a height of 45 degrees Positioning the head (arched, lying on the side or behind the head parallel to the floor of the room if possible, maintain this situation for 1.5 days) Using a suitable and comfortable headband on the forehead |
| Nausea and vomiting | Anti-nausea drugs |
| Telogen effluvium or hair loss due to environmental shock | 5% minoxidil solution 2 times a day |
| Folliculitis or inflammation and infection of the hair follicle | warm compress Antibiotics (topical, oral) |
Pain after surgery due to disorder It is in the reaction signals to pain from peripheral nerves that may be cut during surgery or stretched and with conventional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or pain relievers Stronger like oxycodone or paracetamol is controlled with 30 mg codeine.
Sense of stretching and stiffness of the skin in the wounds Harvesting area (hair bank) after the implantation procedure with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Local relief may be achieved by moisturizing the hair removal area two to three times a day subside.
Using an ice pack on the area Hair removal for at least 15 minutes and 4 times a day can help to reduce pain
Numbness and numbness often on the forehead (after nerve block in the area above the eye/spinal nerve) or on the middle area of the scalp and The tip of the head occurs after the removal of the skin strip by the FUT method. Numbness usually resolves within 3 to 6 months, but can take up to It can last for 18 months and rarely causes permanent sensory damage.Swelling of the face
Facial swelling in the form of swelling on the forehead On the third day, the surgery begins and continues to the areas around the eye socket and down to the face does For some patients, swelling and ecchymosis (bruising) around the eyes happen The problem causes a lot of concern on the part of the patient, but after 3 to 4 days or so, often in It subsides on the seventh day after the operation. Swelling of the skin, usually due to the injection of large amounts of salt In anesthetic materials, it occurs either due to seroma or hematoma from implant incisions. Researchers in a research, skin swelling after surgery as the most common complications of hair transplant They named.
from triamcinolone acetonide first to The composition is used in anesthetic solution and subcutaneously. Corticosteroid use Food is also included in post-operative care for a short period of time. In this article, Dr. Tommy Huang, intramuscular betamethasone 1 mg per 10 kg of body weight for two days followed by prednisolone 20 mg orally prescribed daily for 2 days. Although There is no clear evidence, some claim the addition of corticosteroids Systemic and 50 mg triamcinolone acetonide to mL 50 combination of lidocaine, swelling after surgery from Reduces 20% to less than 5%.
It is said that Abbasi solution (100 ml NSS salt solution, epinephrine 1 mL (1:1000) and triamcinolone 40 mg), It reduces post-operative swelling by 95-97%. Triamcinolone mg 40 Muscle can also reduce swelling and severity be it.
However, even after using steroids And doing all these preventive measures, in case of swelling around the eyes, does not do much We can do to prevent its development. Thus, a method for placement The head is arched, lying on its side, or parallel to the back of the head with the floor for 1.5 days whenever possible, it was suggested by Dr. Hovan And as a result of this test, 94.5% of the patients in his research from the statistical population (N = 1200), without swelling or swelling up to 1 cm below Anterior hair growth line (swelling degree 0) reached with 80.7% satisfaction rate were sick
Using a suitable and comfortable headband
On the forehead and above the eyebrows, a knotted headband, or a compression bandage under the hairline
Controlling the abnormal accumulation and progression of water and interstitial fluids under the skin towards the forehead.
Due to gravity, it is useful. Keeping the head elevated to reduce venous and lymphatic pressure
from the level of the heart in the first week or leaning back at an angle of at least 45 degrees in 24 hours
First after grafting is recommended.
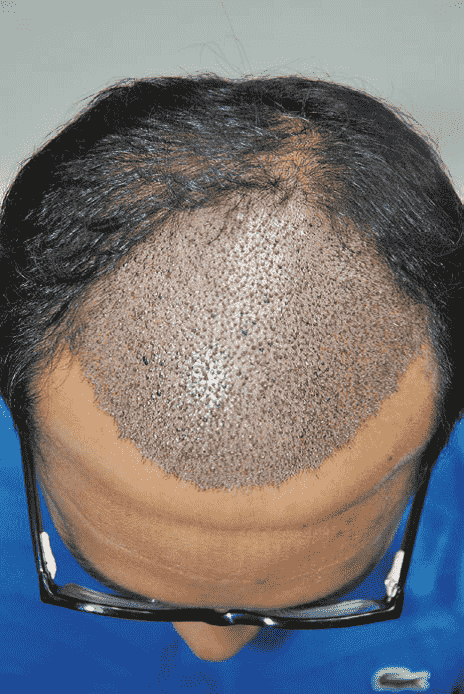
Image 2. Forehead swelling
If the swelling continues, these procedures should be repeated in a few days to be Post-operative swelling can also be reduced with an ice pack and placing it on the forehead. After the operation, he controlled.
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting after surgery, usually on the night of surgery, as an effect Side effects of drugs used during surgery such as sedatives (diazepam, midazolam), drugs Analgesics, including codeine, antibiotics, and anesthetics, may occur. often Cases of immediate nausea after surgery and during surgery are usually due to vasovagal reaction.
Postoperative nausea and vomiting to several patient-related factors that
It depends on the sensitivity of patients and includes female gender, non-smoker
being, anxiety, previous history of postoperative nausea and vomiting, motion sickness or nausea
Car and movement, and migraine.
Prolonged exposure to nauseous anesthesia (eg, opioids) of the strongest evidence of risk
Nausea and vomiting after surgery.
2. Revive yourself and your staff with training Update cardiopulmonary and first aid. Ideally, a complete emergency trolley to Along with all the appropriate medicines for emergency cases, it should be ready and present in the clinic. 3. Total volume of anesthetic used It is widely influenced by the duration of the operation. Whatever the team specialized in performing surgery It is more efficient, the implantation procedure is completed faster and less anesthesia injection is required was And finally, the risk of poisoning with local anesthesia will be lower. 4. Awareness and familiarity with simple actions which calms hiccups and relieves vasovagal reactions. If not Success in these actions, use the right drugs for the conditions.5. Phone number of internist, cardiologist, pulmonologist, or anesthesiologist Have it available for immediate reference if needed. 6. Completely to all patients both Explain common and uncommon complications that can be encountered before surgery. all The information should be completely in the instructions before and after the operation and in the consent form be written A patient who is well informed about the condition usually has less problems had Agreement and friendly communication with the patient is essential. 7. Giving antibiotics to the patient, before And after the operation, it depends on the opinion and discretion of the surgeon. To avoid infection, the emphasis should be on aseptic techniques during surgery. In case of infection, prescribing antibiotics They have priority with a wide range. In the case of frequent and severe infections, always culture and test Antibiotic sensitivity will help to better guide medical management. 8. From asking teachers and colleagues Do not be afraid in the field of hair transplant surgery! Their wisdom and experience is very valuable.
Complications of skin strip removal in hair transplantation
Background
FUT hair transplant is currently a method It is the gold standard in hair graft harvesting and it has an excellent result in terms of beauty and in most cases it leaves the least scars. However, due to popularity The rise of FUE hair transplants, which are exaggeratedly advertised as scar-free and pain-free is, the number of operations performed in this way (FUT) decreased to 51% of all hair restoration surgeries has been found FUT one The method is relatively safe, but like any other surgery, even with the presence of an experienced doctor It can have common and unusual complications.
Bleeding and hematoma
Every surgery inevitably has unexpected bleeding and hematoma, and from It cannot be prevented. But in hair transplantation by FUT method, the probability of its occurrence is less It reaches from 1%.
Prevention
Preoperatively, identification of patients with high blood pressure and disorders Hereditary bleeding like Willebrand's disease is very important. Patients should also be asked Take nutrients such as vitamin E and blood-intensifying drugs such as aspirin and warfarin stop at least 1 week before the operation.
Coordinating with the doctor responsible for the operation regarding the discontinuation of these drugs and not Exacerbation of existing medical conditions is also important.
During this procedure, to prevent bleeding, inject sufficient amounts of Tumsen anesthetic solution, and then make a cut and separate the follicles from the skin surface as much as possible. Using clamps and forceps for traction, avoiding electrocautery for coagulation, and approximation And accurate proximity during suturing will be useful.
Treatment
Most bleeding can be stopped with gentle pressure for 10 minutes did If this was not enough
More stitches may be needed. With delayed bleeding Due to the hematoma, along with local swelling and sensitivity, the wound should be opened and drained, and the bleeding vessel The donor should be coagulated and sutured again.
Infection
Wound infections in the area of hair removal (donor) by the FUT method are very rare and occur It is only 0.1%.
Prevention
Identification of patients with uncontrolled diabetes and diseases The defect of the immune system is very important.
During surgery, the wound of the hair removal area (donor) must be disinfected and cleaned and rinsed with a saline solution to remove the remains and parts of the transferred hair be.
Many hair surgeons use prophylactic antibiotics do not recommend, but
The author and researcher of this article regularly take oral antibiotics prescribes just before the operation.
Treatment
If the hair removal area is due to sensitivity, painful swelling, secretions
If pus and redness become inflamed, bacterial culture should be taken from the wound and antibiotics should be used
Topical and systemic (eg, cephalosporins, penicillins, and tetracyclines) should be initiated.
but this is very unusual.
Pain
The pain in the FUT method is more than the FUE method and this is the main reason FUE method is increasing in popularity. This pain is caused by tension and inflammation around the wound, but this is in Often times even in extensive hair transplants (planting 2500 or more grafts per square centimeter on the head with small distances) is negligible and therefore controllable. Less than 10% of patients need to take drugs They have painkillers for more than 3 days and painkillers that are widely used Acetaminophen contains codeine. However, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are the preferred drugs They are the authors of this article because narcotics and sedatives have more restrictions And the side effects of nausea and blood pressure are more serious.
Neuralgia and neuroma
Neuralgia refers to severe paroxysmal pains related to the nerves of the head Neck refers to neuroma, nerve swelling or pain caused by the growth or tumor of nerve tissue and although it is very rare, there are also patients who implant immediately after the operation By FUT method or during it from pain They suffer from throbbing or tingling and are sensitive to pain. That this pain is caused by injury to Sensory nerves, especially the occipital nerve (back of the head) is large, small or third while the sign Giving any abnormal appearance of the wound in the area of the hair bank is not observed.
The researcher of this article once encountered a disease that was implanted into FUT method prescribed by another doctor and complained of severe pain and an elastic mass around the wound in the hair bank area. After performing a biopsy, a trauma neuroma was diagnosed, which is a rare lesion.
Treatment
The following strategies have been reported to relieve neuralgia, but Surgery should be considered for neuroma:
• Local anesthesia and steroid injection
• Botulinum toxin injection (Botox) type A
• Radio neuromodulation
Tingles and tingles
Temporary numbness in the upper part of the section of the hair bank cut in the back of the head.
It is inevitable that it is due to the presence of sensory peripheral nerves on the surface of the skin
are cut This symptom usually lasts for several months but can last up to 2 years
kill If major nerve branches are cut, permanent numbness may occur, but fortunately
The author and researcher of the article has never encountered this case.
Kloid/hypertrophic scar
Statistics of keloid scar formation and hypertrophic scar on the scalp It is low compared to other parts of the body, although its prevalence is higher in Asia The white race is European and Caucasian. The author of the article only two cases of keloid scar formation experienced in the last 25 years, but hypertrophic scars in Asian races very They are not unusual and rare (image 1 and 2)
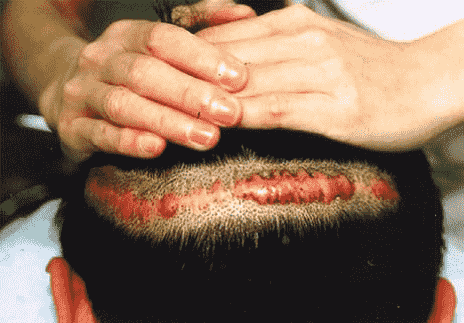
Image 1. Keloid scar
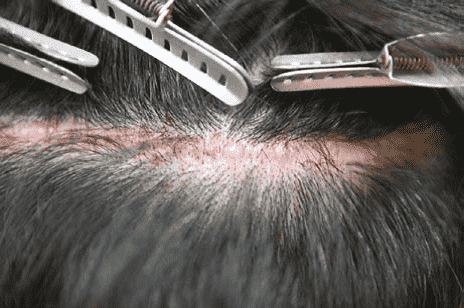
Image 2. Hypertrophic scar
Prevention
If there is no history of keloid or hypertrophic scars, identifying patients It is impossible for this problem to happen to them before the operation, and performing a pre-operation test for All patients are inoperable.Treatment
A series of intralesional steroid injections and the use of silicone gel Medical grade is recommended. Most hypertrophic scars resolve within 2 years. For steps Next, the possible FUE method is a preferred option, but the patient may have financial reasons or unwillingness to shave Sir would like to do the next sessions again with the FUT method. In these cases, It is important to obtain the patient's consent for repeated risks and to repeat the schedule of subsequent sessions. inside ActionCare and precision as much as possible to avoid stretching and minimize Bleeding is very important to reduce the risk of scarring.
Wound opening and necrosis
This is a very rare complication caused by local ischemia (anemia). which is due to the tight closure of the area, and the combination with other conditions such as infection, bleeding and others Circulatory disorders have occurred due to uncontrolled diabetes or other conditions (Fig. 3)
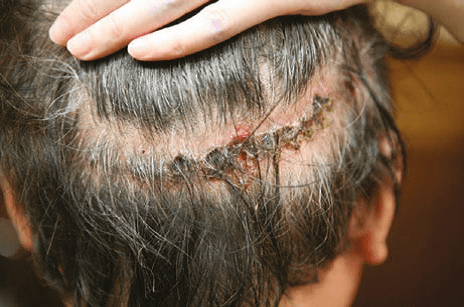
Image 3. Necrosis and effluvium
Treatment
The wound should be cleaned and sutured again. If possible If there is no infection prevention and there is a lot of stretching, use of systemic antibiotics It is mandatory and the wound should be opened and the possibility of treatment with the intention of secondary healing of the wound should be provided.
Effluvium
Sometimes the hair around the hair bank suddenly falls out. which is called shock-induced shedding in the donor area. This shedding, 1 to 9 weeks It happens after the operation, but it is more common between 3 and 5 weeks. And usually with firmness Closing (stitching) the wound area is related but can be missed even during the first session It is accompanied by scalp pain and is more common in women.
Bertram states that this phenomenon is an anagen (active phase). hair growth) than telogen effluvium, and due to tightly closing the wound area, local blood circulation disorder, and local ischemia caused by anesthetic agent Thomson, adrenaline and the toxic effect of absorbable suture falls.The patient is explained that this situation after 100 days It heals on its own and no treatment is required (Figure 4).
Stretching and expansion of the scar
This problem is the biggest patient concern for the FUT procedure, although mostly the scar Lines are undetectable unless the hair is very short. Recent techniques to Scar reduction helps (Table 1), but in 5% of patients after the first session, And in 10 to 15% of them, after the next sessions, wounds with sizes of more than 3 mm are created. which is due to the following factors (pictures 5 and 6):
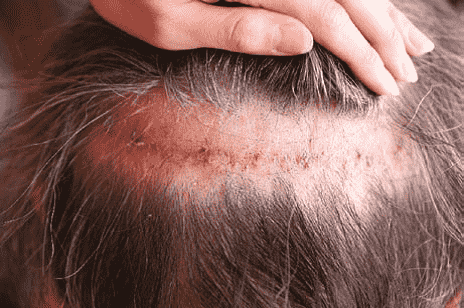
Image 4. Effluvium
Table 1 Techniques and management of scar widening or stretching
| identification Patients who are prone to ulcer spread |
| Evaluation Elasticity of the scalp |
| Scale loose skin |
| use From the laser light to magnify the harvest area |
| use from the laxometer |
| avoid From excessive tension of the suture |
| to cut Part of the scalp |
| use from intraoperative hyaluronidase |
| to Minimizing the duration of follicle transfer sessions |
| Technique open |
| use From the trichophytic suture |
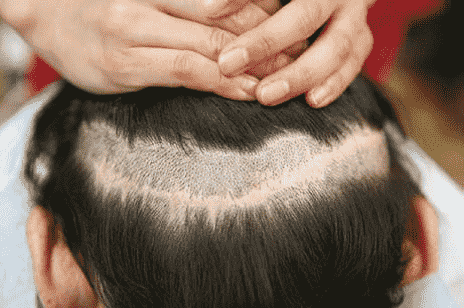
Image 5. Scar expansion and stitch marks
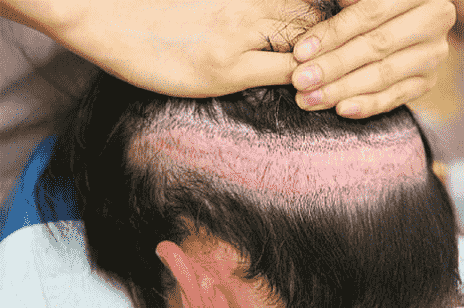
Image 6. The widening of the scar after several sessions of hair transplantation
- Predisposing conditions of the patient
- Younger patients with lax scalp are usually more likely than older patients whose scalp It is hard, they mostly suffer from scar expansion in the area of the hair bank (back of the head).
- – Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (disorder Genetic in collagen metabolism with signs of skin and vascular fragility and increased elasticity skin, etc.)
- Wrong design
- Too low body position/Bad shape
- Wrong techniques
- Too tight suture leading to excessive stretching/Excessive bleeding/Incision or division of the follicle Too much
Treatment
- Re-stitching
- Several reports on how hair bank area scars heal (with/without There is the use of tissue expanders, linear/zigzag, single layer/double layer/three layer) but none cannot guarantee the best solution.
- Camouflage with FUE method
- Placing hair grafts on scar areas is a good option, but many patients They prefer the grafts to be implanted in the lower back areas of the head, rather than on the scars caused by Hair transplant by FUT method.
- micropigmentation or scalp micro scalp
Complications of the planting area hair
Complications of the first few weeks (first to fourth week)
Complications after the operation The name of any type of adverse, unwanted and direct result of surgery that affects the patient is defined In hair transplant surgery, postoperative complications with a report and estimate of the overall complication rate Only 4.7% is very unusual.
Pain
After planting steps Hair, some of my patients (the author of the article) from a tolerable pain, usually more in the area The hair bank complains to the transplant area. Pain can be controlled with oral pain relievers He did, and I paracetamol 500 mg every 4-6 hours together with orticoxib 120 mg once a day I prescribed for 2 days. After that patients stop their medication and more discomfort It is not reported.
It usually doesn't happen
When my patients complain of severe pain, and in such a situation, for patients
Opioid analgesics are prescribed along with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Whose acne is it? Pustule / Pimple
I always tomorrow On the day of surgery, the patient after the first shampoo after the operation and to check the bank area I visit and examine the hair and implant area. Sometimes, purulent follicular acne
And small red pimples They appear on the planting area. On the fifth day, after the implantation, the patients again for Sutures are removed, and few of them show pustular and inflammatory lesions give.
Patients usually from Do not complain of pain or sensitivity to touch in the affected area, but experience itching and burning there is While these skin lesions may be suspected to be of infectious origin, to When isolating pathogenic organisms in warm staining and identifying the type of bacteria If it is negative, they are known as sterile waste. Possible explanations for the formation of this Pustules and boils include the body's reactions to external factors, possibly to glove powder Surgery, hair needling, etc. In a research, the occurrence of bacteria in the blood, in scalp surgery and neck, it was found that out of 45 patients, acne-causing bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes) occurred in 2 patients, and Staphylococcus hominis bacteria occurred in only 1 patient, that is, only 7%. This is recommended Current guidelines of the American Heart Association against the use of prophylactic antibiotics in patients Does not support artificial heart valves for head and neck surgery.
Management includes evacuation pustule by scraping it with a sterile needle and applying gentle pressure using the tip of the ear The eraser is for removing the material inside.
Then to the patients It is recommended to do spa compress for 3 to 5 minutes twice a day. with Using these two methods, the problem can usually be controlled. When infection is suspected We are, warm staining to identify bacteria, wound culture and antibiotic sensitivity test should be done be done Use of antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins or macrolides For people who are resistant to conventional methods and if there is evidence of infection on staining or Cultivation is assigned.
Inflation
One of the most common Complications in the recipient or hair transplant area are swelling and edema, mostly within 3 days to a week It is determined after the operation. Patients often suffer from swelling along the front of the head, forehead and surrounding area Eye to upper cheek area complain, and sometimes additional swelling with impotence be accompanied in opening the eyes. Edema or swelling is not red, warm and painful. that some of Whether or not patients experience edema may depend on the composition of the Thomson anesthetic used on the recipient area of the hair follicles, the amount injected, and the duration of the operation have.
After the operation, the size
Treatment to control swelling includes short-term oral steroid treatment, sleeping at an angle of 45 degrees,
Adhesive tape or headband below the hairline, using ice packs or frozen pea packs
It will be 20 minutes. Among all the strategies to control postoperative swelling in the surrounding area
Eye, a more effective method was discovered in which the combination of 100 ml of normal saline + lidocaine
2% + 1 epinephrine 1/1000 + 40 mg triamcinolone
It is used in the hair transplant area during surgery.
Redness of the hair transplant area
During the first week after implantation, the hair transplant or recipient area has A little redness or erythematous. This phenomenon is harmless and may be accompanied by a little swelling and it resolves itself in about 2 to 4 weeks.
Side effects during the first month
whose formation
Approximately 4 weeks after hair transplant, there may be cysts in the hair transplant area appear and appear as soft lumps with a diameter of 0.5 It is up to 1 cm. These cysts are skin-colored or slightly red, without hair growth on top The lesion and their overlying skin may be stretched and shiny. Patients generally They are not painful, but some may itch. Creating cysts seems It is due to the micrografts getting stuck in the subcutaneous tissue, so that the oil secretes It is accumulated by the sebaceous glands without any outlet until the hair shaft falls out. Carrying grafts is another explanation for the cause of these cysts.
often by using spa compresses twice a day quickly and They disappear within a week. Some of them need to empty their contents to The upper part of the cyst is cut with a No. 15 blade. Discharge of an oily substance Sometimes it will be seen with pus. The presence of erythema (redness of the skin), pain and sensitivity is possible indicates an infection, in which case I would start prescribing antibiotics. choice Among the antibiotics in general, penicillin is for gram positive bacteria.
Post-operative effluvium/hair loss due to shock
All hair transplant doctors experience these side effects as Resident hair loss in and around the transplant recipient area as well as the donor or bank area Hair is described. This happens between 2 and 4 weeks after the hair transplant operation and is impossible It is a prediction. The size of the affected area varies from a small spot to an area as large as 5x4 cm.
Effluvium after surgery may be an anagen or telogen effluvium. According to some, the cause of this effluvium is trauma or shock caused by hitting the existing hair when it is created
Gaps and compromised blood flow. Usually effluvium caused by surgery, spontaneous
4 months after shedding is resolved; However, some very short hair may be able
not to be restored and permanently destroyed.
Complications of surgery in the fourth month
Remaining hair pieces (remaining root)
Patients may around the 4th to 6th month after the hair transplant operation, Notice the roots without hair growth of 1 to 2 mm. This hair is not during the process Telogens are shed and not grown together with other grafts. in case of outside By removing these remnants of the hair root, cut stems that cannot grow hair are observed, and so on In this order, it is recommended to remove all of them, because they are unnatural and may be reactive give inflammation
If you frequently see hair root remnants in patients, It is very important to evaluate the method of cutting grafts by your hair transplant team. in Ideally, pear-shaped follicular unit micrografts have a close epidermis (skin). To the hair, they contain a delicate cap of skin on the transparent skin ridges, and amount They have a little bit of fat in the depth of the skin ridges to be grasped with forceps or tweezers.
Numbness and numbnessNumbness and numbness often occur in the hair transplant recipient area and usually It continues for several weeks to several months (2 to 3 months) after the operation.
The patient should make sure that the sensation in this area goes away with time be made To minimize anesthesia, it is important that the incisions are as deep as It should be placed right under the bulbs (bulbs) of the hair so as to avoid unnecessary nerve damage be.
Raising the surface of the skin
When the hair transplant recipient area is completely healed And the grafts start to grow in the fourth month after the operation, some patients may Their attention should be drawn to the indentation of the skin tissues around the transplanted follicle, which is somewhat higher It is placed from the surrounding tissue and is called cobblestoning, and if round grafts are used And large hair occurs when micrografts or follicular units are used are known as Tenting. The occurrence of this condition is due to the use of large hair grafts round, using grafts that are poorly prepared with epidermis or skin attached, and very deep slits leading to overhanging of the inserted graft at least 1/3 of the length The whole is connected by surgeons.
To avoid these conditions, cutting with the correct depth should be considered be created along the length of the graft. After insertion, raise the grafts just slightly above the cut surface And only use properly prepared and cut grafts. Actions Electrodesiccation is related in order to improve the skin surface and the use of grafts Extra tissue, microdermabrasion or shaving the raised part.
Indentation
Unlike the condition of raising the skin surface, indentation of the skin and tissue It is around the hair grafts (perifollicular). This situation is in the form of a hollow, a hollow The hole that is seen in the orange peel state shows itself. The reason for this is placement Hair grafts deep into the incisions or making excessively deep incisions in the area The hair bank is so that the graft moves in its place and moves or from the inside The slices fall out.
To avoid indentation, the grafts should be slightly above the surface Inserted slices. Indentation is difficult to correct and usually requires scar punching, electrodessication, or microdermabrasion of the skin around the indentations.
keloid / scar
Keloid is a type of scar that is an overgrowth of granular tissue (around the wound) which is slowly replaced by type 1 collagen. They are initially in the face Pink, rubbery, stretchy, and shiny plaques are found in the wound area, but then from the range The main wound spreads. Keloids are found only in humans and in 5 to 15% of wounds occurs. This condition affects both sexes equally, although in women And probably because of the cosmetic and cosmetic consequences related to changing the body shape, the percentage of incidence is higher has shown.
Frequency of keloid occurrence in people whose skin is pigmented has more, 15 times more than people whose skin has less pigments. However, there is good blood flow and storage in the scalp and the probability of keloid is very low is Collecting this information throughout the history is vital and necessary so that patients can be correctly be advised and guided.
Current keloid control includes treatment with intralesional corticosteroids (cortone), 5-fluorouracil, bleomycin, interferon, cryotherapy (cold therapy) and verapamil is Other treatment methods are the use of local silicone gel/sheet or the use of lasers It is like pulsed color laser and Nd:YAG laser with long radiation time. I usually inject triamcinolone I use 40 mg/mL intralesion with amounts dependent on the size of the colloid, 1 month injection is done for about 2-3 months , and with this, small to medium keloids are smoothed.
Complications of the operation in the sixth month and after that
Hair growth with an unnatural appearance
When the hair starts to grow in the fourth month after the operation, initially Before growing with normal length, density and thickness, it has an unnatural appearance. Grafts first They may be wavy or knotted and unnatural when growing, but after a while months, they become smooth and take on the natural texture of the patient's hair. Early growth is possible Different diameters and calibers, often with finer threads, but sometimes with thicker threads have more.
Grafts with different growth direction
The rule of hair transplant is to follow the natural angles close to the existing hair
The person himself is the location of the grafts in the scalp. Usually the angle of the hair shaft
It varies from 90 degrees in the crown of the hair (back and middle part of the head) to 30 degrees in the hair growth line in the front of the head.
In the skin behind the head and On both sides, the angle of the hair is very accurate and may be almost flat against the scalp comment I am looking for fine and thin hair available in the hair transplant (recipient) area and I only follow the example of their growth and angle.
Abnormal hair growth line
Hair growth line that is too high or too low in the process of hair transplant It will create an unnatural appearance. To create a symmetrical and attractive face, law Follow a third that has a ratio of chin to tip of the nose of 1/3, tip of the nose to the top of the area The ridge between the two eyebrows is another third, and above the area between the two eyebrows to the hairline is one Another third.
It is easier to correct a high hairline because It can be lowered during the next hair transplant session. Correction of the hair growth line that is over The lower limit is more difficult. Because treatments such as punching and graft removal , separation and cutting with No. 11 blade and magnification. Also possible laser Hair removal to remove unwanted grafts or reduce the hairline in the eye be taken.
Another common mistake in creating a hairline is that too much Be smooth The hairline is actually not a straight line, but an irregular jagged area, and Aligning and placing the grafts along a straight line creates a synthetic appearance will be In addition, only single hair grafts should be used for the hair growth line. Placing two or three hair grafts in the hair growth line makes this area look misshapen The result is easy to guess that the person has done hair transplant.
poor graft growth
The best results of hair transplant surgery can be seen during 6 to 8 months after evaluated by surgery, although some doctors believe that hair growth can be up May the twelfth month continue.
When the recommended conditions during the operation and aftercare If not performed correctly, hair growth in patients may be poor.
Poor growth in hair transplantation to growth less than 90% during at least 8 months after the operation It is said Dr. Jerry Cowley in a survey found that in private practice moderate growth Weak 6% and in the range of 0-25%. The most important factors determining graft survival, Preventing physical shock or trauma to the grafts and ensuring adequate oxygen delivery It is required for implanted hair follicles.
Result
The side effects discussed above are the ones that often occur in hair transplant surgery
can be seen The moral and principle message and rule for all surgeons is that our profession
be well controlled and in terms of requirements, instructions, procedures and care
required for a successful hair transplant operation. In this way we can
Minimize the complications caused by the operation and give the patients the best results they deserve
to give them as a gift.
Complications of FUE hair transplant
Introduction
Today, most patients use the follicular unit extraction technique or FUE according to the nature It is less invasive compared to skin strip implantation technique or FUT technique for hair transplantation They prefer This method has the advantage of using scattered micro-scars instead of linear scars And also the lack of stitches, however, the FUE method is not completely without complications And there are problems that may occur in this method, which are divided as follows:
1. Complications of donor area or hair bank1.1 Post-operative general discomfort
2.1 Special complications caused by extraction Follicles
2. Complications of the recipient area (hair transplant area)1.2 Complications caused by the creation of the recipient area And hair transplant in it
2.2 Specific complications of grafting
3.2 Complications related to beauty
3. Medical complicationsComplications of the recipient area or hair bank
General discomfort after the operation
FUE hair transplant is a relatively non-invasive and safe cosmetic surgery. However, some The following problems have been reported by patients:
Discomfort after surgery in the hair bank area
Pain and discomfort after surgery in the hair bank area in patients who They have had hair transplant by FUE method, there is. Pain may occur in the evening or night of surgery occur, but it usually disappears in the next few days. The researchers of this article antidote Prescribe mild painkillers such as paracetamol, especially for the first 5 days, to reduce pain and inflammation They do.
Secret
After the patient is placed on a pillow for implantation, Pressure is placed on the hair bank area, which leads to the secretion of serum fluid and blood. sick You may be worried by seeing this fluid on the first morning of the day after the operation. Therefore, we We recommend that the patient place a dark colored towel on the pillow to prevent recoil to catch any discharge etc.
In rare cases of bleeding in the hair bank area, the patient should be treated with Use sterile gas to apply firm and constant pressure for several minutes. Usually not necessary There is no other action.
Tingling, numbness/itching or burning of the skin
Tingling or itching in the hair bank area after the FUE procedure is unusual, and in
The occurrence is limited to small areas.
Severe itching
Some patients after recovery and restoration, itching in the bank area They experience hair. The itching will usually disappear after cleaning the scalp properly became However, sometimes we have to advise the patient to use aloe vera gel for Use to soften the desired area and reduce itching.
In case of severe itching, steroid lotions and antihistamines It is also recommended.
Specific side effects related to the FUE method in the hair bank area
White scars in the hair bank area
Many people mistakenly think that FUE is a non-residual procedure It is to leave scars; However, this is not accurate. Donor areas or hair bank Patients in the FUE method are usually left with round, white spot-like scars Atrophic color is improved. These scars are hairless, pigmentless, fibrotic and palpable are Although these scars are usually not visible unless the hair is covering it Areas should be completely shaved, in some cases scars can be seen in the examination of short hair Observe closely, especially if excessive hair removal is done. Also, if groups Follicles are removed continuously and without pause, some of these scars can fuse together and create a bigger wound that is more visible. Because these wounds are less Be visible, certain measures recommended by doctors in improving the hair bank area It is useful. These actions include:
• Use of ACell MatriStem injection treatment in hair bank areas. this Treatment method, by reducing or eliminating fibrotic scars, help to heal wounds and scars does
• Removal of finer follicular units. It means that as Intentionally, only a few hairs are removed from each follicular unit and the rest of the hair remains. this hair The rest continued to grow and created a more beautiful area so that this The area will not become hairless.
• Using smaller punches for a better scar effect. Punch size Larger than 1 mm compared to smaller punches of mm 1, leading to creation The scar becomes more noticeable. However, the result of using punches Smaller, higher grade cuts and fewer hairs per graft. by using From punch size 1 mm, average hair per unit Follicles can exceed 2.5 while the size is 0.75 mm, the average number of hairs up to 2.1 in Each graft is reduced. Therefore, between the punch size and the number of hairs per follicular unit In order to achieve the best results, balance must be established.
The researchers of this article do not use the first two options. They are from
The third option, smaller punches (mm 0.8 or 0.9) to maintain the balance between the number of hairs in each
Graft (they try to keep this number around 2) and the size of the scar used
do.
They are because pale scars in patients of Indian race and Colored skin is characterized by a higher contrast of skin pigments compared to the white race They are more prominent, they do not use 1.0 mm punches (Images 1 and 2).
They extract the grafts in a zigzag fashion, with Ensure that there are no two gaps in the hair bank area, to avoid overlapping of the grafts harvested, they do not fuse or become one. With this method, when the grafts to If they are taken continuously, the appearance of these points will be less clear and noticeable.
تصویر 1. تضاد بیشتر اسکار در بیمار هندی
تصویر 2. تضاد کمتر در بیمار سفیدپوست
اسکار شبیه بیدخوردگی یا ظاهری شبیه زائده های سیفیلیسی
بعضی از پزشكان افراطی در روش تهاجمی، گرافت ها را از ناحیه بانک مو بیش از حد برداشت می كنند. نتیجه این کار می تواند ظاهری ناهنجار شبیه بید خوردگی یا زائده های سیفلیتیک در این ناحیه باشد (تصویر 3) که زمانی که بیمار موهای خود را تا حد زیادی کوتاه کند، بسیار مشخص و برجسته به نظر خواهد آمد. از این جهت برای جلوگیری از ایجاد نواحی تکه تکه منجر به ریزش مو، فاصله دار کردن استخراج گرافت ها به طور مناسب به شیوه زیگزاگ اهمیت دارد (تصویر 4).
افلوویوم پس از عمل
پس از جراحی، ممکن است در ناحیه بانک مو افلوویوم رخ دهد (تصویر 5)، اما نسبت به ناحیه گیرنده یا کاشت مو کمتر شایع است . این شرایط به صورت ریزش موی پراکنده یا موضعی به مدت 4-6 هفته پس از عمل کاشت مو به روش FUE اتفاق می افتد. This hair loss is temporary and resolves after 3 to 4 months.

Image 3. Scar similar to willow erosion

Image 4. Zigzag pattern in the extraction of follicles

Image 5. Effluvium or shedding of the hair bank area

Figure 6. Grafts buried under the skin
This phenomenon can cause a stop due to excessive harvest Disturbance in blood flow. In this way, our researchers harvested the grafts in one session 2000 to 2200 hair strands are limited and as a result effluvium is observed in the hair bank area. will not
Grafts buried in the skin
This condition is usually seen when using slow punches. During the extraction of follicles, when the punch quickly and without control into the dermis or
Enter the middle layer of the skin, the hair follicle into the skin, where it needs to be implanted
will be pressed. Our assistant researchers removed the buried grafts at the same time
Follicles come out; Otherwise, it may cause cyst formation
(Image 6).

Image 7. Folliculitis in the area of the hair bank

Figure 8. Mucous cysts in the hair bank area
If the hair grafts are not completely removed and the components If it stays buried in the skin layer, folliculitis (inflammation or infection of the hair follicle) occurs give (image 7).
Mucous cystsSometimes in the FUE method, the grafts can be moved under the surrounding skin
change location, in this situation, if they do not come out of the skin, it may happen later with production
Multiple painless swellings in the hair bank region can form cystic masses (picture 8).
Possible reasons for the formation of these subcutaneous cysts are: From:
- Deep separation through the entire mesh skin: should FUE punches to scrape around Each follicular unit should only be used to the depth of the middle surface of the skin. so that the grafts are still attached to the mesh skin. If deep separation from full depth If the mesh skin is done, these attached grafts are lost and can easily be under
- Excessive swelling can extend into the subcutaneous layer, causing the graft to separated grafts are easier to pull down and absorb.
- Buried grafts that fall out during extraction
Slow punches through Deeper penetration can cause the cutting of connected grafts in the deeper layers of the skin transfer of grafts.
Necrosis or dead tissue in the hair bank area
If the extraction of grafts is not done correctly, in the bank area Rarely, necrosis also occurs.
Transparent or thin appearance in the hair bank area
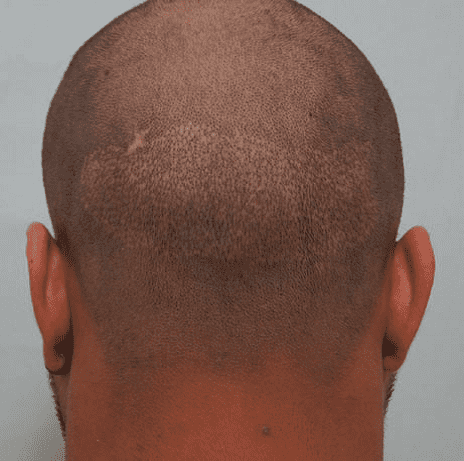
If more than 20% of scalp hair in the hair bank area is removed in one session, Harvesting is considered excessive, and may lead to thinning and low back Look at the appearance of the hair bank area and the hair loss is fragmented (image 9).
Image 9. Low back appearance due to excessive hair removal in the area
hair bank
The researchers of this article prefer to have multiple sessions within 6 to 8 months to harvest the grafts. They usually remove 20% of the follicles in the first session They harvest 15-20% in the second session and 10-15% in the third session, leaving 50% of the hair in the hair bank area to improve the appearance. The hair does not look thin.
implanted hair loss
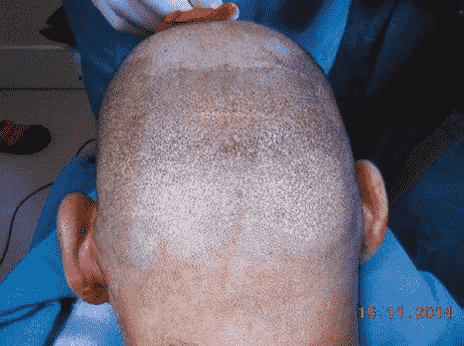
When grafts from outside the safe area, especially in patients Younger people experience persistent hair loss, these grafts can be harvested later due to advancement Natural pattern of hair loss. This process is usually with grafts taken from the margin The posterior bone occurs at the back of the head and thus after the implanted hair falls out, the piece Abnormal baldness or low back occurs in the transplant recipient areas. This condition It can also lead to the formation of white spots in the area of the crown of the hair, which increases shedding The hair and the rise of the hair margin become more obvious. Extraction of grafts from the safe area of the hair bank always It is more reliable, divided into eight major and six minor regions by John Cole is While the above method is useful to a great extent, article researchers have their own method His invention to define the safe area of the hair bank in the back of the head through his observations of patients have grade VII. They have determined the safe area of the hair bank by two parallel lines It is marked in the upper and lower parts of the back of the head. Upper line, upper border It connects the two earlobes and the lower line, the lower part of the two external auditory canals connects Always limit the number of grafts taken outside these areas It is very important to prevent the risk of low back in the future in these areas.
Summary
To fully understand the possible complications related to the FUE procedure in order to avoid
These complications and achieving better results are important. Appropriate selection and advice
The patient, using adequate precautions during each stage of the implantation procedure, and follow-up
Useful measures after the operation guarantee the best possible result for the patient as well as the surgeon.
Folliculitis in hair transplantation:
The point of view of dermatologists
Folliculitis in hair restoration surgery
Folliculitis is a type of follicle-centered infection (inflammation or infection hair follicle) which is usually with the surface part of the pilosebaceous unit (associated with sebaceous glands) mainly It begins with the opening of the funnel-shaped hair follicles. Usually this happens in every area Hair appears on the body as an erythematous pustule. This phenomenon can be He classified based on the depth of invasion (superficial and deep) and its microbial root.
In hair transplantation, the type of folliculitis that we usually see, the type Superficial (picture 1) is in the form of small pustules in the opening of the follicle Hair appears. And they may quickly turn into multiple appendages after a few days (Image 2). According to Bonagan and Patovanish, appendages start to appear from 2 days to 6 months after The link of the follicular unit is variable.

Image 1. Superficial folliculitis

Image 2. Multiple folliculitis
The laboratory culture of these appendages may be negative; For this reason, They may be referred to as "non-infectious" folliculitis. This condition may be caused by factors be accompanied mechanically such as friction, obstruction or follicular trauma, examples of which are grafts Hair and hair removal. In a 2014 study by Loganathan et al., sterile folliculitis, It was identified as a complication after hair transplantation, which constituted 23.29% of their research cases would give.
In the same way, Salanitri and his colleagues, the overall complication rate of a series of 533 cases of hair transplants performed from 1995 to 2006 reported 4.7%, which Folliculitis accounted for almost one-fifth of its cases with 1%.
However, folliculitis after hair transplantation may be due to infection Bacteria develop. Staphylococcus aureus, among other reasons, was found to be the most common pathogen It is in scalp folliculitis. Of course, it is possible to take antibiotics by draining the pustules treated locally and if the appendages are multiple, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics Start systemic for the patient.
Superficial or surface folliculitis may go to deeper layers progress and it is likely to turn into cork.
These appendages appear as deep and rooted nodes which may become painful when touched. The occurrence of such appendages even in cases where the operation The surgery is performed under very strict sterile conditions. The hair transplant surgeon must take the patient's history Examine and look for possible predisposing factors such as diabetes, blood disorders and defects complex in the function of neutrophils.
Pseudofolliculitis is a type of non-infectious folliculitis that occurs mostly in
Dark skin (black skin) is seen after shaving. This happens when
The growing hair follicle gets stuck in the skin and instead of leaving the scalp, it twists and turns
It grows inside the wall of the follicle.
This pathological process of folliculitis is still being explored and debated is whether transplanted grafts are buried in the deep layers of the scalp and as a result They grow inside the skin. To control such conditions, simply remove the involved follicle with They pull out.
Decalvans folliculitis is another type of challenge folliculitis It is suggestive that it may occur in the hair bank area as well as the recipient area. This is an appendage usually in the form of follicular-centered and erythematous pustules with hyperkeratous scales ( horn-shaped) and greasy starts around the affected entrance. Appendages may be in the areas Vertex (top and back of the head) may begin and progress to regional baldness. this The condition can also present as "folliculitis of tangled and sticky hairs", why? Many hair follicles may grow out of a single expanded follicle. Etberg and his colleagues in 2009 reported a case of developing folliculitis decalvans in punch grafts It has been described 20 years after hair transplantation. This disorder may be called coin declension Quaid is called "Quinquaid's decalvans", because its cause is still unknown.
Its symptoms include inflammatory alopecia, which leads to a swampy appearance Scalp thickening along with pustules, corrosion, scabs and crusts. Staphylococcal infection Related to this disorder, it is not the cause of its occurrence, but the opportunistic infection caused by the existing inflammation Before, it can cause this disorder.Management of these conditions is generally difficult because the progress of this The disease is characterized by increasing and decreasing And it can take several years. Use of systemic antibiotics for staphylococcal eradication Oreos is recommended.
However, after stopping the drug, the recurrence of the disease is also observed. Prescription drugs related to relapse can include rifampicin along with minocycline, acid Oral fusidic with topical mupirocin and fusidic acid with erythromycin. Injection Intralesional steroids may help reduce redness and relieve itching. use It can also be used as an intranasal topical antibacterial to eradicate the source of staphylococci It is useful.
Abstract
The abstract table is shown here (Table 1)
| Table 1. Summary of folliculitis topic hair transplant | |
| Summary of different types of folliculitis in hair transplantation and its related characteristics 1. Superficial folliculitis Folliculitis Sterilfolliculitis bacterial | - 2 days to 6 months after hair transplant - along with traction, blockage, follicular damage - Along with sweating, Staphylococcus aureus infection |
| 2. Deep folliculitis | - It may turn into cork Finding predisposing factors such as diabetes, blood dyscrasias, immune disorders the body |
| 3. Pseudofolliculitis | - Due to the growth of hair follicles and the hair being buried under the skin |
| 4. Folliculitis decalvans treatment difficult | - in the form of "complicated and attached folliculitis" - Erythematous follicular pustules on the vertex (top and back area head) (+) Sensitivity, swampy appearance, corrosion, scabbing |
Folliculitis after hair transplant surgery: from another point of view
Follicle caused by deep placement of grafts
Follicular unit transplant (FUT) is the primary method Hair restoration is done all over the world. To do FUT properly, the importance of matching Graft size/length is well known with cut size/depth. Hair follicles among patients It varies from 3 to 6 mm and can be different based on the race and personal characteristics of the person be Therefore, the depth of incision should be evaluated for each patient. A fixed length blade Have or without depth control can be used in some patients in a deep way Terry penetrates the subcutaneous fat. Improper control of the depth and placement of the graft afterwards can causing problems such as indentation, raising the skin surface and using grafts, folliculitis, Epidermal cysts, hair growth under the skin and other problems (Figure 1). Wang When adjusting the depth of the blade, he measured several grafts to determine the average depth, but V It did not accurately measure the changes in graft length in a patient over a certain period of time. cutting depth Correct varies from one disease to another, but it was previously believed that there was little difference It exists during the graft in the same person. Despite performing appropriate surgical techniques for repair Hair to create the appropriate depth for the recipient areas of the graft, the problems related to the control of the fracture depth It still occurs in some patients.
A study to assess whether there is a significant difference in graft length
There is a patient over time, it was done. According to this research, the length of the graft can
Be significantly different in the same person: most Korean patients have a length difference of 1 to
showed 1.5 mm, but 18.5% of them had a difference of 2 mm, 4.2% of patients, 2.5
mm difference and 1.7% difference of 3 mm between the longest and shortest graft in a single hair follicle (Table
1) showed. These differences are also seen in the follicular unit with 2 follicles
But it is less than 3 Folikol.
a
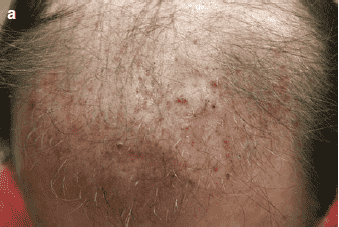

Figure 1. (a) Folliculitis, (b) Indentation. The cause of complications is the deep placement of grafts
Table 1. Length difference between the longest and shortest graft in 119 A Korean patient with hair loss with male pattern MPHL
| Follicular unit | 0.5 mm | 1.0 mm | 1.5 mm | 2.0 mm | 2.5 mm | 3 mm | total |
| Single hair follicle | 2(1.7%) | 42(35.3%) | 46(38.6%) | 22(18.5%) | 5(4.2%) | 2(1.7%) | 119(100%) |
| Double follicle | 12(10.1%) | 57(47.9%) | 36(30.3%) | 10(8.4%) | 1(0.8%) | 3(2.5%) | 119(100%) |
| Triple follicle | 43(36.1%) | 43(36.1%) | 26(21.9%) | 7(5.9%) | 0(0%) | 0(0%) | 119(100%) |
Most white patients, the difference is 1 to 1.5 mm per unit
follicular with a single hair follicle, but 4.2% showed a difference of 2 mm and 8.3% of them showed a difference of 2.5 mm.
In the FU method with
There was a single graft and a significant difference in the FU method with 2-3 grafts, but in Korean patients
E was less (Table 2). Therefore, the difference in graft length in both Asian and Caucasian races
European, with greater differences seen in Asian patients compared to European patients
will be
Table 2. The length difference between the longest and shortest graft in 24 A white patient with hair loss with a male pattern of MPHL
| Follicular unit | 0.5 mm | 1.0 mm | 1.5 mm | 2.0 mm | 2.5 mm | 3 mm | total |
| Single hair follicle | 5(4.2%) | 12(50.0%) | 4(16.76%) | 1(4.2%) | 2(8.3%) | 0(0%) | 24(100%) |
| Double follicle | 5(20.8%) | 9(37.5%) | 8(33.3%) | 2(8.4%) | 0(0%) | 0(0%) | 24(100%) |
| Triple follicle | 9(37.5%) | 11(45.8%) | 4(16.7%) | 0(0%) | 0(0%) | 0(0%) | 24(100%) |
Reasons of graft length differences, (1) genetically determined length differences, (2) graft length variation according to the hair growth cycle, and (3) transfer and placement during preparation It is a graft. Therefore, if we make only one deep incision in an individual, long grafts in The incision site will accommodate, but the short grafts will be placed in the deeper layer. as For example, if a patient has only one single hair follicle of 6 mm, 5 mm, 4 mm and have 3 mm in the area of the hair bank, and if we do the cuts at a depth of 6 mm then a 6 mm graft will fit properly in the incision site, but the graft 3 mm, will be placed 3 mm deeper than the proper depth, which can lead to The occurrence of folliculitis, cysts and indentation (picture 1).
Sometimes during the preparation of grafts in the FUT and FUE method, grafts are possible cut To avoid deeper sites in the transplant recipient area, these follicles Cut ones should also be placed superficially compared to healthy follicles.
In order to prevent complications such as indentation, raising the surface Skin after placement of hair grafts, poor retention of grafts, folliculitis, and cysts. We should classify the grafts in an individual of the same length and size in our group and Create a suitable cutting depth based on each group. With this method, control the depth of the graft and Its placement, the researcher of this article reduced these complications in most of his patients in the last 4 years data or prevented their occurrence (picture 2).
Transplanted hair as an external organ in the skin of the area Receiver
Transplanted hair usually falls out between 2 and 4 weeks after surgery they become But some transplanted hairs continue to grow without shedding. A small part The hair neither falls nor grows: they remain only in the transplant recipient area. These hairs act like a foreign organ and can cause folliculitis (Fig 3). This hair can be removed by vigorous shampooing or forceps, after 4 weeks It will be removed from the operation and folliculitis will be reduced with this method.
Valuable tips
1. The difference in graft length in each patient is possible It is attention. 2. Make cuts with the same depth every time It may produce an inadequate graft surface in the gap with respect to the length of the graft: low insertion The depth or appropriate, or deep grafts. 3. Matching the length of the graft and the length of the cut, proper placement of the graft in the cut Enables: creation of 3 mm gap for 3 mm grafts and gap 6 mm for a 6 mm long graft 4. Measure the length of all grafts and Grouping them according to the length of the grafts is necessary to place the graft under depth control. 5. This graft placement is under depth control It can prevent folliculitis, indentation, and even poor longevity.

Picture 2. Folliculitis and indentation after grafting depth control method: (a) No folliculitis In 5 weeks
It is not visible after surgery. (b) any omission; 1 year after the operation, it is not observed.

Image 3. The remaining hair that shows that the hair has not grown and to
The face of a foreign organ remains and causes folliculitis.
Prevention and treatment of folliculitis after surgery
Context
The scalp in the transplant recipient area can have an inflammatory reaction A wide range of stimuli such as infection, wound or physical injury, or exposure chemicals during the hair transplant process.
In this context, reports of the occurrence of folliculitis after surgery, Variable from 1.1% to 20% is available. The severity of folliculitis ranges from mild and superficial inflammation to mild erythema and pustules Scattered to intense and deep inflammation with widespread erythema and numerous cysts, pustules and includes corks. The recommended treatment includes warm water compress, topical antibiotic ointment, Corticosteroid with moderate effect, cut and drain, and systemic antibiotics.
Our approaches
Seventy five percent of all patients undergoing hair transplant in our center are Ahl
East Asia and 15% are from Southeast Asia. More than 80% of all patients for follow-up and checkup 1 day, 1 week, 1 month,
They return 4 months, 8 months and 12 months after the operation. Here we have another perspective
Regarding the nature, prevention and treatment of postoperative folliculitis in the hair transplant recipient area
we do We divide folliculitis into three categories according to the onset and possible cause:
Traumatic folliculitis, external organ folliculitis and infectious folliculitis.
Traumatic folliculitis
Pustules appear soon after the operation. in this The condition is more likely to be inflammation than infection. Clean the wound with an ear cleaner usually It leads to no growth or only small growth of Staphylococcus aureus. Burying the epidermis in When creating the graft recipient site, cutting the hair graft during implantation, and implanting the hair spicule (needle). With the graft it may lead to an inflammatory reaction. The release of skin fat from damaged sebaceous glands seen during cutting may also play a key role.
groups at risk
Previously untreated folliculitis, furunculosis, and moderate acne vulgaris To severe, oily skin or previously untreated seborrheic dermatitis skin appendage, hypertrophic sebaceous glands or cysts Sebaceous glands should be taken into consideration when removing the skin strip.
Treatment
The most effective method is to pierce the pustule with a sharp needle And then press each pimple with an ear swab. The inflamed area should be cooled with water and povidone iodine shampoo should be washed. In addition, the combination of steroid antibiotics Topical can be used. We have systemic antibiotics such as doxycycline 100 mg, daily or ciprofloxacin We prescribe 500 mg twice a day for 5-10 days for selected cases To be honest, this is more for our peace of mind. Patients should be constantly directed The occurrence of new pustules should be monitored. It is possible to subside the inflammation It should take 3 weeks (picture 1).

Picture 1. Traumatic folliculitis on the 18th day
Prevention
Clear evidence that the use of sterile gloves during cutting And the placement of grafts reduces folliculitis after the operation is not available. Anti management Prophylactic antibiotics before hair transplantation, such as cephalosporins, remain controversial stayed We do not use antibiotics routinely because of more drug allergies It is dangerous from folliculitis. At-risk patients are asked to increase the daily dose of doxycycline to 100 mg and 2% ketoconazole shampoo for a week before Use action. However, the most effective preventive measure is the use of steroids Systemic immediately after surgery. Our protocol is prednisolone 10 mg per dose daily for 4 days to significantly reduce the incidence of folliculitis as well as facial swelling gave.
Foreign organ folliculitis
Inflammation can also lead to one or more reactions in the skin The recipient area of the transplant or blockage of the openings of the hair components. After 3 weeks of implanted follicles enters the catagen and telogen phase. After that, the immune system, hair remains It treats the isolated as an alien or foreign member (Figure 2). If this remains If the remaining hair is removed or destroyed, the folliculitis will subside on its own. If If folliculitis is not treated, it may block the pores of the skin. Another peak of inflammation can 3 to 4 months later, when the newly grown hairs are able to penetrate and exit the skin If they are not, it will happen. This may eventually lead to hair getting stuck or buried in the hair under the skin or become a type of chronic recurrence of folliculitis.

Image 2. External organ folliculitis during 4 weeks

Image 3. J-shaped hair
groups at risk
Asians with very large and thick hair, dense, placement Grafts without trimming and shaving, and cut or damaged follicles planting.
Prevention
Massage gently with the tips of the fingers in a circular motion A safe face should be included in the shampooing process after surgery to remove loose hair. which is recommended to start one week after the operation.
Treatment
In the center of each pustule, always a spicule (needle) of hair, remnants There is a hair shaft separated from the skin bump, which looks like the letter "J". This is so called J-shaped hair is easy It can be removed using a pair of tweezers (picture 3). Purulent boil should be with pressure Drain the ear cleaner. When widespread folliculitis occurs, use of topical antibiotic ointment Betadine steroid and shampoo can be used at home for the next 5 days. Antibiotics Systemic is rarely needed unless the patient is suspected of having a secondary infection.
Infectious folliculitis
Infection can occur at any time when the skin's defense barrier is disrupted
to occur In any case of severe or persistent folliculitis that is not helped by the above measures, you should
It was suspicious. Shaving and cutting hair just before the implant procedure has shown a 3% increase in surgical infection.
groups at risk
People whose work environment is dusty, lack of continuous washing Scalp, scratching or scraping of the scalp, cross-infection in a hospital setting, or special conditions Immunosuppressive clinical conditions such as diabetes can increase the risk of diabetes mellitus. Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter, Klebsiella and Proteus as Pathogens have been introduced.
Treatment and prevention
Prior to using antibiotic treatment, purulent material must be cultured become This is the same as managing any post-operative wound infection.
final result
Although this condition is not life threatening, scattered pustules are Due to their unpleasant and characteristic appearance, they cause discomfort to patients. Most patients They want to keep their hair transplantation a secret without attracting the attention of others. If we allow low-grade chronic inflammation to continue for more than a few months or years slow, may lead to scar alopecia with follicular damage and hair loss. always one There is concern that folliculitis may affect graft viability and survival. Fortunately, With proper preventative measures and treatment, most folliculitis resolves normally and rarely affect the final results.